4.1 Security Checking from Tuxedo to Mainframe
The following figure illustrates the process flow for security verifications from TMA TCP Gateway to a mainframe.
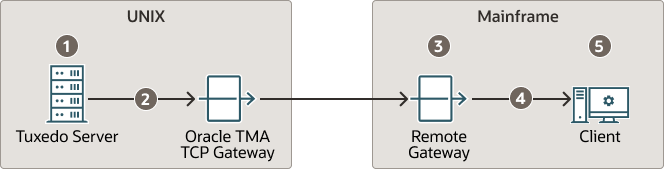
Figure 4-1 Security Checking for Tuxedo to Mainframe Transactions

- When the client program performs a
tpinit(), the user’s Tuxedo identity is validated against thetpusrfile. - When the client program issues a
tpcall()ortpacall(), Tuxedo verifies (against thetpaclfile) that the user is authorized to invoke the gateway service. - When the gateway establishes the initial connection, connection security information (specified as
RMTNAMEandPASSWORDin theGWICONFIGfile) is passed from the TMA TCP Gateway to the remote gateway. If theRMTNAMEandPASSWORDvalues match the values configured on the remote gateway, the connection is established.With each request, the TMA TCP Gateway passes the user’s Tuxedo identity to the remote gateway.
Note:
To pass authority checking, the user’s Tuxedo identity must match the mainframe user ID exactly. - The remote mainframe gateway initiates a proxy to act on behalf of the specified user ID.
- The proxy calls the specified service using system security to check authorization.
Parent topic: Setting Up Security for Oracle TMA TCP Gateway