2.1 Overview of Oracle Exadata Storage Using Oracle ASM
Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) is the original cluster volume manager and file system used to manage Exadata storage resources.
Note:
Starting with Exadata System Software release 24.1, Oracle Exadata Exascale transforms Exadata storage management by decoupling Oracle Database and GI clusters from the underlying Exadata storage servers. Exascale software services manage pools of storage that span the fleet of Exadata storage servers and service all the database server clusters.
For information about Exascale, refer to the Oracle Exadata Exascale User's Guide.
The following image shows Oracle ASM disk groups created from Oracle Exadata Storage Server grid disks. It represents a typical, but simplified configuration, that can be used as a model for building larger storage grids with additional storage servers and disks.
Figure 2-1 Sample Oracle Exadata Storage Server Grid
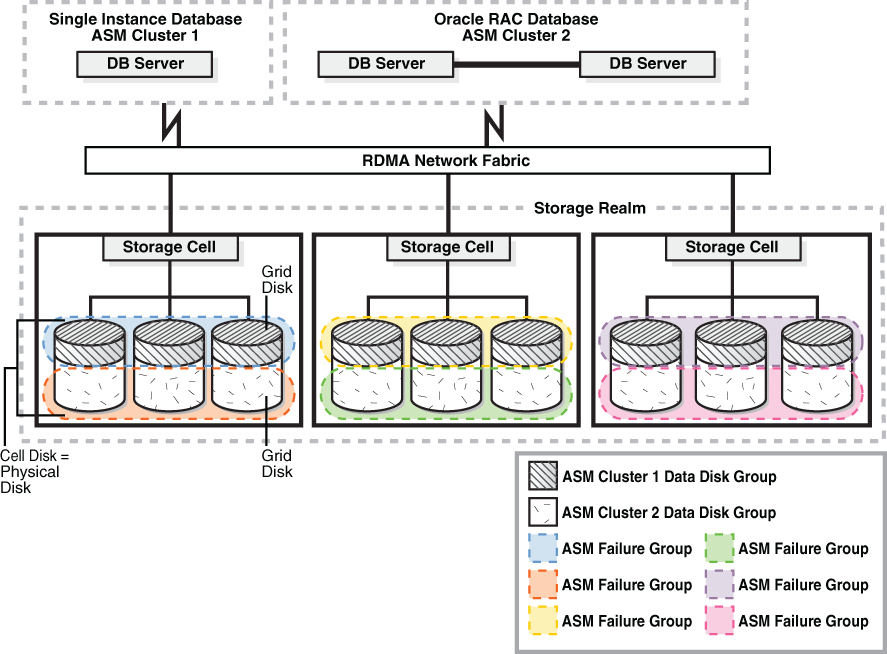
Description of "Figure 2-1 Sample Oracle Exadata Storage Server Grid"
This example storage grid illustrates the following:
- The storage servers in the grid use an RDMA Network Fabric network to connect to the database servers that have a single-instance database or Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) database installation.
- Each storage server contains multiple physical disks.
- Each cell disk represents a physical disk and a LUN.
- Each cell disk is partitioned into grid disks.
- Oracle ASM disk groups are created using the grid disks.
Oracle ASM failure groups are created to ensure that files are not mirrored on the same storage server, enabling the system to tolerate the failure of a storage server. The number of failure groups equals the number of storage servers. Each failure group is composed of a subset of grid disks in the Oracle ASM disk group that belong to a single storage server.
Parent topic: Administering Oracle ASM on Exadata