3.1.2.5 geoFeature Element
The <geoFeature> element has the following
definition:
<!ELEMENT geoFeature (description?, property*,
geometricProperty)>
<!ATTLIST geoFeature
typeName CDATA #IMPLIED
id CDATA #IMPLIED
render_style CDATA #IMPLIED
text_style CDATA #IMPLIED
label CDATA #IMPLIED
label_always_on (TRUE|FALSE) "FALSE"
marker_size CDATA #IMPLIED
radius CDATA #IMPLIED
attribute_values CDATA #IMPLIED
orient_x CDATA #IMPLIED
orient_y CDATA #IMPLIED
orient_z CDATA #IMPLIED
selectable_in_svg (TRUE|FALSE) "FALSE"
onclick CDATA #IMPLIED
hidden_info CDATA #IMPLIED
><geoFeature> elements are used to provide
individual geospatial entities to be rendered on a map. The main part of a
<geoFeature> element is the geometry
(<geometricProperty> element), which must be supplied in
compliance with the OGC GML v1.0 Geometry DTD (described in Geometry DTD (OGC)).
typeName is an optional attribute that is ignored by
the current release of MapViewer.
id is an optional attribute that can be used to
uniquely identify the feature among all the geospatial features on the SVG map. (See
the explanation of the selectable_in_svg attribute.) Otherwise,
this attribute is ignored by MapViewer.
render_style is an optional attribute. When it is
omitted, the geoFeature is not rendered. If it is supplied, its
value must be the name of a style stored in the user's USER_SDO_STYLES view.
text_style is an optional attribute. If it is supplied
(and if the render_style and label attributes are
present and valid), it identifies the style to be used in labeling the feature. If
it is not specified, a default text style is used.
label is an optional attribute. If it is supplied (and if the
render_style and label attributes are present and valid), it identifies text that is
used to label the feature.
label_always_on is an optional attribute. If it is set
to TRUE, MapViewer labels the features even if two or more labels will overlap in
the display of a theme. (MapViewer always tries to avoid overlapping labels.) If
label_always_on is FALSE (the default), when it is impossible
to avoid overlapping labels, MapViewer disables the display of one or more labels so
that no overlapping occurs. The label_always_on attribute can also
be specified for a theme (theme element, described in theme Element). Specifying label_always_on as TRUE for a feature in the geoFeature element
definition gives you control over which features will have their labels displayed if
label_always_on is FALSE for a theme and if overlapping labels
cannot be avoided.
marker_size is an optional attribute. If it is supplied with a point
feature, and if render_style is a marker-type style, the specified
size is used by MapViewer in rendering this feature. This provides a mechanism to
override the default value specified for a marker style.
radius is an optional attribute. If it is supplied, it specifies a
number or a comma-delimited list of numbers, with each number representing the
radius of a circle to be drawn centered on this feature. For geodetic data, the unit
is meters; for non-geodetic data, the unit is the unit of measurement associated
with the data.
attribute_values is an optional attribute. If it is supplied, it
specifies a value or a comma-delimited list of values to be used with bucket ranges
of an advanced style (for example, values for pie chart segments or bucket values
for variable markers).
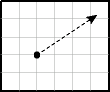
orient_x and orient_y optionally specify a virtual
end point to indicate an orientation vector for rotating a marker symbol (such as a
shield symbol to indicate a highway) or text at a specified point.
(orient_z is reserved for future use by Oracle.) The value for
each must be from -1 to 1. The orientation start point is assumed to be (0,0), and
it is translated to the location of the physical point to which it corresponds.
The following figure illustrates an orientation vector of approximately 34 degrees (counterclockwise from the x-axis), resulting from specifying orient_x="0.3" orient_y="0.2". (To have an orientation that more precisely matches a specific angle, refer to the cotangent or tangent values in the tables in a trigonometry textbook.)
selectable_in_svg is an optional attribute that
specifies whether or not the feature is selectable on an SVG map. The default is
FALSE; that is, the feature is not selectable on an SVG map. If this attribute is
set to TRUE and if theme feature selection is allowed, the feature can be selected
by clicking on it. If the feature is selected, its color is changed and its ID is
recorded. You can get a list of the ID values of all selected features by calling
the JavaScript function getSelectedIdList() defined in the SVG map.
(For feature selection to work correctly, the id attribute value of
the feature must be set to a value that uniquely identifies it among all the
geospatial features on the SVG map.) For information about using JavaScript
functions with SVG maps, see Appendix B.
onclick is an optional attribute that specifies the name
of the JavaScript function to be called when a user clicks on the feature. The
JavaScript function must be defined in the HTML document outside the SVG definition.
This function must accept only four parameters: the theme name, the key of the
feature, and x and y, which specify the coordinates (in pixels) of the clicked point
on the SVG map. For information about using JavaScript functions with SVG maps, see
Appendix B.
hidden_info is an optional attribute that specifies an
informational note or tip to be displayed when the mouse is moved over the feature.
To specify multiple lines, use "\n" between lines. For example,
hidden_info="State park with\nhistorical attractions" specifies
a two-line tip. (To enable the display of hidden information in the map, you must
specify infoon="true" in the <map_request>
element, as explained in map_request Attributes.)
The following example shows a <geoFeature> element specification
for a restaurant at longitude and latitude coordinates (-78.1234, 41.0346). In this
case, the feature will be invisible because the render_style and
text_style attributes are not specified.
<geoFeature typeName="Customer"
label="PizzaHut in Nashua">
<geometricProperty>
<Point srsName="SDO:8265">
<coordinates>-78.1234,41.0346</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
</geoFeature>The following example shows a <geoFeature> element specification
for a point of interest at longitude and latitude coordinates (-122.2615, 37.5266).
The feature will be rendered on the generated map because the
render_style attribute is specified. The example specifies some
label text (A Place) and a text style for drawing the label text. It also instructs
MapViewer to draw two circles, centered on this feature, with radii of 1600 and 4800
meters. (In this case, the srsName attribute of the
<Point> element must be present, and it must specify an
Oracle Spatial and Graph SRID value using the format
"SDO:<srid>". Because SRID value 8265 is associated with a
geodetic coordinate system, the radius values are interpreted as 1600 and 4800
meters.)
<geoFeature render_style="m.star"
radius="1600,4800"
label="A Place"
text_style="T.Name">
<geometricProperty>
<Point srsName="SDO:8265">
<coordinates>-122.2615, 37.5266</coordinates>
</Point>
</geometricProperty>
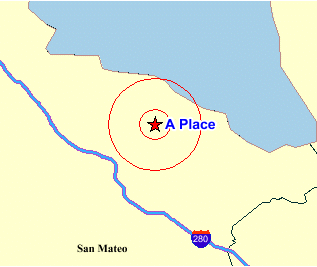
</geoFeature>The following figure is a map drawn using the
<geoFeature> element in the preceding example. The
feature is labeled with the text A Place, and it is represented by a red star marker
surrounded by two concentric circles.
Figure 3-4 Map with <geoFeature> Element Showing Two Concentric Circles
Parent topic: Map Request DTD