Downloading Patch Recommendations and Patches
This section describes the different patching modes that can be used:
Patching in Online and Offline Mode
You have the flexibility to choose between Online and Offline patching.
- Online Mode: Online mode is useful when Enterprise Manager can connect to My Oracle Support (MOS) using an Internet connection, enabling Enterprise Manager to download the latest Oracle Patch Recommendations. Using this mode, search and download patches from MOS and create gold images to include these patches.
In addition, you can access community information, knowledge articles, service requests, and automatically resolve patch conflicts with a merge patch directly from MOS.
For patching in online mode see: Setting up MOS Connection for Patch Recommendations and Patch DownloadsNote:
Cloud Control does not upload data to MOS. It only uses MOS to download the latest updates. - Offline Mode: Offline mode is used when Enterprise Manager cannot connect to My Oracle Support. In this mode, you can search patches that were manually uploaded to the Software Library. In offline mode, you cannot do the following:
- Search and download patches from My Oracle Support.
- View additional information about the patch.
- Access community information, knowledge articles, service requests.
- View the Related Activity region.
For patching in offline mode see: Setting Up the Infrastructure for Patching in Offline Mode (Not Connected to MOS)Note:
By default, the patching mode is set to online. If you want to switch to offline, go to Setup, select Provisioning and Patching, and then select Offline Patching.
Out-of-Place Patching
Out-of-Place patching is a mechanism where the gold image containing the required patches is deployed into a new home. Once complete, you migrate the database instances to run from the new home, ensuring minimal downtime.
Note:
If you have to apply patches to address critical issues without waiting for the new gold image to be published, the patching flow will clone the existing home and apply the required patches. The database can then be migrated to the new home. For more information see: Emergency PatchingIf you choose to migrate only a few instances per session, make sure that you migrate the rest in the next session. This way, you can control database downtime in the data center by dividing the migration activity. This is particularly useful when you have multiple database instances running out of an Oracle home.
Patching in Rolling and Parallel Mode
While patching Oracle Real Application Cluster (Oracle RAC) targets, Oracle Grid Infrastructure targets (whether or not they are part of Oracle Exadata), or Oracle Data Guard targets you can choose to patch the instances of the cluster either in rolling or parallel mode.
Note:
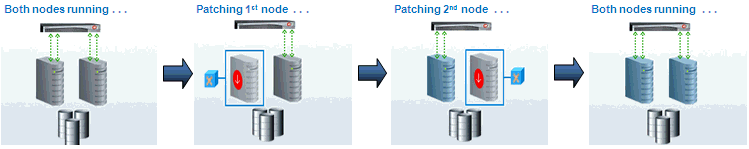
Non-rolling updates are deprecated and no longer available, starting with Enterprise Manager 13c Release 5 Update 17 (13.5.0.17).- Rolling Mode: In Rolling mode the nodes of the cluster are patched individually, one by one. For example, if you are patching a. Oracle Grid Infrastructure target that has five nodes, the first node is shut down, patched, and restarted. Then the process is rolled over to the next node until all the nodes are patched successfully.
Note:
The ReadMe of the patch states whether or not you can use Rolling Mode to apply your patches. Use this mode after ensuring that all patches in the gold image support rolling mode.The following image illustrates how a two-node Oracle RAC target gets patched when rolling mode is used.Figure 17-3 Rolling Mode of Patching
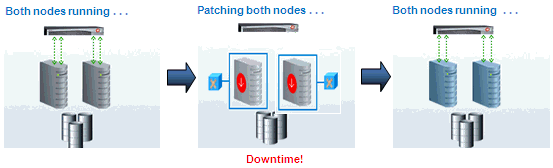
- Parallel Mode: In Parallel mode all the nodes are patched at the same time, all the nodes are shut down and the patch is applied on all of them at the same time.
The following image illustrates how a two-node Oracle RAC target gets patched when parallel mode is used.
Figure 17-4 Parallel Mode of Patching