2.3.1 Bootstrapping the Oracle Tuxedo Domain
A domain is a way of grouping objects and services together as a management entity. A Oracle Tuxedo domain has at least one IIOP Listener/Handler and is identified by a name. One client application can connect to multiple Oracle Tuxedo domains using different Bootstrap objects.
Bootstrapping the Oracle Tuxedo domain establishes communication between a client application and the domain. There are two mechanisms available for bootstrapping, the Oracle mechanism and the CORBA Interoperable Naming Service (INS) bootstrapping mechanism specified by the OMG. Use the Oracle mechanism if you are using Oracle CORBA client software. Use the CORBA INS mechanism if you are using a client ORB from another vendor. For more information about bootstrapping the Oracle Tuxedo domain, see the CORBA Programming Reference in the Oracle Tuxedo online documentation.
One of the first things that client applications do after startup is create a Bootstrap object by supplying the host and port of the IIOP Listener/Handler using one of the following URL address formats:
-
//host:port -
corbaloc://host:port -
corbalocs://host:port
For more information about the Bootstrap URL address formats, see Using Security in CORBA Applications in the Oracle Tuxedo online documentation.
The client application then uses the Bootstrap object or the INS
bootstrapping mechanism to obtain references to the objects in a
Oracle Tuxedo domain. Once the Bootstrap object is instantiated,
the resolve_initial_references() method is invoked by
the client application, passing in a string id, to
obtain a reference to the objects in the Oracle Tuxedo domain that
provide CORBA services.
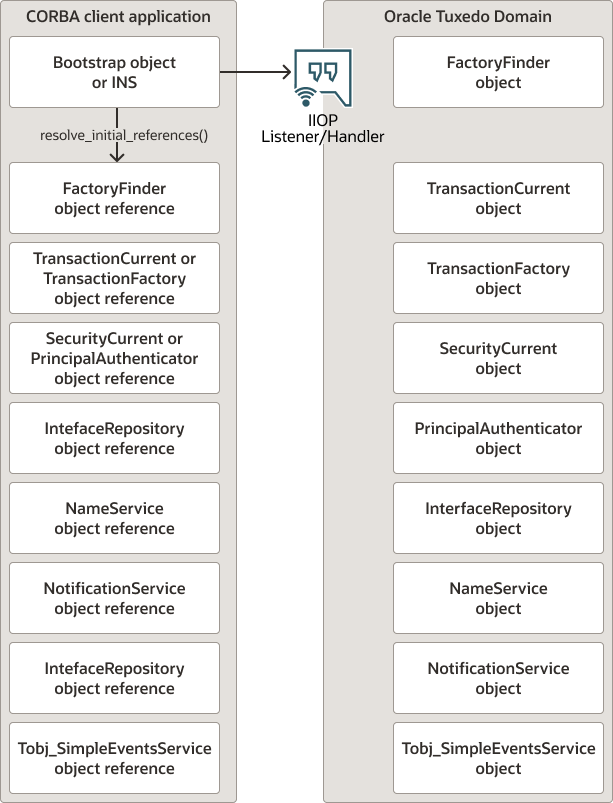
The following figure illustrates how the Bootstrap object or INS mechanism operates in a Oracle Tuxedo domain.
Figure 2-2 How the Bootstrap Object or INS Operates
Parent topic: Oracle Tuxedo CORBA Architectural Components