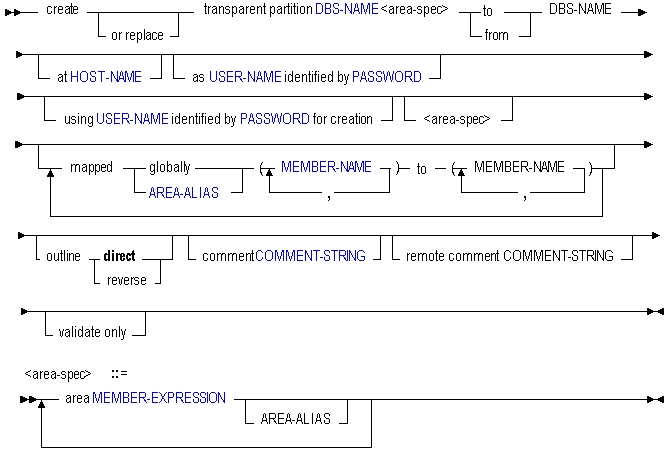
Create Transparent Partition
The MaxL create transparent partition statement helps you create or validate a transparent partition between two Essbase databases.
A transparent partition allows users to manipulate data that is stored in a target cube as if it were part of the source cube. The remote data is retrieved from the data source each time that users at the data target request it.
Keywords
Use the MaxL create transparent partition statement to create a partition in the following ways:
- create transparent partition
-
Create a transparent partition. A transparent partition enables users to access data from the data source as though it were stored in the data target. The data is, however, stored at the data source, which can be in another application, in another cube, or on another Essbase instance.
- create or replace transparent partition ...
-
Create a partition definition, or replace an existing partition definition.
- create transparent partition ... area...
-
The area specification is where you define the partition areas to share with the other cube. Optionally, nickname the area using an area-alias.
- create transparent partition ... to DBS-NAME
-
Use the to clause to create a partition definition between the current source cube and the second cube (the target).
- create transparent partition ... from DBS-NAME
-
Use the from clause to create a partition definition between the current target cube and the second cube (the source).
- create transparent partition ... at HOST-NAME
-
Use the at clause, with a host name, to specify the discovery URL (ending in /agent) of the remote cube.
- create transparent partition ... as USER-NAME identified by PASSWORD
-
Use the as clause to provide the name and password of a default partition user who can connect to both cubes. Essbase uses the login information to:
-
Transfer data between the source and the target for replicated and transparent partitions. Security filters can be applied to prevent end users from accessing privileged data.
-
Synchronize outlines for all partition types.
-
- create transparent partition ... using USER-NAME identified by PASSWORD for creation
-
Use the using clause to create the partition using a different user than the one being set as the default partition user. This can be useful when you want to specify a read-only user account as the default partition user.
- create transparent partition ... mapped...
-
Use the mapped clause to define the member-name mapping for shared sections of both cubes, if member names for sections that map are different in the two cubes.
- create transparent partition ... outline...
-
Use the outline clause to specify the direction in which outline synchronization should proceed, if necessary. The default direction is the same as the data-refresh direction.
- create transparent partition ... comment
-
Use the comment clause to create a comment to describe the source half of the partition definition.
- create transparent partition ... remote comment
-
Use the remote comment clause to create a comment to describe the target half of the partition definition.
- create transparent partition ... validate only
-
Use the validate only clause to validate the existing partition definition described by this statement, without actually creating it.
Notes
-
Multiple area specifications are allowed, provided they are separated by whitespace. Multiple mappings are allowed, provided they are separated by whitespace. All area aliases used in a mapping should be associated with the target, and the direction of the mapped clause should go from source to target.
-
The first DBS-NAME is the local cube, and the second DBS-NAME is the remote cube.
-
Creating a partition to the remote site means the current cube is the source. Creating a partition from the remote site means the current cube is the target.
-
Aggregate storage cubes can be the source, the target, or the source and target of a transparent partition. Outline synchronization (refresh outline statement) is not currently enabled for partitions that involve aggregate storage cubes.
Example
create or replace transparent partition sampeast.east
area '@CHILDREN("Eastern Region"), @CHILDREN(Qtr1)' sourceArea
to samppart.company at "https://myserver.example.com:9001/essbase/agent"
as partitionuser identified by 'password'
area '@CHILDREN(East) @CHILDREN(Qtr1)' targetArea;Creates a transparent partition between the source, sampeast.east, and the target, samppart.company. The partition is defined only for the areas specified by the area aliases
sourceAreaandtargetArea.
create or replace transparent partition source.source
area 'DimensionA' sourceAreaA
area 'DimensionB' sourceAreaB
to target.target at "https://myserver.example.com:9001/essbase/agent"
as smith identified by 'password'
area 'ParentMemberA' targetAreaA
area 'ParentMemberB' targetAreaB
mapped targetAreaA (ChildA) to (Child_a)
mapped targetAreaB (ChildB) to (Child_b)
; Creates a partition from cube Source to cube Target where the partitioned areas between them are DimensionA and DimensionB on the source, corresponding to ParentMemberA and ParentMemberB (respectively) on the target. Differences in member names between the two partitioned areas are resolved during the partition creation, using the mapped clauses. Area aliases are used after each area specification, so that members can be mapped specifically for each area.