About Cache Instances
A cache instance is defined as a single row in the cache group's root table together with the set of related rows in the child tables.
A cache instance is the smallest unit of data transferred when data is loaded from an Oracle database into a cache group in a TimesTen database.
Cache operations act on cache groups (not on individual tables) and on cache instances (not individual rows). Normal SQL operations, such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE, operate directly on the cache tables and their rows.
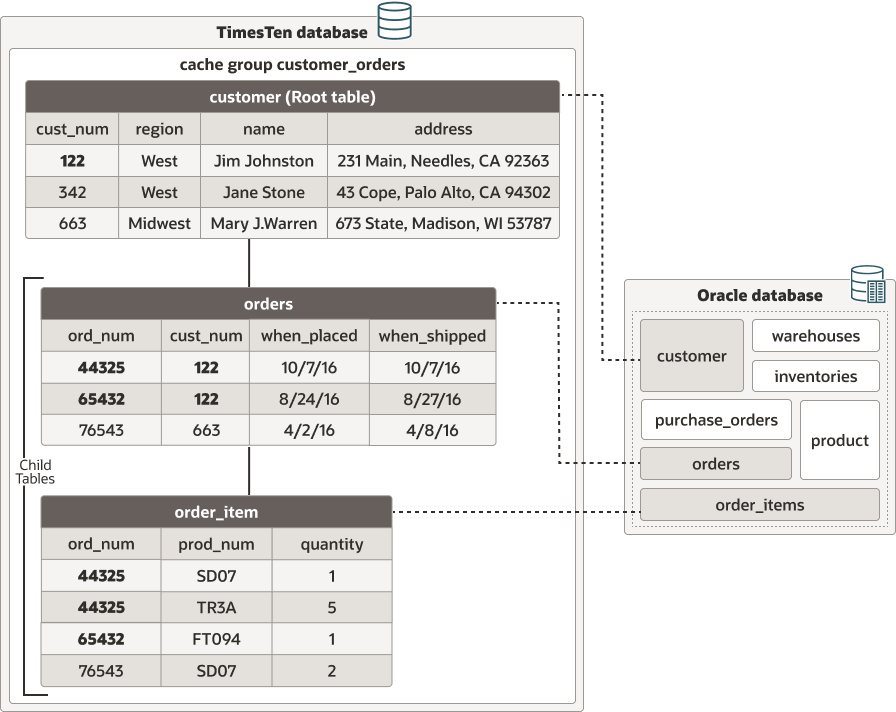
The following graphic shows three cache tables in the customer_orders cache group. This cache group caches data from the customers, orders, and order_items tables in the Oracle database. It shows multiple related Oracle database tables in the same cache group with a root table and one or more child tables. Cache tables defined in a multiple-table cache group must be related to each other in a TimesTen database through foreign key constraints.
-
The root cache table is
customers. -
The
ordersandorder_itemcache tables are child tables. Theorderscache table has a foreign key ofcust_numto show the relationship with thecustomercache table. Theorder_itemcache table has a foreign key oford_numto show the relationship with theorderscache table.
Because of the relationships between the cache tables, the cache instance identified by the row with the value 122 in the cust_num primary key column of the customers table includes:
-
The two rows with the value 122 in the
cust_numcolumn of theorderscache table (whose value in theord_numprimary key column is 44325 or 65432), and -
The three rows with the value 44325 or 65432 in the
ord_numcolumn of theorder_itemcache table