6.9 Executing PGQL Queries Directly Against Oracle Database
This topic explains how you can execute PGQL queries directly against the graph in Oracle Database (as opposed to in-memory).
Property Graph Query Language (PGQL) queries can be executed against disk-resident property graph data stored in Oracle Database. PGQL on Oracle Database (RDBMS) provides a Java API for executing PGQL queries. Logic in PGQL on RDBMS translates a submitted PGQL query into an equivalent SQL query, and the resulting SQL is executed on the database server. PGQL on RDBMS then wraps the SQL query results with a convenient PGQL result set API.
This PGQL query execution flow is shown in the following figure.
Figure 6-1 PGQL on Oracle Database (RDBMS)
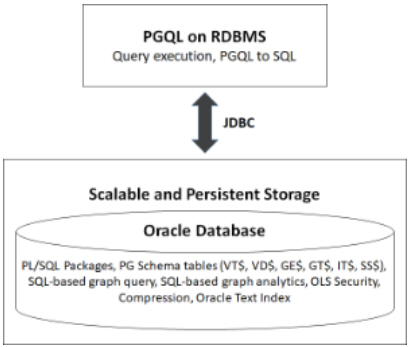
Description of "Figure 6-1 PGQL on Oracle Database (RDBMS)"
The basic execution flow is:
-
The PGQL query is submitted to PGQL on RDBMS through a Java API.
-
The PGQL query is translated to SQL.
-
The translated SQL is submitted to Oracle Database by JDBC.
-
The SQL result set is wrapped as a PGQL result set and returned to the caller.
The ability to execute PGQL queries directly against property graph data stored in Oracle Database provides several benefits.
-
PGQL provides a more natural way to express graph queries than SQL manually written to query schema tables, including VT$, VD$, GE$, and GT$.
-
PGQL queries can be executed without the need to load a snapshot of your graph data into PGX, so there is no need to worry about staleness of frequently updated graph data.
-
PGQL queries can be executed against graph data that is too large to fit in memory.
-
The robust and scalable Oracle SQL engine can be used to execute PGQL queries.
-
Mature tools for management, monitoring and tuning of Oracle Database can be used to tune and monitor PGQL queries.
- PGQL Features Supported
- Creating Property Graphs through CREATE PROPERTY GRAPH Statements
- Dropping Property Graphs through DROP PROPERTY GRAPH Statements
- Using the oracle.pg.rdbms.pgql Java Package to Execute PGQL Queries
- Modifying Property Graphs through INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE Statements
- Performance Considerations for PGQL Queries
Parent topic: Property Graph Query Language (PGQL)