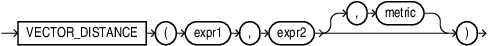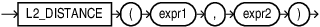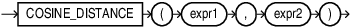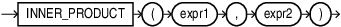VECTOR_DISTANCE
VECTOR_DISTANCE is the main function that you can use to calculate
the distance between two vectors.
Purpose
VECTOR_DISTANCE takes two vectors as parameters. You can optionally specify a distance metric to calculate the distance. If you do not specify a distance metric, then the default distance metric is cosine. If the input vectors are BINARY vectors, the default metric is hamming.
You can optionally use the following shorthand vector distance functions:
-
L1_DISTANCE -
L2_DISTANCE -
COSINE_DISTANCE -
INNER_PRODUCT -
HAMMING_DISTANCE -
JACCARD_DISTANCE
All the vector distance functions take two vectors as input and return
the distance between them as a BINARY_DOUBLE.
-
If you specify a metric as the third argument, then that metric is used.
-
If you do not specify a metric, then the following rules apply:
-
If there is a single column referenced in
expr1andexpr2as in:VECTOR_DISTANCE(vec1, :bind), and if there is a vector index defined onvec1, then the metric used when defining the vector index is used.If no vector index is defined on
vec1, then theCOSINEmetric is used. -
If there are multiple columns referenced in
expr1andexpr2as in:VECTOR_DISTANCE(vec1, vec2), orVECTOR_DISTANCE(vec1+vec2, :bind), then for all indexed columns, if their metrics used in the definitions of the indexes are the same, then that metric is used.On the other hand, if the indexed columns do not have a common metric, or none of the columns have an index defined, then the
COSINEmetric is used.
-
-
In a similarity search query, if
expr1orexpr2reference an indexed column and you specify a distance metric that conflicts with the metric specified in the vector index, then the vector index is not used and the metric you specified is used to perform an exact search. -
Approximate (index-based) searches can be done if only one column is referenced by either
expr1orexpr2, and this column has a vector index defined, and the metric that is specified in the vector_distance matches the metric used in the definition of the vector index.
Parameters
-
expr1andexpr2must evaluate to vectors and have the same format and number of dimensions.If you use
JACCARD_DISTANCEor theJACCARDmetric, thenexpr1andexpr2must evaluate toBINARYvectors. -
This function returns NULL if either
expr1orexpr2is NULL. -
metricmust be one of the following tokens :-
COSINEmetric is the default metric. It calculates the cosine distance between two vectors. -
DOTmetric calculates the negated dot product of two vectors. TheINNER_PRODUCTfunction calculates the dot product, as in the negation of this metric. -
EUCLIDEANmetric, also known as L2 distance, calculates the Euclidean distance between two vectors. -
EUCLIDEAN_SQUAREDmetric, also calledL2_SQUARED, is the Euclidean distance without taking the square root. -
HAMMINGmetric calculates the hamming distance between two vectors by counting the number dimensions that differ between the two vectors. -
MANHATTANmetric, also known as L1 distance or taxicab distance, calculates the Manhattan distance between two vectors. -
JACCARDmetric calculates the Jaccard distance. The two vectors used in the query must beBINARYvectors.
-
Shorthand Operators for Distances
Syntax
-
expr1 <-> expr2<->is the Euclidean distance operator:expr1 <-> expr2is equivalent toL2_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2)orVECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, EUCLIDEAN) -
expr1 <=> expr2<=>is the cosine distance operator:expr1 <=> expr2is equivalent toCOSINE_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2)orVECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, COSINE) -
expr1 <#> expr2<#>is the negative dot product operator:expr1 <#> expr2is equivalent to-1*INNER_PRODUCT(expr1, expr2)orVECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, DOT)
Examples Using Shorthand Operators for Distances
'[1, 2]' <-> '[0,1]'
v1 <-> '[' || '1,2,3' || ']' is equivalent to v1 <-> '[1, 2, 3]'
v1 <-> '[1,2]' is equivalent to L2_DISTANCE(v1, '[1,2]')
v1 <=> v2 is equivalent to COSINE_DISTANCE(v1, v2)
v1 <#> v2 is equivalent to -1*INNER_PRODUCT(v1, v2)
Examples
VECTOR_DISTANCE with metric EUCLIDEAN is equivalent to L2_DISTANCE:
VECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, EUCLIDEAN);
L2_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2);
VECTOR_DISTANCE with metric COSINE is equivalent to COSINE_DISTANCE:
VECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, COSINE);
COSINE_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2);
VECTOR_DISTANCE with metric DOT is equivalent to -1 * INNER_PRODUCT:
VECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, DOT);
-1*INNER_PRODUCT(expr1, expr2);
VECTOR_DISTANCE with metric MANHATTAN is equivalent to
L1_DISTANCE:
VECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, MANHATTAN);
L1_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2);
VECTOR_DISTANCE with metric HAMMING is
equivalent to HAMMING_DISTANCE:
VECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, HAMMING);
HAMMING_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2);
VECTOR_DISTANCE with metric JACCARD is equivalent to JACCARD_DISTANCE:
VECTOR_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2, JACCARD);
JACCARD_DISTANCE(expr1, expr2);
L1_DISTANCE
L1_DISTANCE is a shorthand version of the
VECTOR_DISTANCE function that calculates the distance between two
vectors. It takes two vectors as input and returns the distance between them as a
BINARY_DOUBLE.
Parameters
-
expr1andexpr2must evaluate to vectors and have the same format and number of dimensions. -
L1_DISTANCEreturns NULL, if eitherexpr1orexpr2is NULL.
L2_DISTANCE
L2_DISTANCE is a shorthand version of the
VECTOR_DISTANCE function that calculates the distance between two
vectors. It takes two vectors as input and returns the distance between them as a
BINARY_DOUBLE.
Parameters
-
expr1andexpr2must evaluate to vectors that have the same format and number of dimensions. -
L2_DISTANCEreturns NULL, if eitherexpr1orexpr2is NULL.
COSINE_DISTANCE
COSINE_DISTANCE is a shorthand version of the
VECTOR_DISTANCE function that calculates the distance between two
vectors. It takes two vectors as input and returns the distance between them as a
BINARY_DOUBLE.
Parameters
-
expr1andexpr2must evaluate to vectors that have the same format and number of dimensions. -
COSINE_DISTANCEreturns NULL, if eitherexpr1orexpr2is NULL.
INNER_PRODUCT
INNER_PRODUCT calculates the inner product of two vectors. It takes
two vectors as input and returns the inner product as a BINARY_DOUBLE.
INNER_PRODUCT(<expr1>, <expr2>) is
equivalent to -1 * VECTOR_DISTANCE(<expr1>, <expr2>,
DOT).
Parameters
-
expr1andexpr2must evaluate to vectors that have the same format and number of dimensions. -
INNER_PRODUCTreturns NULL, if eitherexpr1orexpr2is NULL.