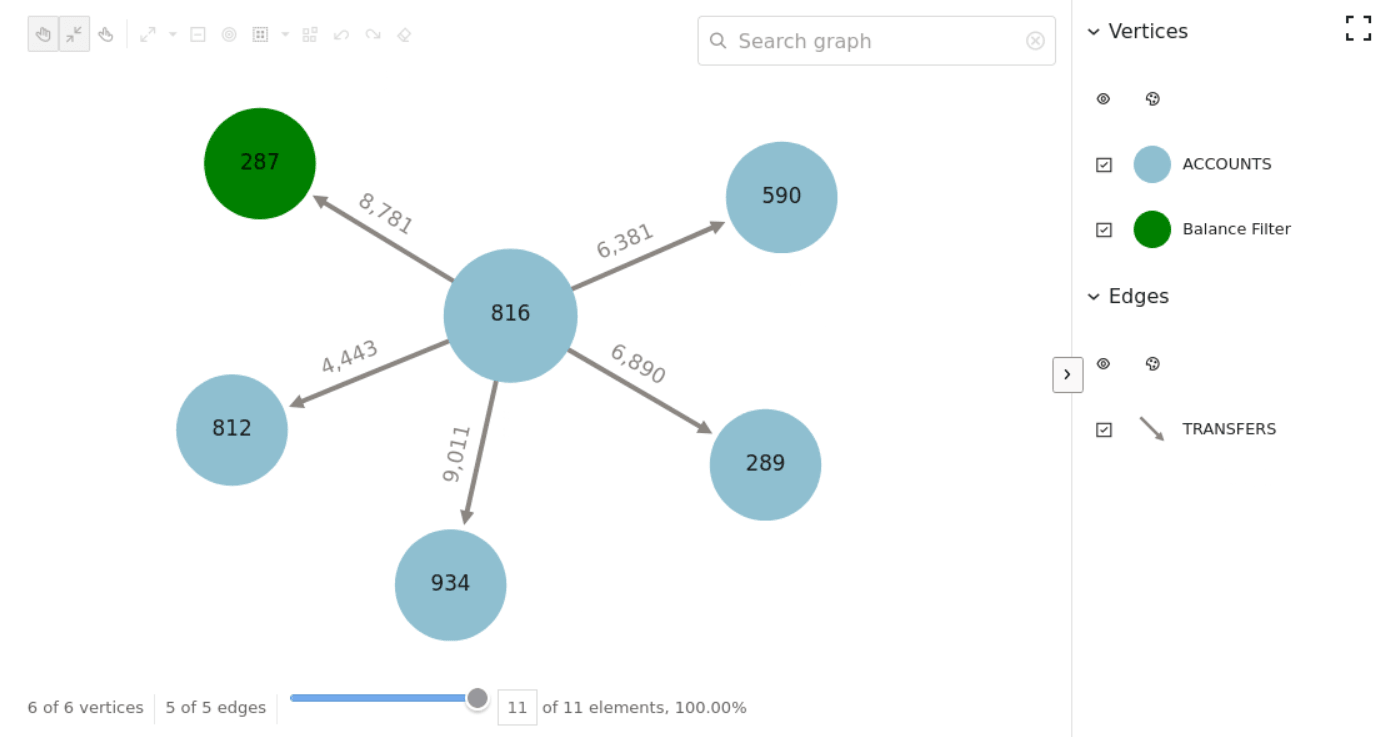
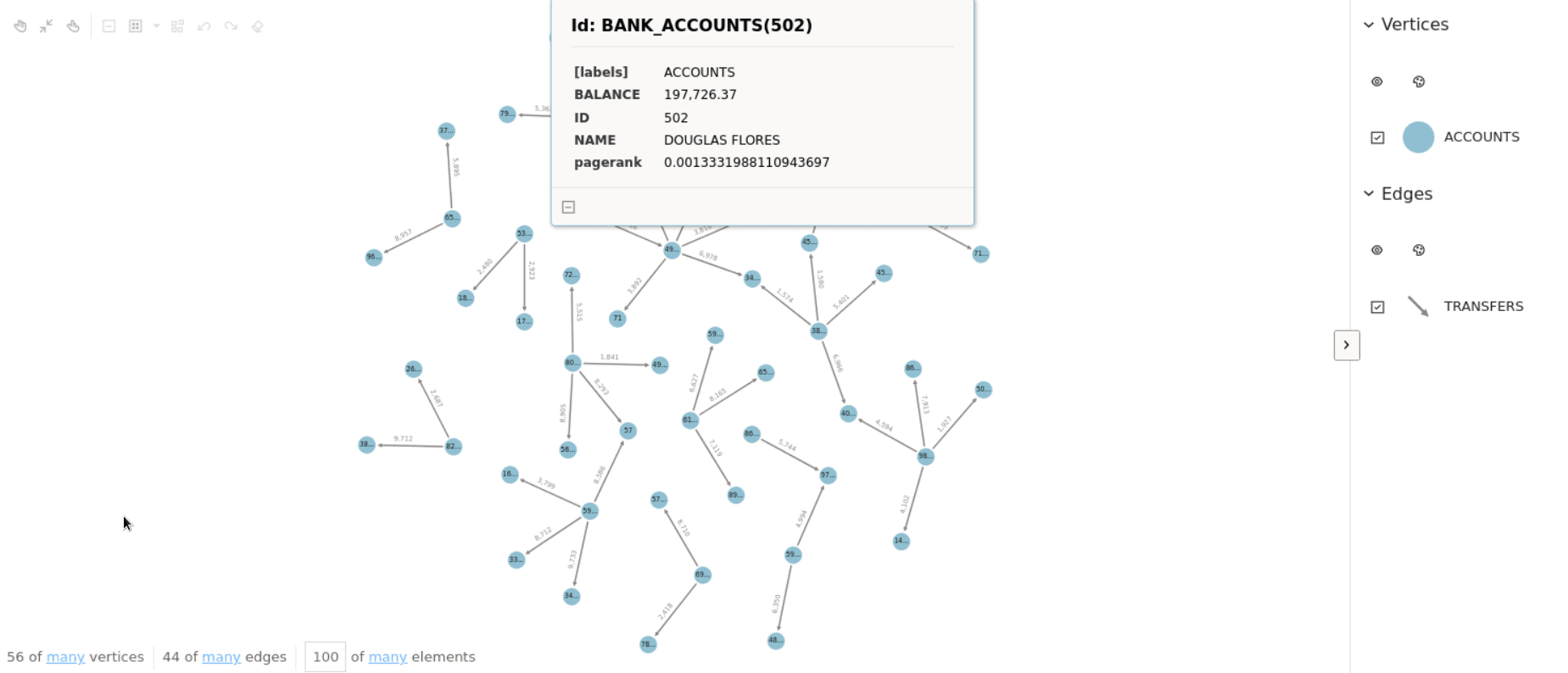
The following example loads the graph into the graph server
(PGX) and runs the Pagerank algorithm on the graph.
from oraclegraph import PgxGraphVisualization
from pypgx import setloglevel
from opg4py import graph_server
setloglevel("ROOT", "WARN")
base_url = "https://localhost:7007"
username = "graphuser"
password = "<password_for_graphuser>"
# Connect to graph server and create a session
instance = graph_server.get_instance(base_url, username, password)
session = instance.create_session("jupyter_session")
loaded_graph = session.read_graph_by_name("BANK_GRAPH", "pg_sql")
analyst = session.create_analyst()
pagerank = analyst.pagerank(loaded_graph, rank = "pagerank")
result_set = loaded_graph.query_pgql("SELECT x, x.pagerank MATCH (x) ORDER BY x.pagerank DESC LIMIT 10")
result_set.print()
The preceding code produces the following output:
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| x | x.pagerank |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=387,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(387)] | 0.007292323575404966 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=406,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(406)] | 0.006730094462320363 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=135,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(135)] | 0.0067205459831892545 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=934,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(934)] | 0.0066348438503635795 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=397,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(397)] | 0.005693569761570974 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=559,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(559)] | 0.005258438311460985 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=352,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(352)] | 0.005216329599236731 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=330,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(330)] | 0.005093350408942337 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=222,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(222)] | 0.004682551613749817 |
| PgxVertex[provider=BANK_ACCOUNTS,key=4,ID=BANK_ACCOUNTS(4)] | 0.004569682370461632 |
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------