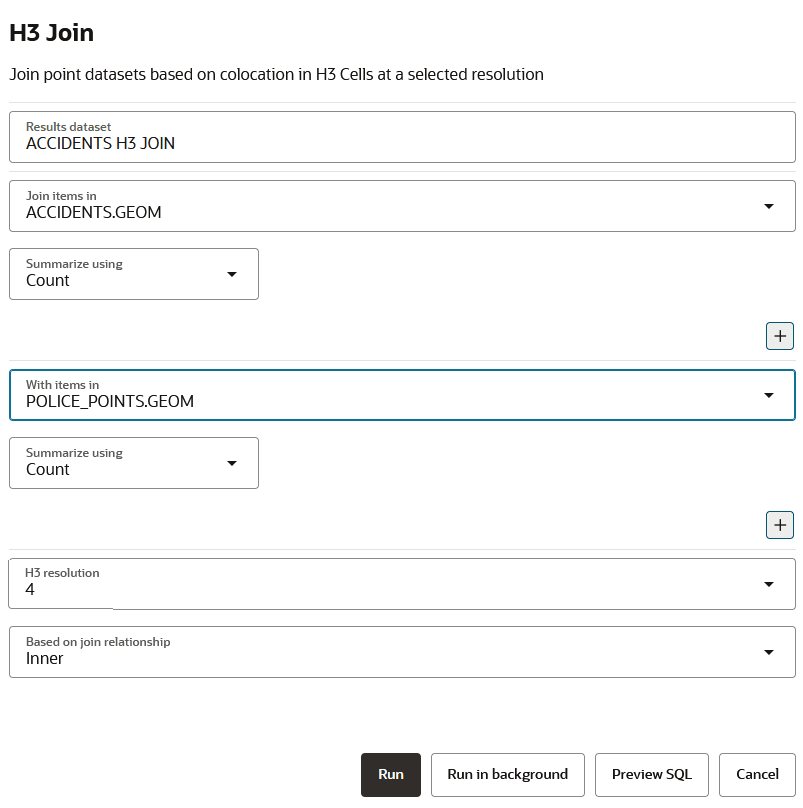
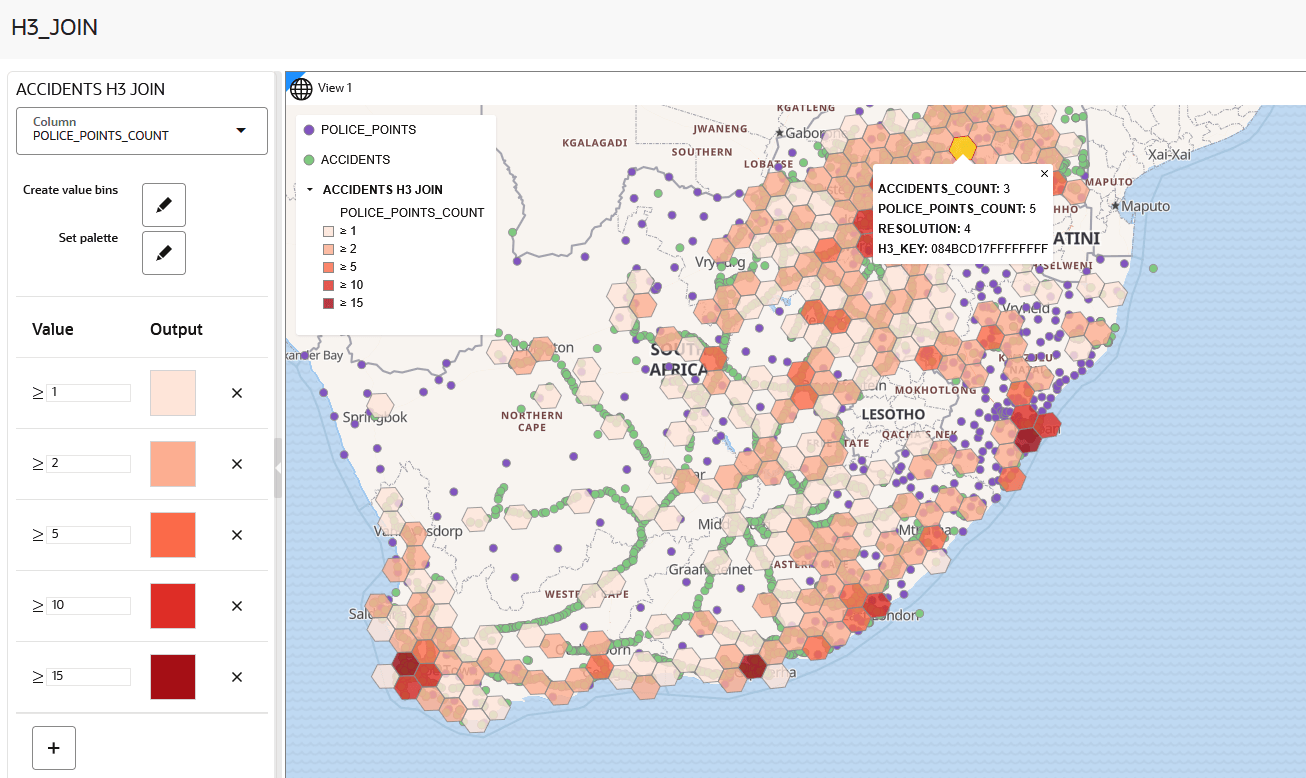
5.10 Joining Point Datasets Using H3 Aggregations
You can join two point datasets and perform a spatial analysis based on their colocation within H3 (Hexagonal Hierarchical Spatial Index) cells at a selected resolution in Spatial Studio.
In the H3 Join analysis, H3 aggregations are obtained based on
the specified aggregation operation(s) on a given column (or no column in case of
Count) for both participating point datasets. These aggregated results are
then joined together using the H3 key of each hexagon as the join key. Note that all
this is performed on the specified single resolution.
You can perform the H3 Join analysis as described in the
following steps:
The instructions assume that you have two datasets with point geometries
added in your Active Project page.
Parent topic: Performing Analyses in Spatial Studio