3 Executing NF Test Cases using ATS
This section describes how to execute NF (NRF ,NSSF, Policy, SCP, SEPP and UDR) Test Cases using ATS.
Executing BSF Test Cases using ATS
This ATS-BSF release is a converged release comprising of scenarios (test cases) from BSF. ATS 1.3.2 is compatible with BSF 1.6.0.
To execute BSF test cases, you need to ensure that following prerequisites are fulfilled.
Prerequisites
- Deploy OCBSF.
- Install Go-STUB in the same namespace where ocbsf is installed.
- ATS Prometheus Metrics validation works only when the installation has a single pod for each microservice in the BSF deployment.
- Users can customize test cases in the custom test case folders (cust_newfeatures, cust_regression and cust_performance). They can add new test cases, remove unwanted test cases and modify existing test cases. It does not impact the original product packaged test cases available in the newfeatures, regression and performance folders. For more details, you can refer to Custom Folder Implementation.
- In the application-config configmap, configure the following
parameters with the respective values:
primaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.<namespace_gostubs_are_deployed_in>.svc:8080Example:
primaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.ocats.svc:8080 #secondaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.ocats.svc:8080 (comment out the secondaryNrfApiRoot)- nrfClientSubscribeTypes=BSF
Note:
To get all configmaps in your namespace execute:kubectl get configmaps -n <Policy_namespace>
- Diameter Log Level Configuration
- Set the Log level to Debug in Diam-GW POD:
kubectl edit statefulset <diam-gw pod name> -n <namespace>- name: LOGGING_LEVEL_APP
value: DEBUG
- Ensure that the setting for default peer configuration is taken from the
config server:
kubectl edit statefulset <diam-gw pod name> -n <namespace>- name: USE_CFG_SVC
value: "true"
- Set the Log level to Debug in Diam-GW POD:
- Prometheus server should be installed in cluster.
- Database cluster should be in a running state with all the required tables. You need to ensure that there are no previous entries in database before executing test cases.
- User MUST NOT initiate a job in two different pipelines at the same time.
- If Service Mesh check is enabled, then you need to create a destination
rule for fetching the metrics from the Prometheus. In most of the deployments,
Prometheus is kept outside the service mesh so you need a destination rule to
communicate between TLS enabled entity (ATS) and non-TLS entity (Prometheus). You
can create a destination rule as
follows:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion:networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind:DestinationRule metadata: name:prometheus-dr namespace:ocats spec: host:oso-prometheus-server.pcf.svc.cluster.local trafficPolicy: tls: mode:DISABLE EOFIn the destination rule:- name indicates the name of destination rule.
- namespace indicates where the ATS is deployed.
- host indicates the hostname of the prometheus server.
Logging into ATS
Before logging into ATS Jenkins GUI, it is important to get the Worker Node External IP and nodeport of the service, 'ocats-Policy'.
Execute the following command to get the Worker Node External IP:
Example:
kubectl get nodes -owide
Figure 3-1 Worker Node External IP

Execute the following command to get the nodeport:
kubectl get svc -n <BSF_namespace>
Example:
kubectl get svc -n ocbsf
In the below screenshot, 31944 is the nodeport.
Figure 3-2 BSF Nodeport
To login to Jenkins, open the Web Browser and type the URL: http://<Worker-Node-IP>:<Node-Port-of-ATS>. In the above screen, 31944 is the nodeport. Example: http://10.75.225.49:31944
Note:
For more information on ATS deployment in PCF, refer to Policy ATS Installation Procedure.Executing ATS
To execute ATS:
- Enter the username as "bsfuser" and password as "bsfpasswd".
Click Sign in.
The following screen appears showing BSF pre-configured pipelines:
Note:
If you want to modify your default login password, refer to Modifying Login Password- BSF-NewFeatures: This pipeline has all the test cases, which are delivered as part of BSF ATS.
- BSF-Performance: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
- BSF-Regression: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
Figure 3-3 Pre-Configured Pipelines
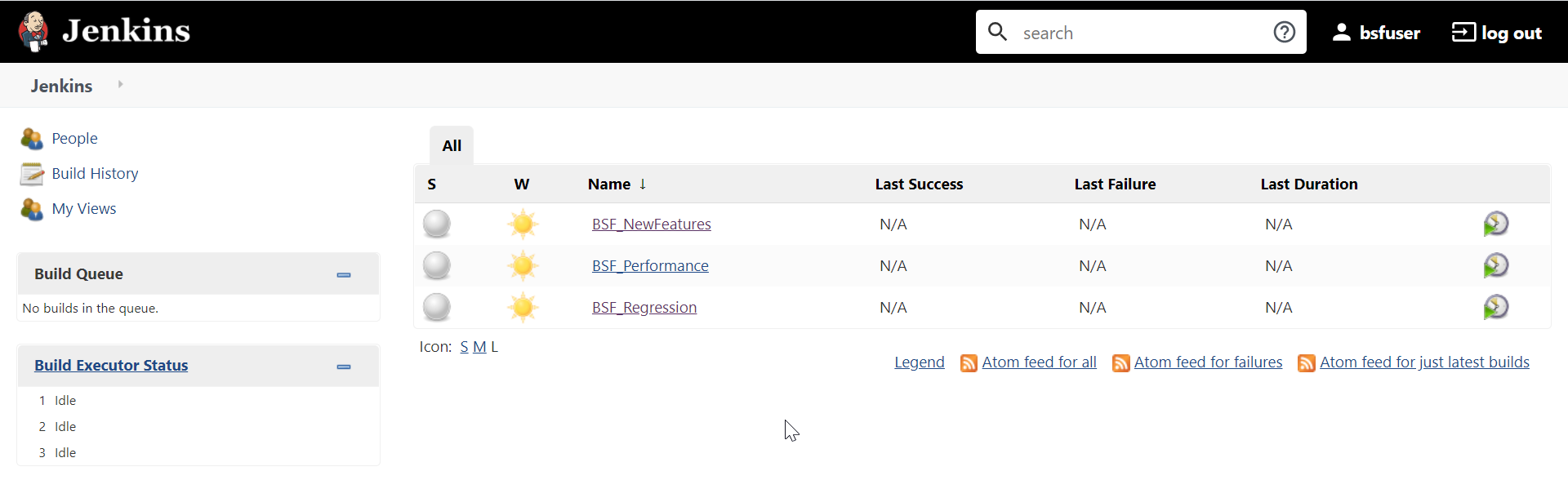
The pre-configured pipelines are explained below:
BSF-New Features Pipeline
- Click BSF-NewFeatures in the Name column and then, click
Configure in the left navigation pane as shown below:
Figure 3-4 BSF-NewFeatures Configure
- The BSF-NewFeatures, General tab appears. Make sure that the screen loads completely.
- Scroll-down to the end. The control moves from General tab to
the Pipeline tab as shown below:
Figure 3-5 BSF - Pipeline Script
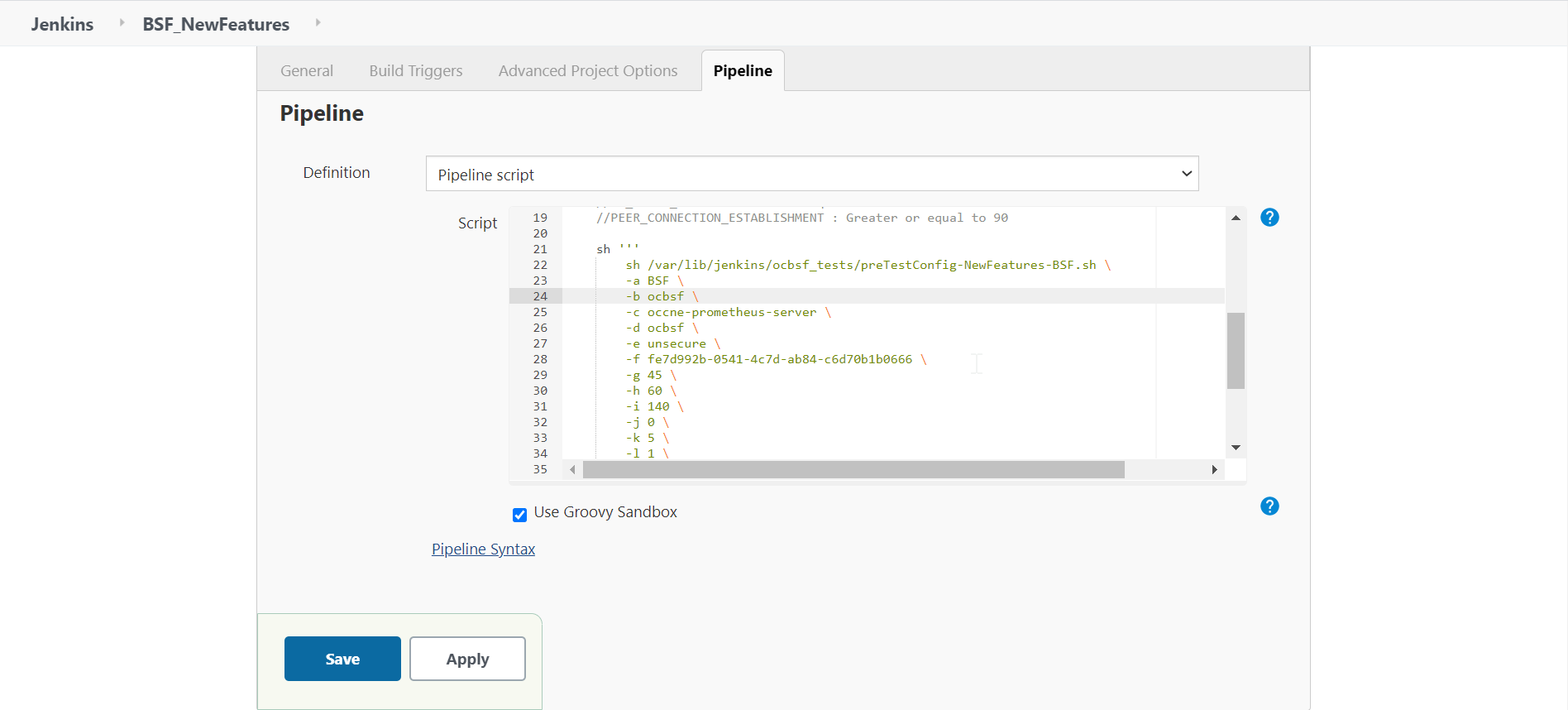 In the Script area of the Pipeline section, you can change value of the following parameters:
In the Script area of the Pipeline section, you can change value of the following parameters:- b: Change this parameter to update the namespace where BSF was deployed in your bastion.
- d: Change this parameter to update the namespace where your gostubs are deployed in your bastion.
- e: Set this parameter as 'unsecure', if you intend to run ATS in TLS disabled mode. Else, set this parameter as 'secure'.
- g: Set this parameter to more than 35 secs. The default wait time for the pod is 35 secs. Every TC requires restart of the nrf-client-management pod.
- h: Set this parameter to more than 60 secs. The default wait time to add a configurations to the database is 60 secs.
- i: Set this parameter to more than 140 secs. The default wait time for Nf_Notification Test Cases is given as 140 secs.
- k: Use this parameter to set the waiting time to initialize Test Suite.
- l: Use this parameter to set the waiting time to get response from Stub.
- m: Use this parameter to set the waiting time after adding BSF Configuration.
- n: Use this parameter to set the waiting time for Peer connection establishment.
- o: Use this parameter to set the waiting time before sending next message.
- p: Use this parameter to set Prometheus Server IP.
- q: Use this parameter to set Prometheus Server
Port.
Note:
DO NOT MODIFY ANYTHING OTHER THAN THESE PARAMETER VALUES. - Click Save after updating the parameters value.
The Policy-NewFeatures Pipeline screen appears.
Note:
It is advisable to save the pipeline script in your local machine that you can refer at the time of ATS pod restart.
Executing BSF Test Cases
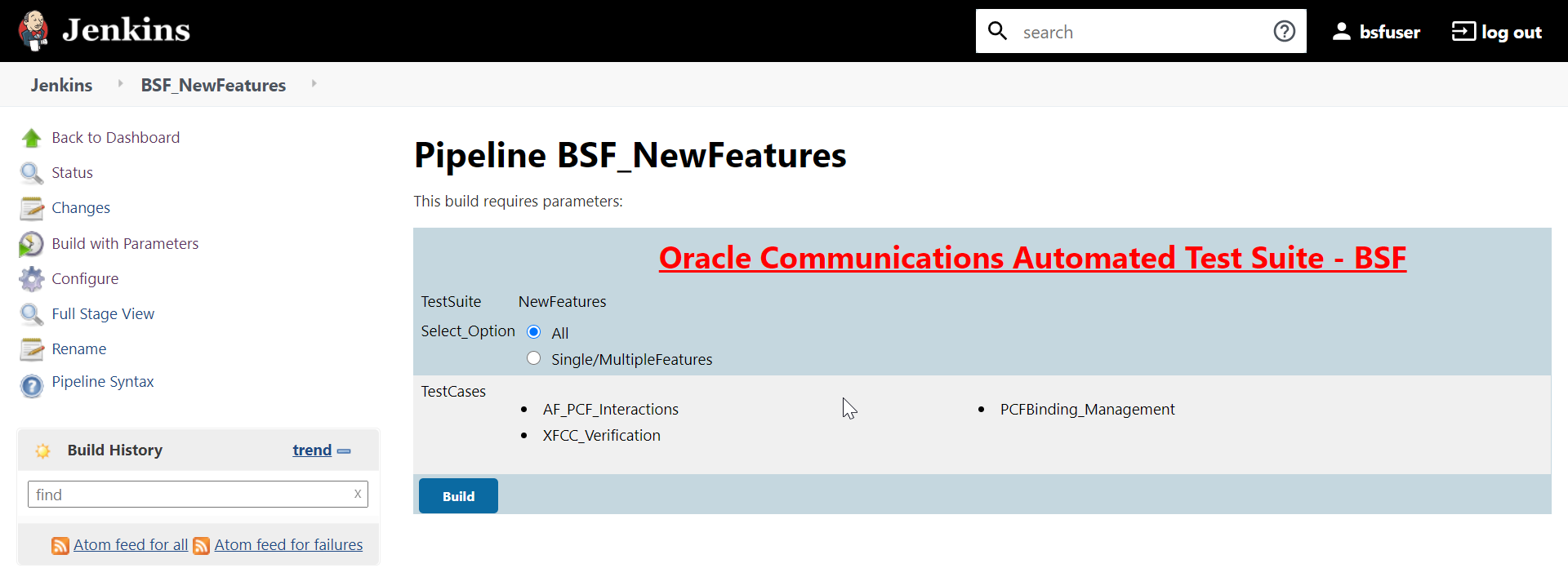
- Click the Build with Parameters link available in the left
navigation pane of the BSF-NewFeatures Pipeline screen. The following screen
appears.
Figure 3-6 BSF - Build with Parameters
Go to Build → Console Output to view the test result output as shown below:
Figure 3-7 Sample: Test Result Output in Console

Figure 3-8 Sample Output of Build Status
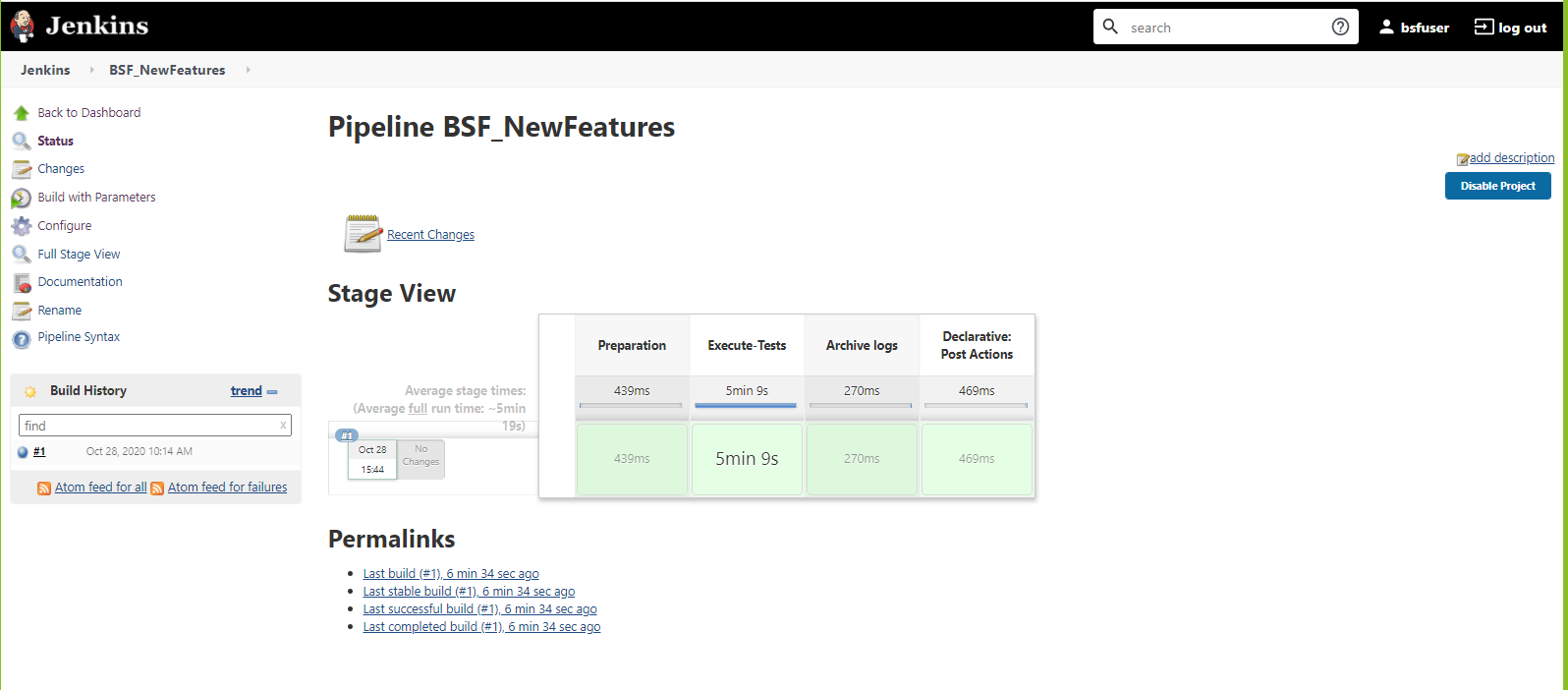
NewFeatures - Documentation
Figure 3-9 BSF-NewFeatures Feature List
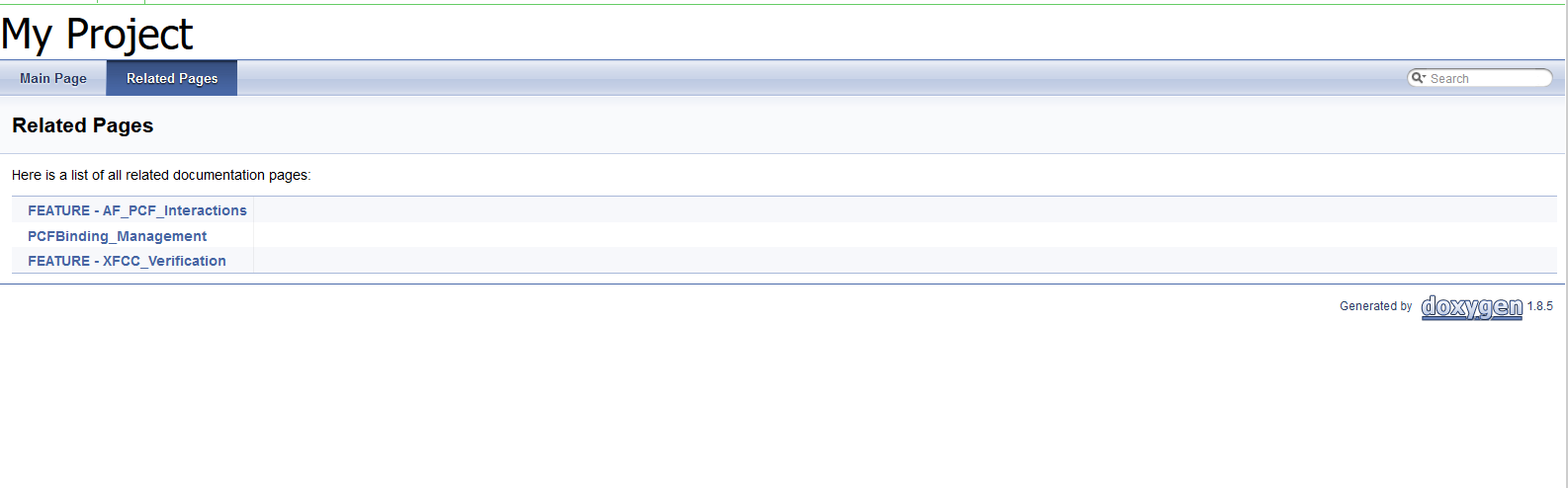
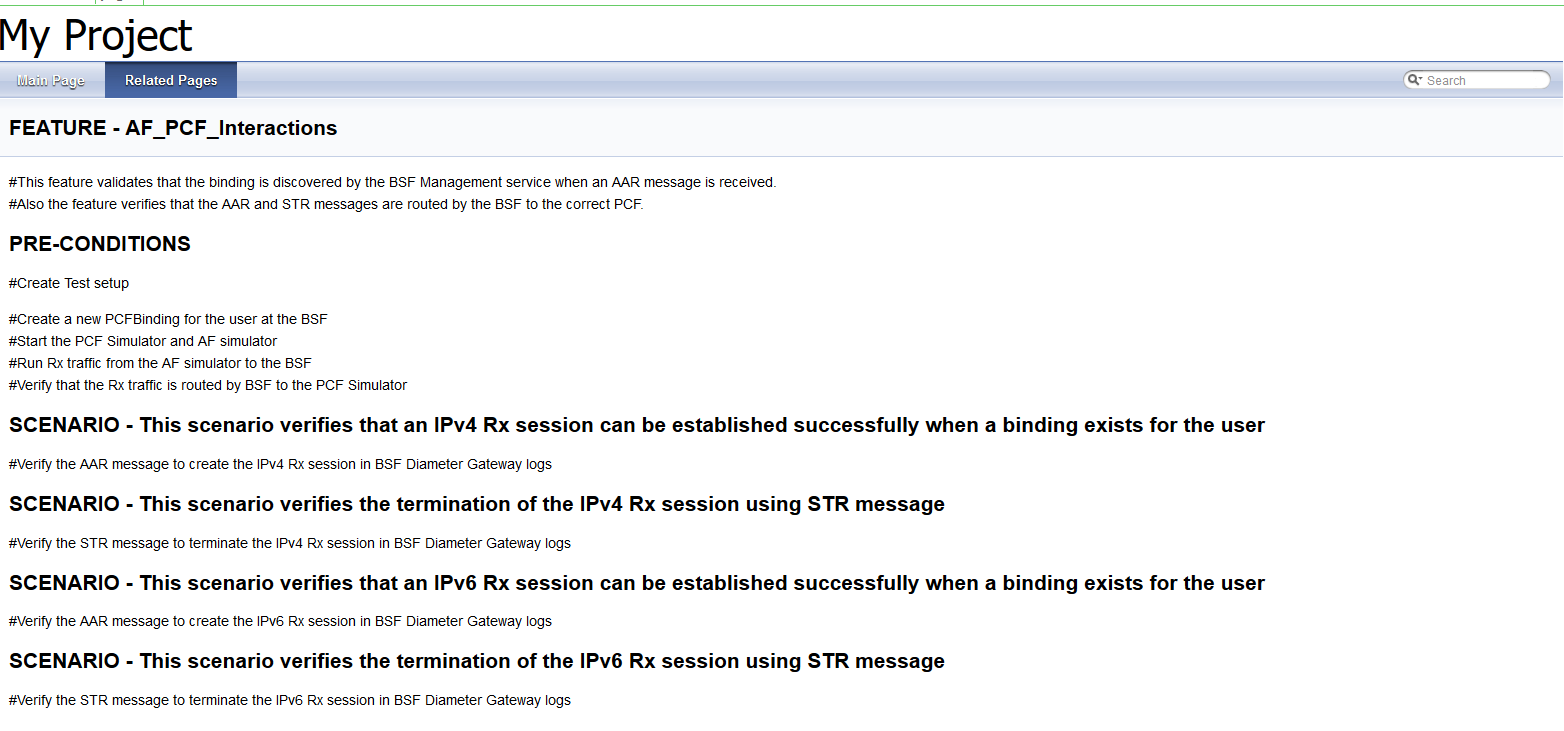
Figure 3-10 Test Cases and Scenarios of Feature-AF_PCF_Interactions
Based on the functionalities covered under Documentation, the Build Requires Parameters screen displays test cases. To navigate back to the Pipeline BSF-NewFeatures screen, click Back to BSF-NewFeatures link available on top left corner of the screen.
Executing NRF Test Cases using ATS
Prerequisite
To execute NRF Test Cases using NRF ATS 1.8.0, you need to ensure that following prerequisites are fulfilled.
- To execute NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature test cases, you need to deploy NRF and NRF ATS, both separately with certain changes.
- To execute Geo-Redundancy test cases, you need to deploy two NRF-1.8.0 with replication enabled. These test cases are executed separately as it requires two different NRFs.
- Users can customize test cases in the custom test case folders (cust_newfeatures, cust_regression and cust_performance). They can add new test cases, remove unwanted test cases and modify existing test cases. It does not impact the original product packaged test cases available in the newfeatures, regression and performance folders. For more details, you can refer to Custom Folder Implementation.
- The user should create certificates/keys (public and private) for AccessToken micro-service before deploying NRF.
- Deploy NRF 1.8.0 with default helm configurations using helm charts to execute all cases test except NF-FQDN-Authentication-Featurecases.
- All micro-services of NRF should be up and running including Accesstoken micro-service.
- Deploy ATS using helm charts.
- The user MUST copy the public keys (RSA and ECDSA) created in the above step to the ATS pod at the /var/lib/jenkins/ocnrf_tests/public_keys location.
- Deploy Stub using helm charts.
- For NRF ATS 1.8.0, you need to deploy two stub servers for executing SLF and Forwarding functionality test cases. The service name for both the STUB servers should be notify-stub-service and notify-stub-service02.
- Ensure Prometheus service is up and running.
- Deploy ATS and Stubs in the same namespace as NRF, as default ATS deployment is with role binding. In addition, deploy test stubs in the same namespace as NRF.
- User MUST not initiate a job in two different pipelines at the same time.
- If Service Mesh check is enabled, you need to create a destination
rule to fetch the metrics from the Prometheus. This is so because in most of the
deployments, Prometheus is kept outside the service mesh and a destination rule
is required to communicate between TLS enabled entity (ATS) and non-TLS entity
(Prometheus). To create a
rule:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion:networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind:DestinationRule metadata: name:prometheus-dr namespace:ocnrf spec: host:oso-prometheus-server.ocnrf.svc.cluster.local trafficPolicy: tls: mode:DISABLE EOFIn the above rule,- name indicates the name of destination rule.
- namespace indicates where the ATS is deployed.
- host indicates the hostname of the prometheus server.
Logging into ATS
Figure 3-11 Verifying ATS Pod
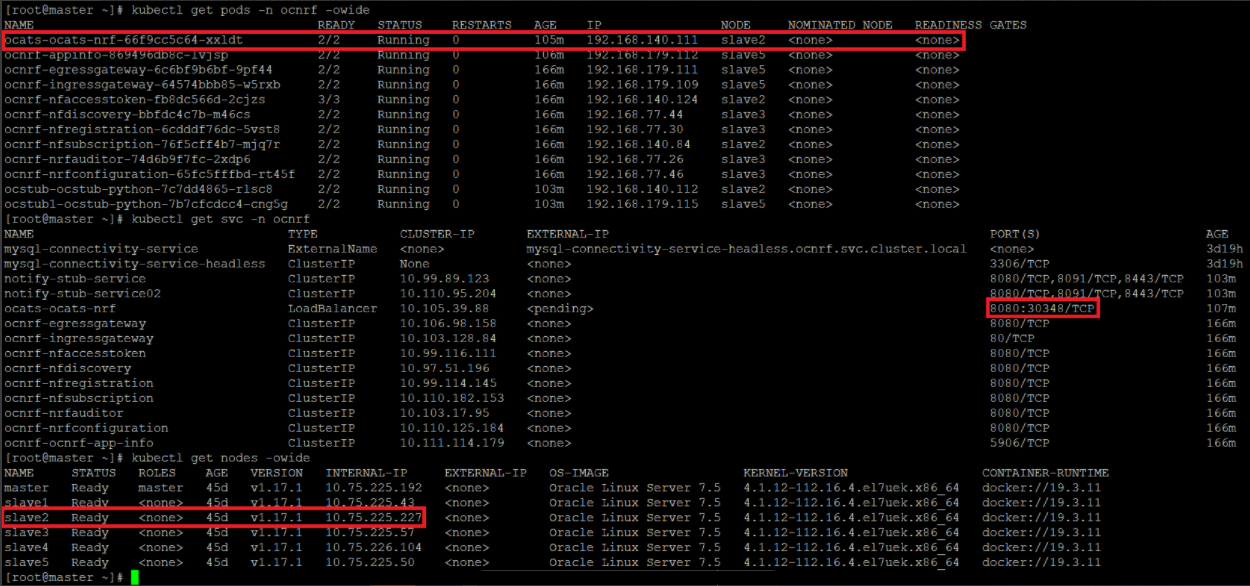
You can use the external IP of the worker node and nodeport of the ATS
service as <Worker-Node-IP>:<Node-Port-of-ATS>
Note:
In the Verifying ATS Pod screen, slave2 is the node where ATS is deployed, 30348 is the ATS nodeport and 10.75.225.227 is the worker node IP, highlighed in red. For more details on ATS deployment, refer to NRF ATS Installation Procedure.Figure 3-12 ATS Login
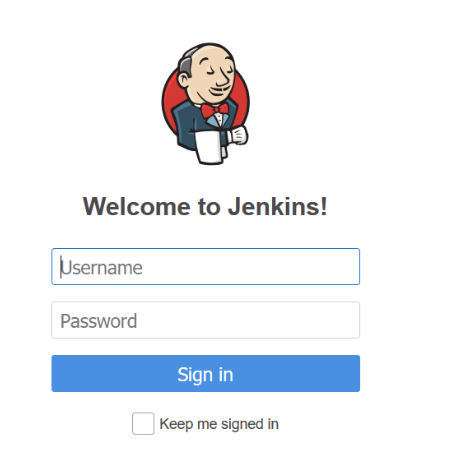
Executing ATS
NRF-NewFeatures Pipeline
- Enter the username as 'nrfuser'
and password as
'nrfpasswd'. Click Sign
in. The following screen appears.
Figure 3-13 NRF Pre-Configured Pipelines
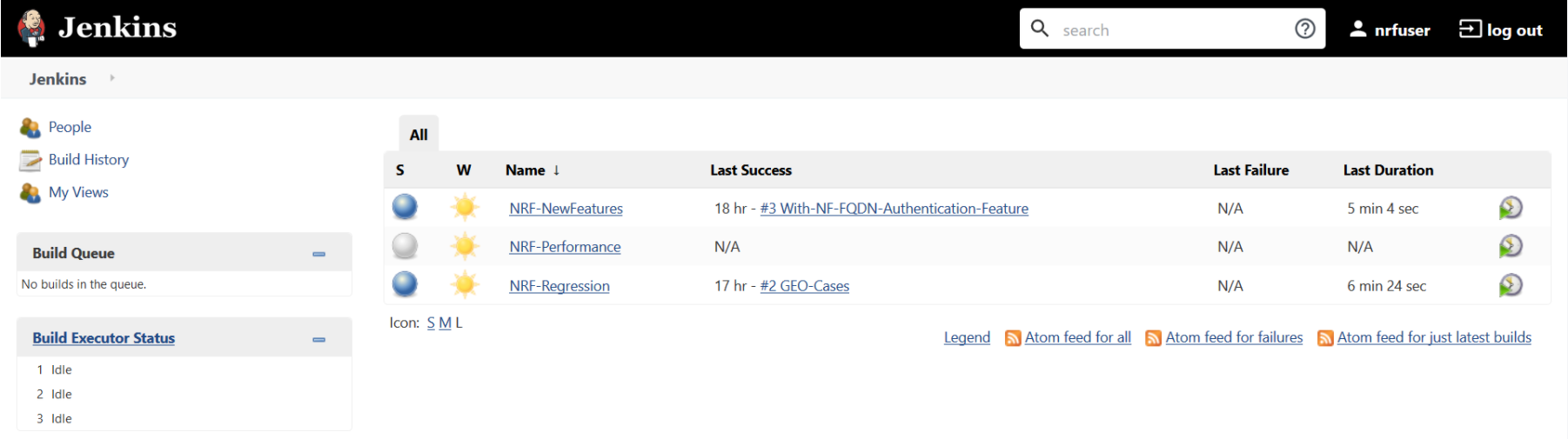
NRF ATS has three pre-configured pipelines.
- NRF-NewFeatures: This pipeline has all the test cases, which are delivered as part of NRF ATS - 1.8.0
- NRF-Performance: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
- NRF-Regression: This pipeline has all the test cases delivered so far in the previous releases.
After identifying the NRF pipelines, the user needs to do one-time configuration in ATS as per NRF deployment. In this pipeline, all the new testcases related to NRF are executed. To configure its parameters:
- Click NRF-NewFeatures in the Name column. Following screen appears:
Figure 3-14 Configuring NRF-New Features
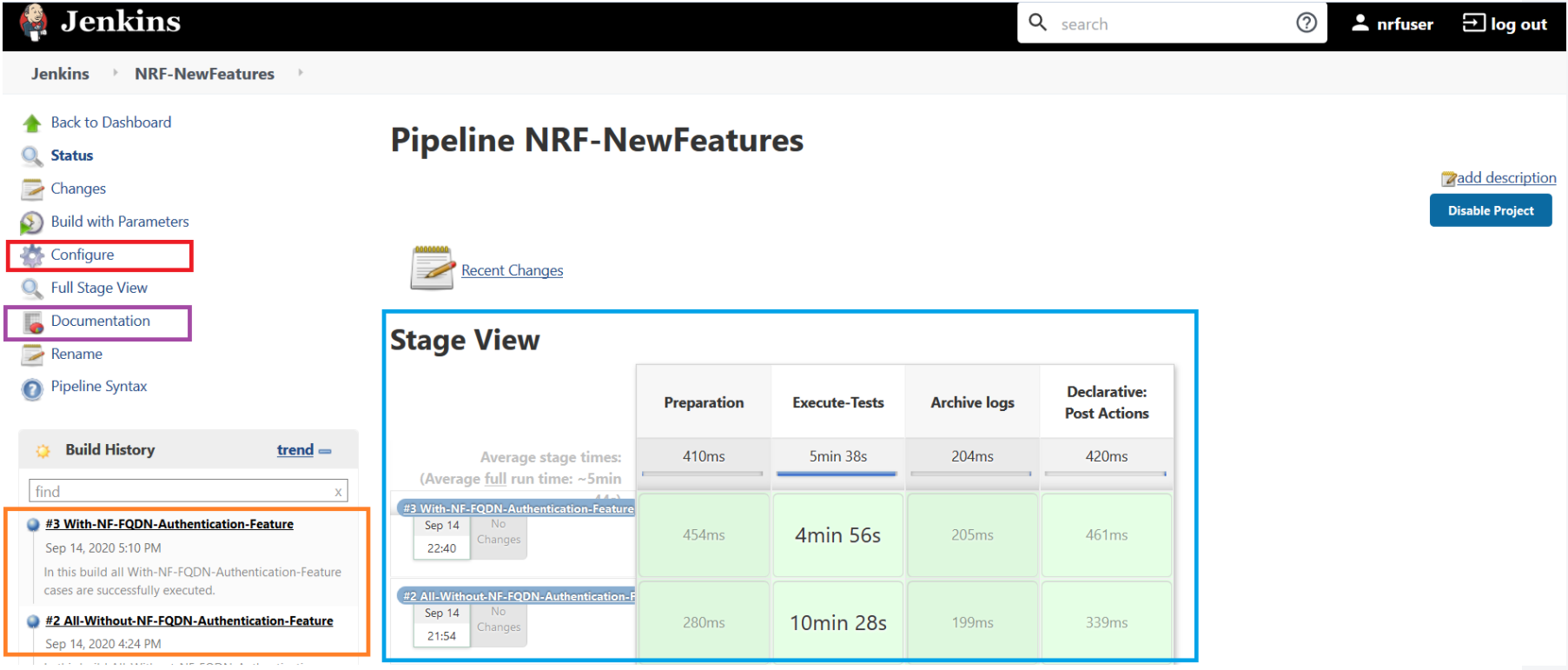 In the above screen:
In the above screen:- Click Configure to navigate to the screen where configuration needs to be done.
- Click Documentation to view the documented test cases, which are part of this NRF release.
- Click the blue dots inside Build History box to view the success console logs of the "Sanity", "All-Without-NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature" and "With-NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature" respectively.
- The Stage View represents the already executed pipeline for the customer reference.
- Click Configure. User MUST wait for the page to load completely.
Once the page loads completely, click the Pipeline tab as shown below:
MAKE SURE THAT THE SCREEN SHOWN BELOW LOADS COMPLETELY BEFORE YOU PERFORM ANY ACTION ON IT. ALSO, DO NOT MODIFY ANY CONFIGURATION OTHER THAN DISCUSSED BELOW.
Figure 3-15 Pipeline Option
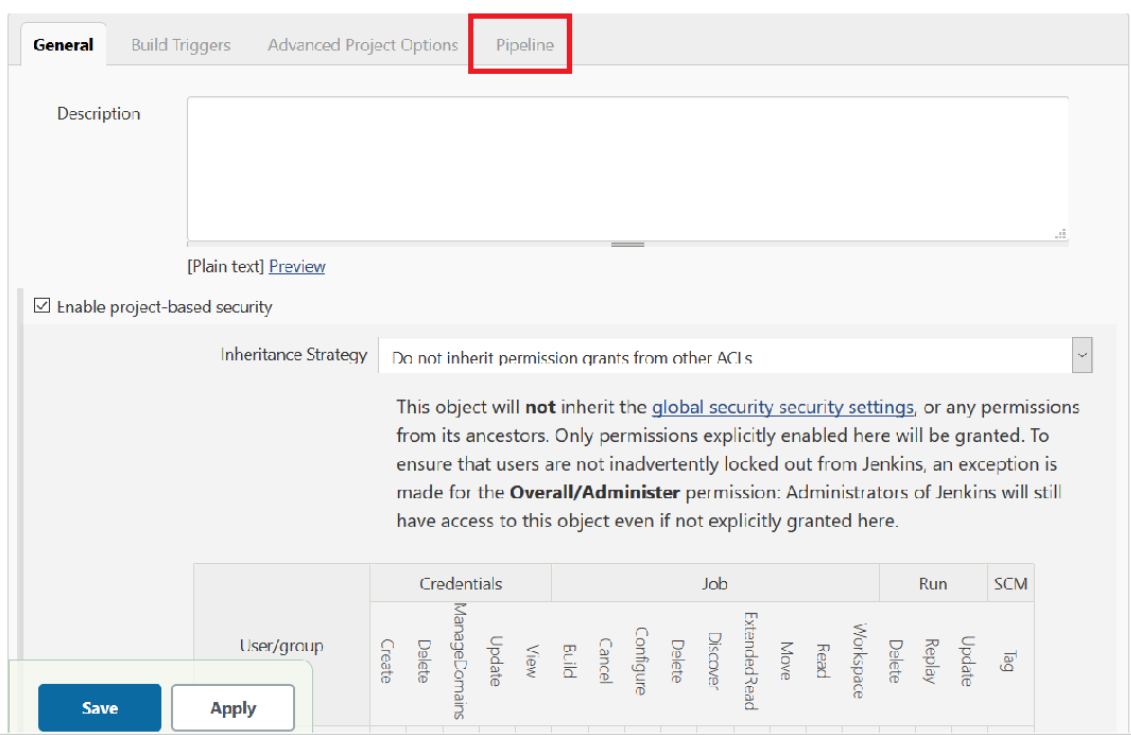
- The Pipeline section of the configuration page appears as shown
below:
Figure 3-16 Pipeline Section
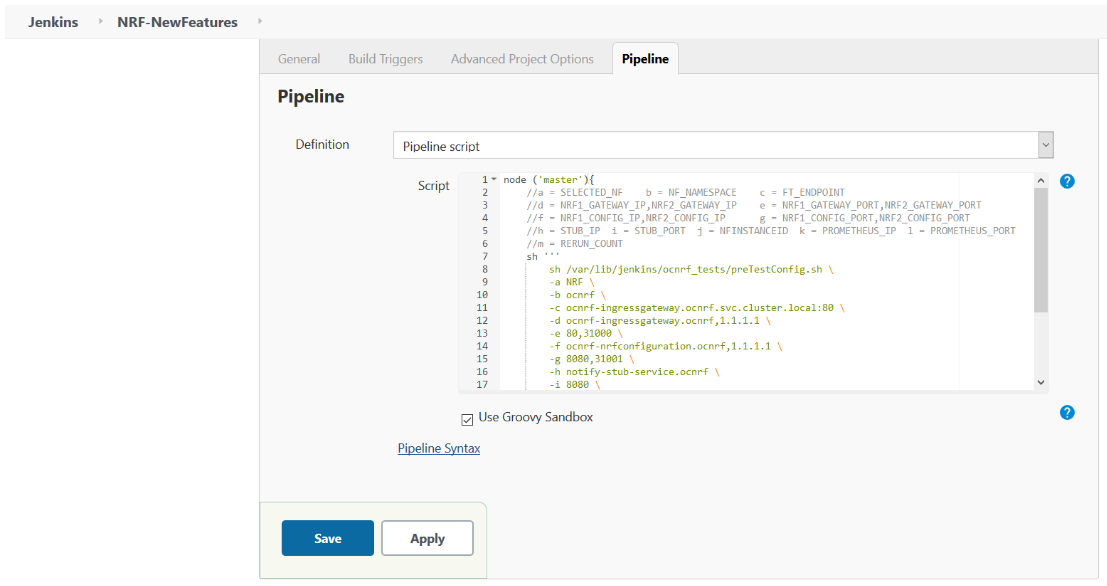 In the above screen, you can change the values of the 'Pipeline script'. The content of the pipeline script is as follows:
In the above screen, you can change the values of the 'Pipeline script'. The content of the pipeline script is as follows:Figure 3-17 Pipeline Script
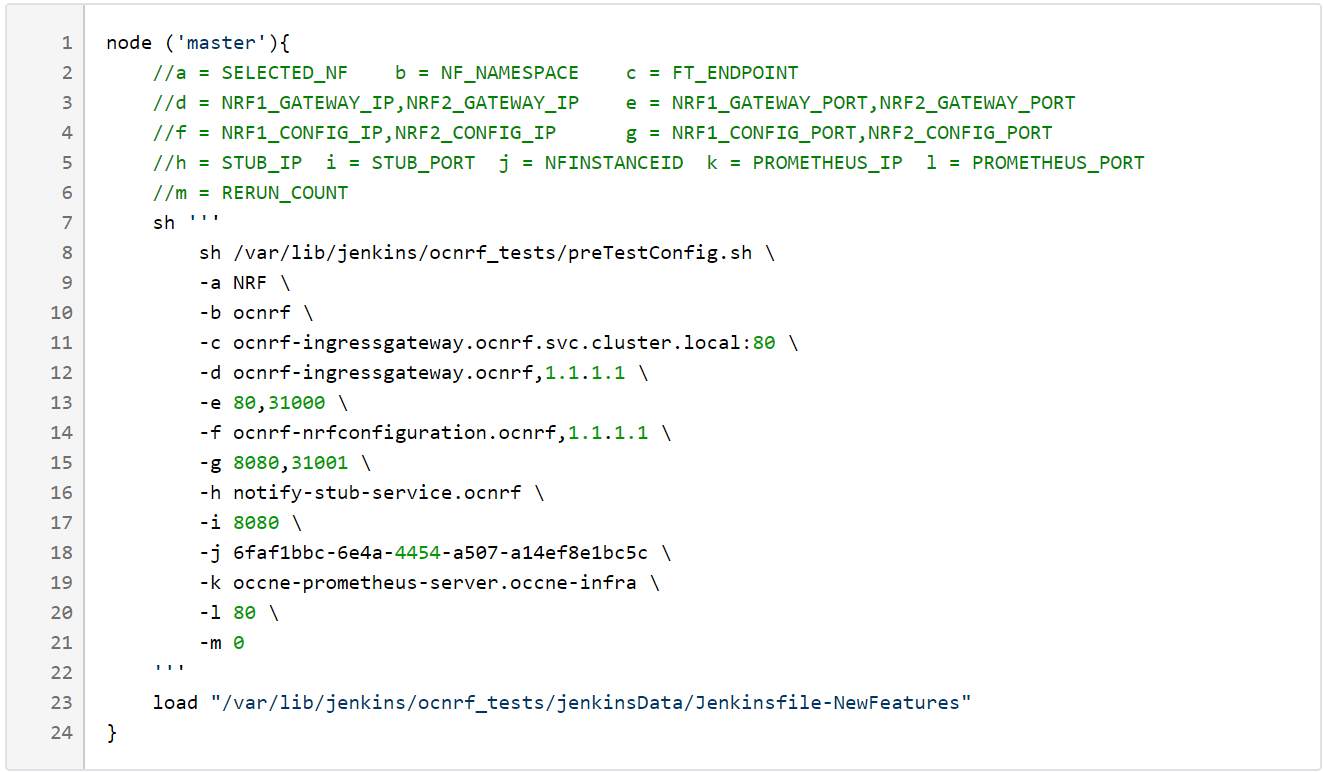
Note:
The User MUST NOT change any other value apart from line number 9 to line 21.You can change the parameter values from "a" - to - "m" as per user requirement. The parameter details are available as comments from line number 2 - to - 6.a: Name of the NF to be tested in capital (NRF). b: Namespace in which the NRF is deployed. c: endPointIP:endPointPort value used while deploying NRF with the help of helm chart. d: Comma separated values of NRF1 and NRF2 ingress gateway service (ocnrf-ingressgateway.ocnrf,1.1.1.1). It is also known as as cluster_domain. A dummy value of NRF2 ingress gateway (1.1.1.1) is provided for the reference. e: Comma separated values of NRF1 and NRF2 port of ingressgateway service (80,31000). A dummy value of NRF2 ingress gateway port (31000) is provided for the reference. f: Comma separated values of NRF1 and NRF2 configuration service (ocnrf-nrfconfiguration.ocnrf,1.1.1.1). It is also known as as cluster_domain. A dummy value of NRF2 configuration service (1.1.1.1) is provided for the reference. g: Comma separated values of NRF1 and NRF2 port of configuration service (8080,31001). A dummy value of NRF2 configuration microservice port (31001) is provided for the reference. h: Name_of_stub_service.namespace (notify-stub-service.ocnrf). i: Port of stub service (8080). j: NRF_Instance ID (6faf1bbc-6e4a-4454-a507-a14ef8e1bc5c). k: Name_of_Prometheus_service.namespace (occne-prometheus-server.occne-infra). l: Port of Prometheus service (80). m: Number of times the re-run of failed case is allowed (default as 0).Note:
You need not to change any value if- OCCNE cluster is used
- NRF, ATS and Stub are deployed in the ocnrf namespace
- Click Save after making neccesary changes. The NRF-NewFeatures screen
appears. Click Build with Parameters. Following screen appears:
Figure 3-18 Pipeline NRF-NewFeatures
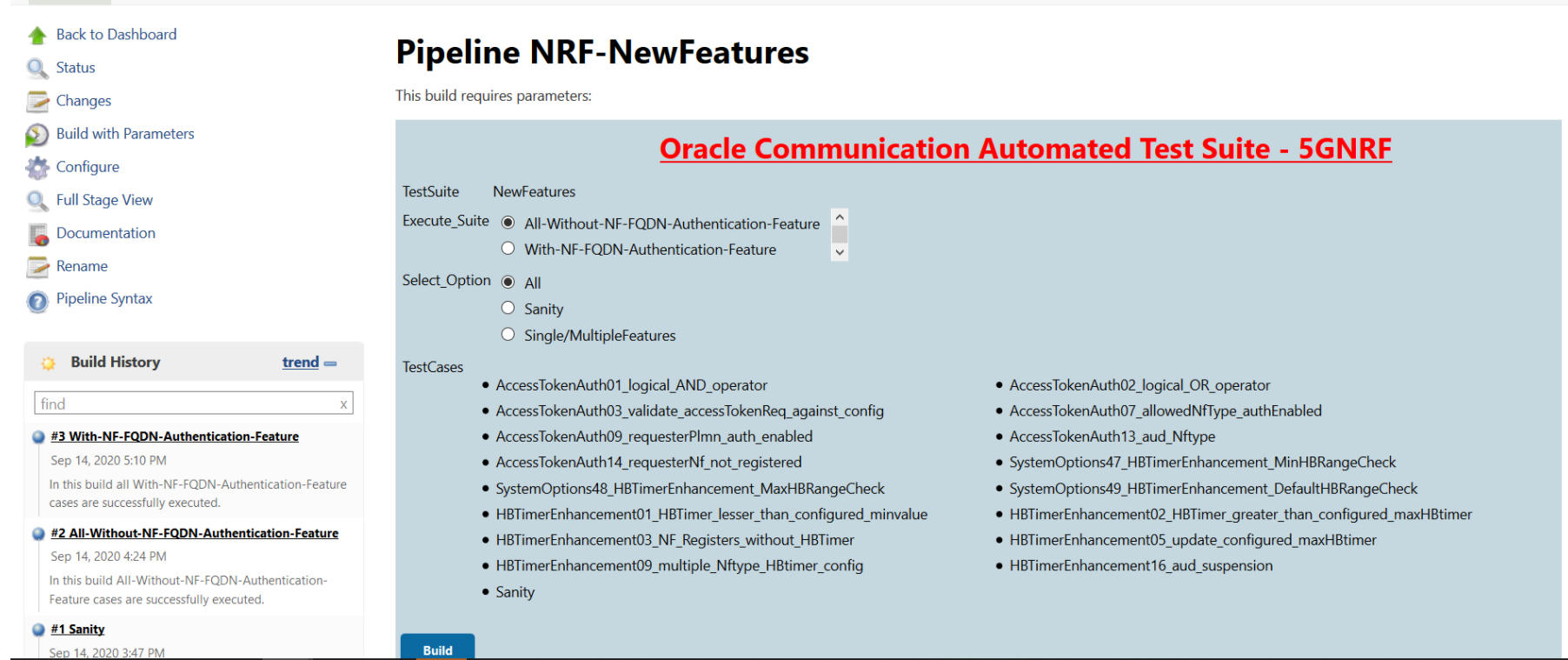 In the above screen, you have Execute_Suite options to execute NRF test cases either:
In the above screen, you have Execute_Suite options to execute NRF test cases either:- All-Without-NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature: This is the default option. It executes all the test cases except NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature.
- With-NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature: It executes all NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature test cases.
In the above screen, there are three Select_Option(s), which are:- All: This is the default option. It executes all the NRF test cases. User just need to scroll down and click Build to execute all the test cases.
- Sanity: It is recommended to execute Sanity
before executing any test case. This helps to ensure that all the
deployments are done properly. When you select Sanity, the following
screen appears:
Figure 3-19 Build Requires Parameters - Sanity
Click Build to execute all the sanity test cases.
Note:
Sanity option is not available when Execute_Suite is set to With-NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature. - Single/MultipleFeatures: This option allows you to select any number of test cases that you want to execute from the list of total test cases available for execution. After selecting the test cases, scroll-down and click Build. The selected NRF test cases are executed.
- NRF Sanity - This feature file contains all the basic sanity test cases of NRF ATS to validate whether the deployment is correct or not. It is advisable to execute these test cases before starting a complete suite.
- Configuration - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "SystemOptions".
- Registration - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "HBTimerEnhancement01".
- AccessToken - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "AccessTokenAuth".
- NF-FQDN-Authentication - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "NfAuthentication".
Figure 3-20 Sample Screen: NRF-ATS Full Execution
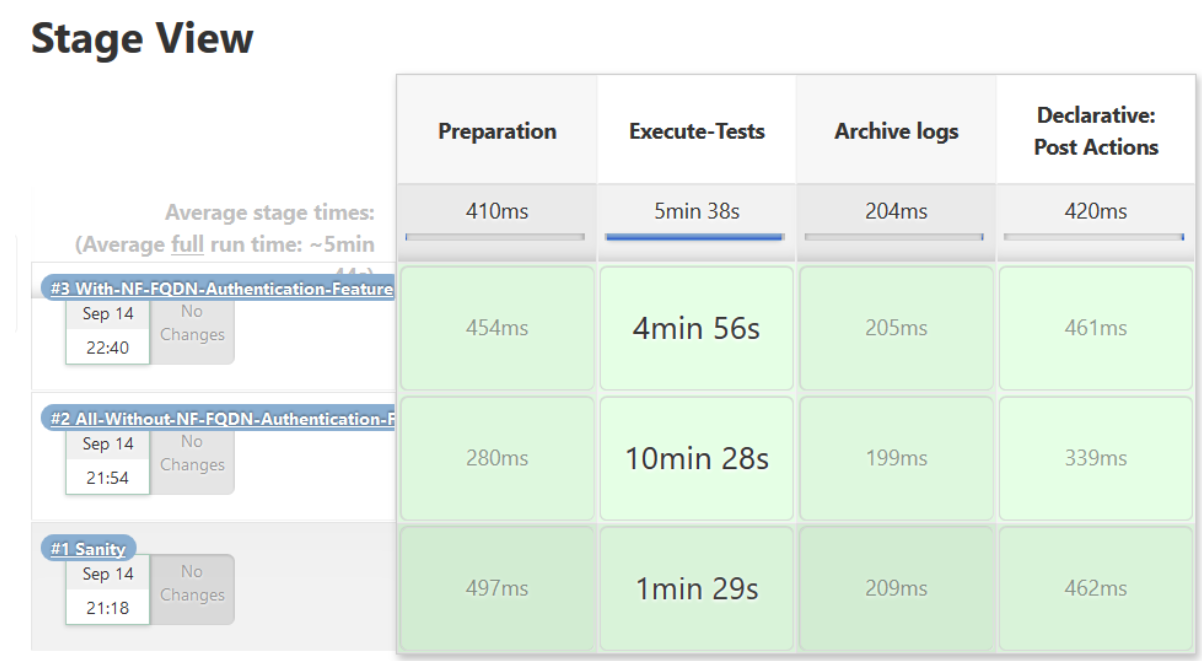
Figure 3-21 Test Cases Result - Sanity
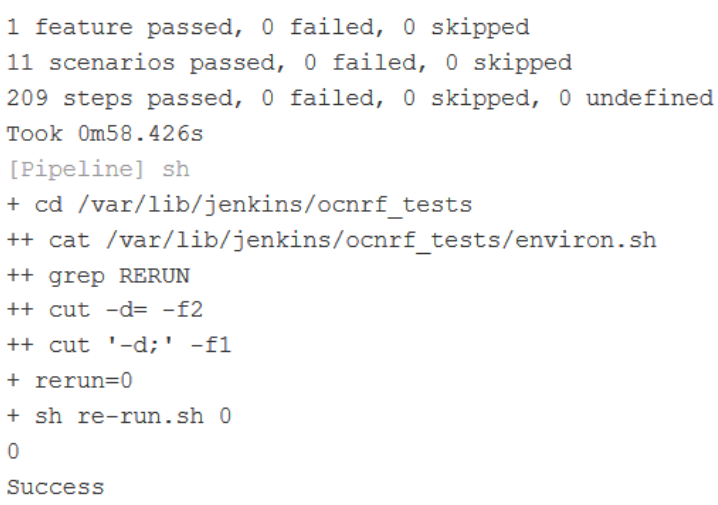
Figure 3-22 Test Cases Result - All-Without-NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature
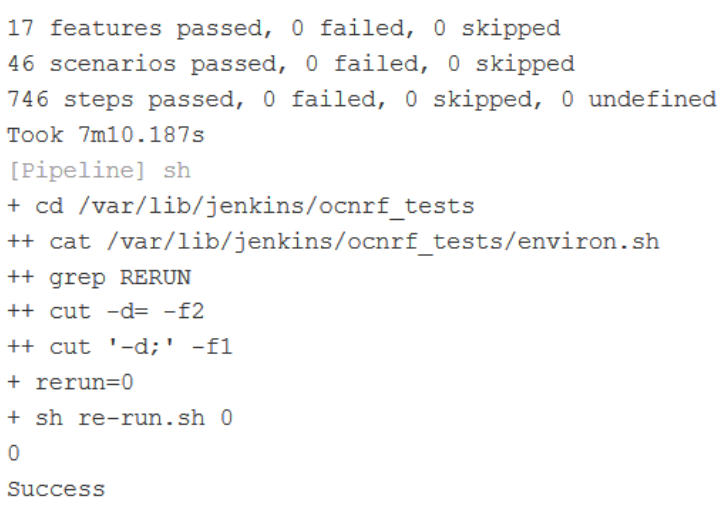
Figure 3-23 Test Cases Result - All-With-NF-FQDN-Authentication-Feature
NRF-NewFeatures Documentation
Figure 3-24 NRF-NewFeatures Documentation

Figure 3-25 Sample Feature: NF_BASIC_SANITY_CASES

Based on the functionalities covered under Documentation, the Build Requires Parameters screen displays test cases. To navigate back to the Pipeline NRF-NewFeatures screen, click Back to NRF-NewFeatures link available on top left corner of the screen.
NRF-Regression Pipeline
This pre-configured pipeline contains all the test cases that are delivered till NRF ATS 1.7.0. However, some test cases are updated as per new implementation of NRF.
The configuration method and parameters are same as the NewFeatures pipeline. Only difference in this pipeline is that it does not have Sanity option. Thus to configure this pipeline, you have to provide NRF2 details.
From this release onwards, GEO will be part of Regression, so please correct it. NRF2 details are required to be provided while configuring the Regression pipeline.
- AccessToken - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "oAuth".
- Configuration - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Config".
- Discovery - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Disc".
- NRF Forwarding - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Forwarding".
- NRF Functional - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Feat".
- Registration - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Reg" and "Upd". These are related to update operation of registered profiles.
- NRF SLF - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "SLF".
- Subscription - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Subs".
- Geo Redundancy - These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Geo".
-
Note:
You need not to change any value if any GEO-Redundancy case is not executed. If any GEO-Redundancy case is executed, you have to provide pipeline script values for NRF-2 in d, e, f and g options as per deployment.
Figure 3-26 NRF-Regression

Figure 3-27 NRF-Regression - All-Without-GEO
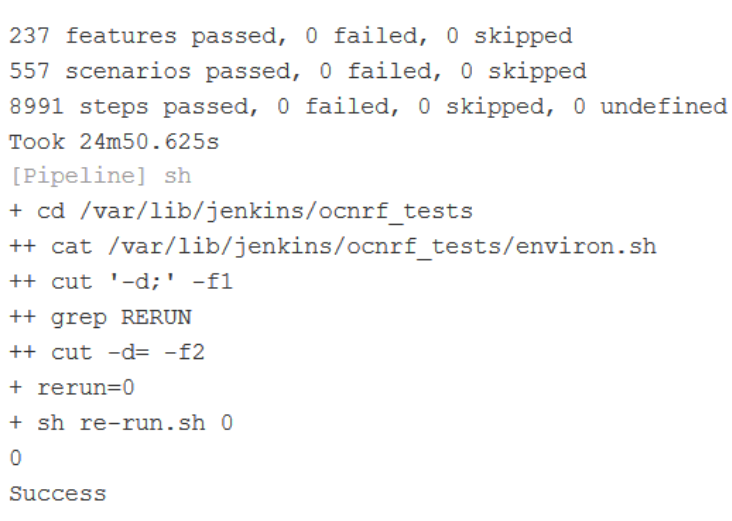
Figure 3-28 NRF-Regression - GEO Cases
NRF-Regression Documentation
Click Documentation in the left navigation pane of the NRF-Regression pipeline to view all the test cases provided till NRF ATS 1.7.0.
- NF_CONFIGURATION_CASES - Lists the cases related to NRF configuration.
- NF_DISCOVERY_CASES - Lists all the discovery microservice related cases.
- NF_FORWARDING_FEATURE_CASES - Lists all the forwarding related cases.
- NF_FUNCTIONAL_CASES - Lists all the functional cases.
- NF_GEO_REDUNDANCY_FEATURE_CASES - Lists all the Geo-Redundancy related cases.
- NF_OAUTH_CASES - Lists all the accesstoken related cases.
- NF_REGISTRATION_CASES - Lists all the registration related cases.
- NF_SLF_FEATURE_CASES - Lists all the SLF related cases.
- NF_SUBSCRIPTION_CASES - Lists all subscription related cases.
Figure 3-29 NRF-Regression Documentation
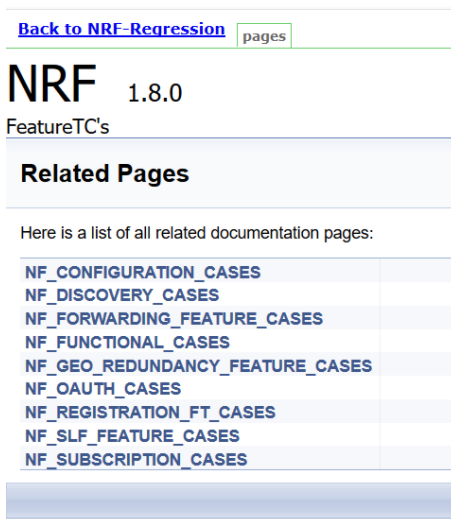
Figure 3-30 Sample Screen: NRF-Regression Documentation
Executing NSSF Test Cases using ATS
To execute NSSF Test Cases using NRF ATS 1.4, you need to ensure that following prerequisites are fulfilled.
- Before deploying NSSF, the user must create certificates/keys (public and private) for AccessToken microservice. The public keys (RSA and ECDSA) must be copied to the ATS pod at /var/lib/jenkins/ocnssf_tests/public_keys location.
- User must deploy NSSF 1.4 with default helm configurations using helm charts.
- All NSSF micro-services should be up and running including AccessToken microservice.
Logging into ATS
Figure 3-31 Verifying ATS Deployment

There are two ways to login to ATS Jenkins GUI.
- When an external load balancer (metalLB in case of OCCNE) is available and an external IP is provided to the ATS service, the user can login to ATS GUI using <External-IP>:8080.
- When an external IP is not provided to the ATS service, the user can open the
browser and provide the external IP of the worker node and nodeport of the ATS
service to login to ATS
GUI.
<Worker-Node-IP>:<Node-Port-of-ATS>Note:
In the Verifying ATS Deployment screen, ATS nodeport is highlighted in red as 32013. For more details on ATS deployment, refer to NSSF ATS Installation Procedure.
Open a browser and provide IP and port details as <Worker-Node-IP>:<NodePort-of-ATS> (As per the above example: 10.98.101.171:32013). The ATS login screen appears.
Executing ATS
- Enter the username as 'nssfuser' and password as 'nssfpasswd'.
Click Sign in.
The following screen appears showing pre-configured pipelines for NSSF individually (3 Pipelines).
Note:
If you want to modify your default login password, refer to Modifying Login Password- NSSF-New-Features: This pipeline has all the test cases that are delivered as part of NSSF ATS - 1.4.
- NSSF-Performance: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
- NSSF-Regression: This pipleine has all the test cases of previous releases. As this is the first release of NSSF-ATS, this pipeline does not show any previous release test cases.
Figure 3-32 Pre-Configured Pipelines
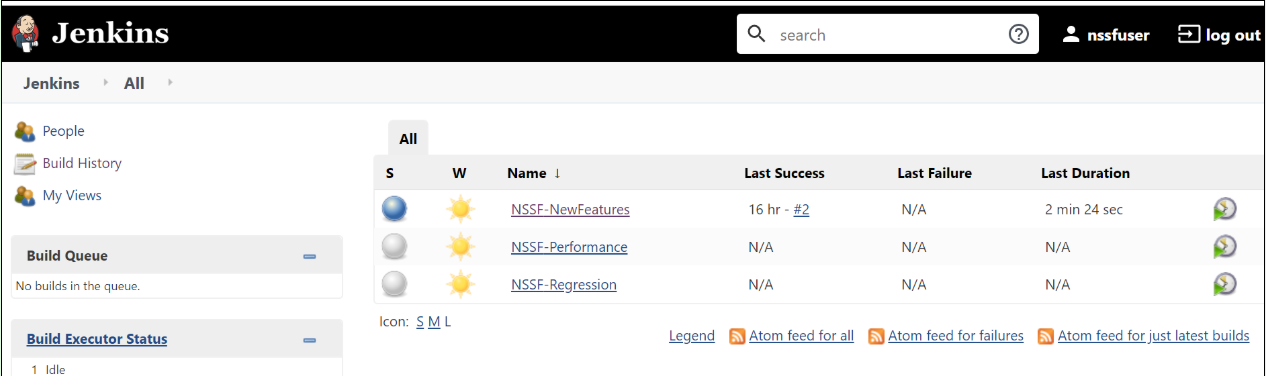 Each one of this pipeline is explained below:
Each one of this pipeline is explained below:- NSSF-NewFeatures Pipeline: After identifying
the NSSF pipelines, the user needs to do one-time configuration
in ATS as per their SUT deployment. In this pipeline, all the
new testcases related to NSSF are executed. To configure its
parameters:
- Click NSSF-NewFeatures in the Name
column. The following screen appears:
Figure 3-33 NSSF-NewFeatures Pipeline
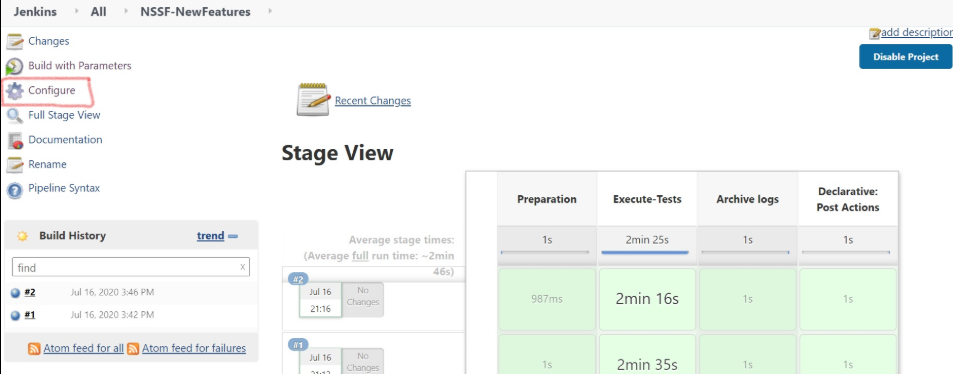 In the above screen:
In the above screen:- Click Configure to navigate to a screen where configuration needs to be done.
- Click Documentation to view the documented test cases.
- Click blue dots inside Build History box to view the success console logs of the "All" and "Sanity" respectively.
- The Stage View represents already executed pipeline for the customer reference.
- Click Configure. Users MUST wait for
the page to load completely. Once the page loads
completely, click the Pipeline tab to reach the
Pipeline configuration as shown below:
MAKE SURE THAT THE SCREEN SHOWN ABOVE LOADS COMPLETELY BEFORE YOU PERFORM ANY ACTION ON IT. ALSO, DO NOT MODIFY ANY CONFIGURATION OTHER THAN DISCUSSED BELOW.
Figure 3-34 NSSF Configure
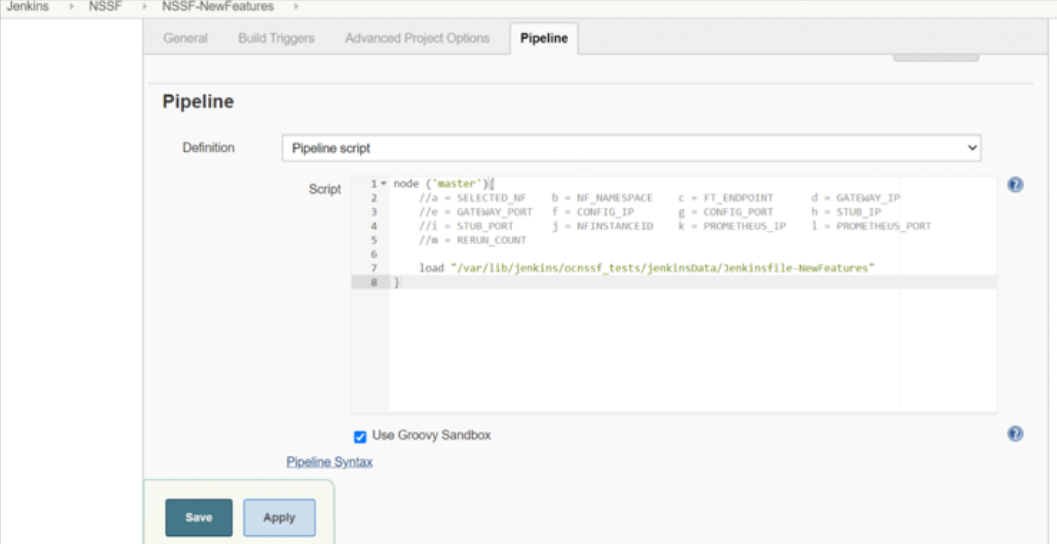
- In the above screen, the values of the
'Pipeline script' needs to be changed. The content of
the pipeline script is as
follows:
node ('master'){ //a = SELECTED_NF b = NF_NAMESPACE c = FT_ENDPOINT d = GATEWAY_IP //e = GATEWAY_PORT f = CONFIG_IP g = CONFIG_PORT h = STUB_IP //i = STUB_PORT j = NFINSTANCEID k = PROMETHEUS_IP l = PROMETHEUS_PORT //m = RERUN_COUNT sh ''' sh /var/lib/jenkins/ocnssf_tests/preTestConfig.sh \ -a NSSF \ -b ocnssf \ -c ocnssf-ingressgateway.ocnssf.svc.cluster.local:80 \ -d ocnssf-ingressgateway.ocnssf \ -e 80 \ -f ocnssf-nssfconfiguration.ocnssf \ -g 8080 \ -h notify-stub-service.ocnssf \ -i 8080 \ -j 6faf1bbc-6e4a-4454-a507-a14ef8e1bc5c \ -k occne-prometheus-server.occne-infra \ -l 80 \ -m 2 ''' load "/var/lib/jenkins/ocnssf_tests/jenkinsData/Jenkinsfile-NewFeatures" }Note:
The User MUST NOT change any other value apart from line number 8 to line 20.You can change only those parameters that are marked as "a" to "m" as per your requirement.
- a - Name of the NF to be tested in capital (NSSF).
- b - Namespace in which the NSSF is deployed
- c - endPointIP:endPointPort value used while deploying the NSSF using the helm chart
- d - Name_of_NSSF_ingressgateway_service.namespace (ocnssf-nssfconfiguration.ocnssf) - this is also known as as cluster_domain.
- e - Port of ingressgateway service (80)
- f - Name_of_NSSF_configuration_service.namespace (ocnssf-nssfconfiguration.ocnssf)
- g - Port of configuration service (8080)
- h - Name_of_stub_service.namespace (notify-stub-service.ocnssf)
- i - Port of stub service (8080)
- j - NSSF_Instance ID (6faf1bbc-6e4a-4454-a507-a14ef8e1bc5c)
- k - Name_of_Prometheus_service.namespace (occne-prometheus-server.occne-infra)
- l - Port of Prometheus service (80)
- m - Number of times the re-run of failed case is allowed (default as 2).
Note:
You do not have to change any value if OCCNE cluster is used and NSSF, ATS and STUB are deployed in ocnssf namespace. - Click Save after making necessary
changes. You are navigated back to the Pipeline
NSSF-NewFeatures screen. Click Build with
Parameters as shown below:
Figure 3-35 Build with Parameters
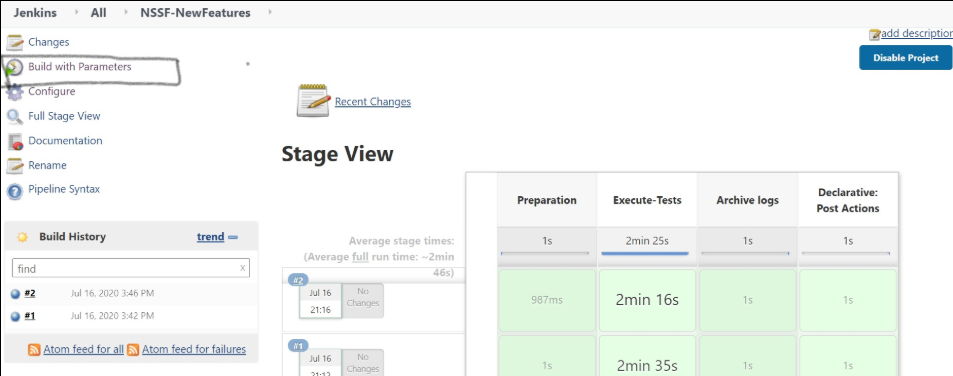
The following screen appears:
Figure 3-36 Build with Parameters Options
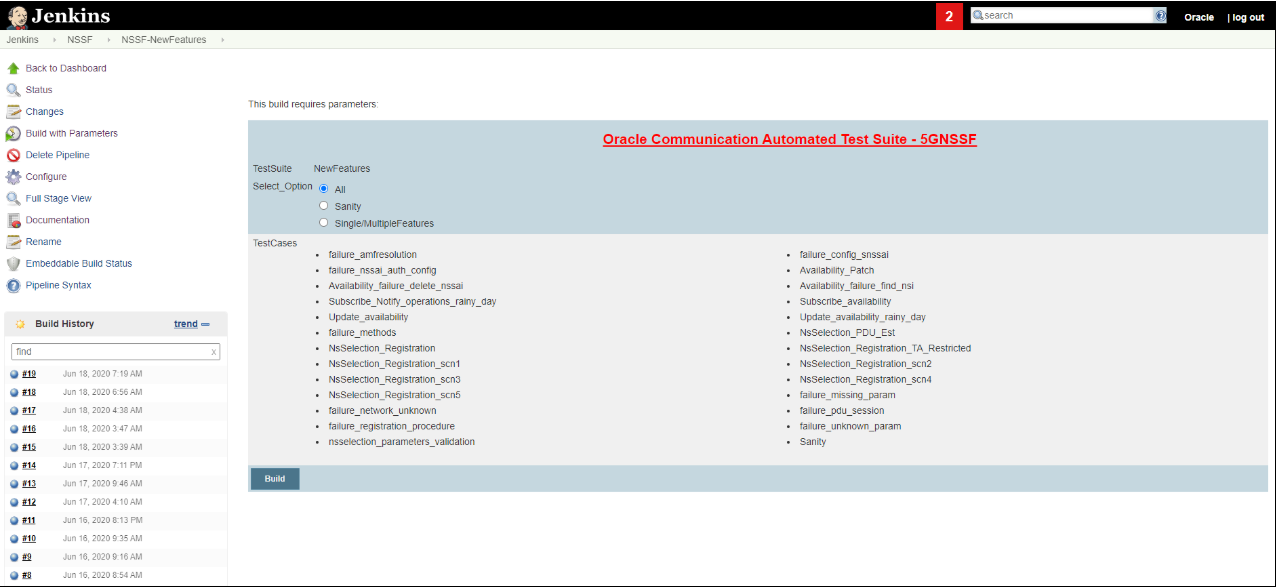
- Click NSSF-NewFeatures in the Name
column. The following screen appears:
Executing NSSF Test Cases
- Click the Schedule a Build with parameters icon present on the
NSSF-NewFeatures screen in the extreme right column corresponding to
NSSF-NewFeatures row as shown below:
Figure 3-37 Schedule a Build with Parameters
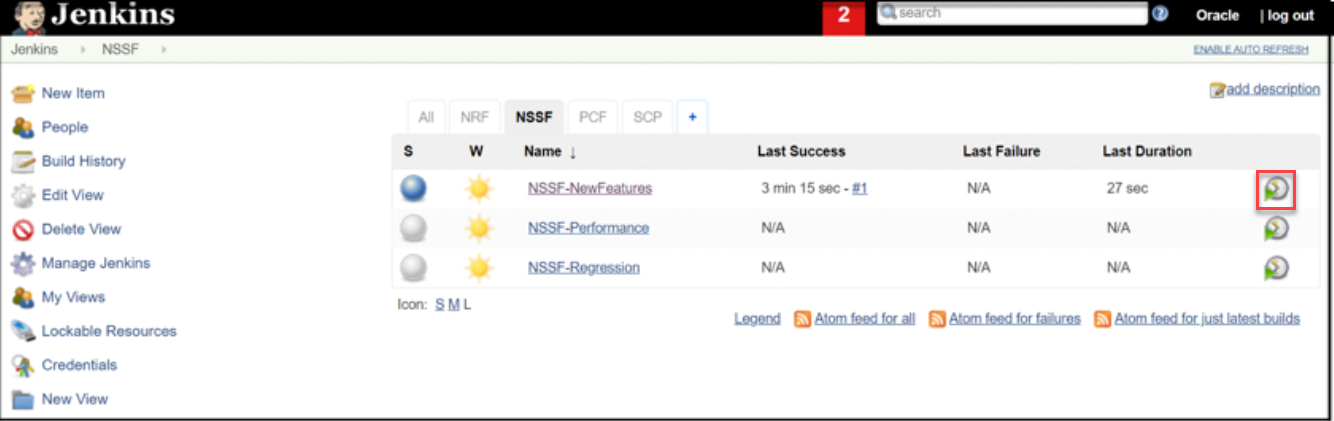
- The following screen appears:
Figure 3-38 Build Screen
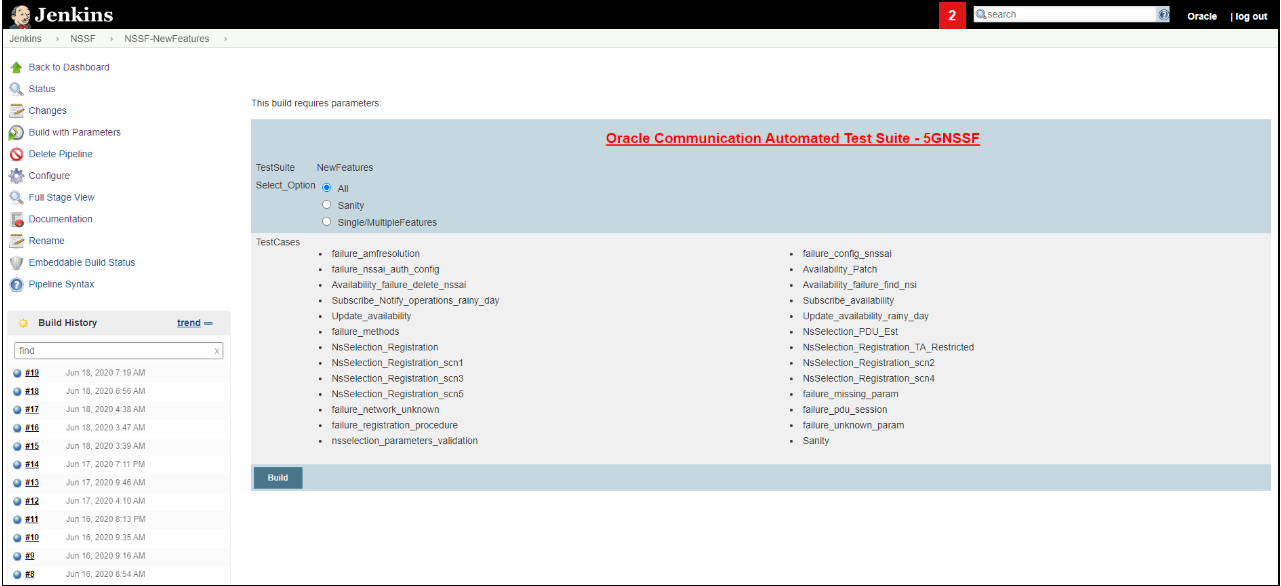
In the above screen, there are three Select_Option(s), which are:
- All: By default, all the NSSF test cases are selected for execution. User just needs to scroll down and click Build to execute all the test cases.
- Sanity: It is recommended to execute Sanity
before executing any test case. This helps to ensure that all the
deployments are done properly or not. When you select Sanity, the
following screen appears.
Figure 3-39 Select_Option(s) - Sanity
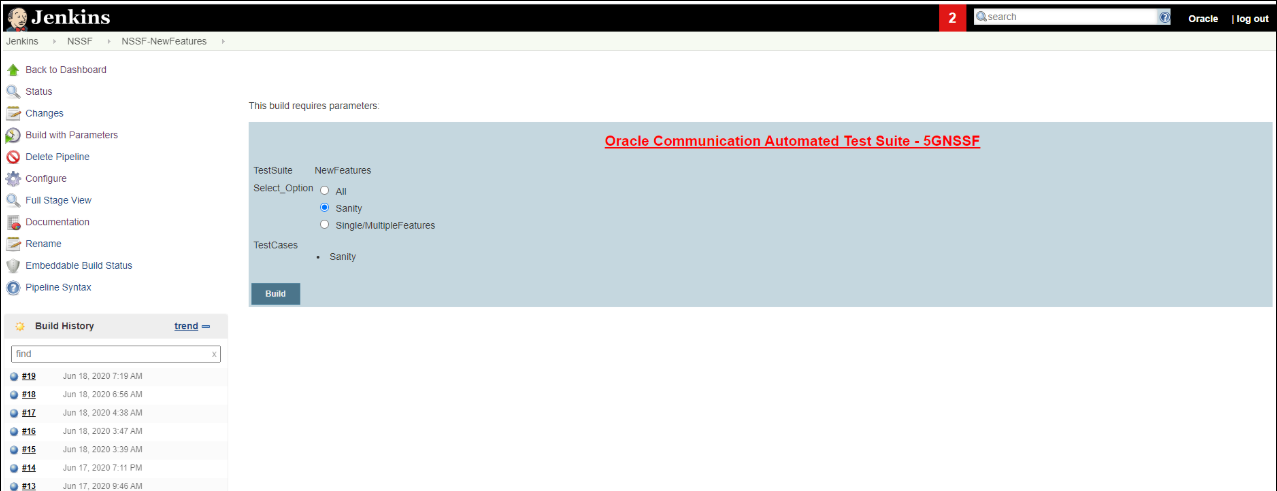
Click Build to execute all the sanity test cases.
- Single/MultipleFeature: This option allows you to select any number of test cases that you want to execute from the list of total test cases available for execution. After selecting the test cases, scroll-down and click Build. The selected NSSF test cases are executed.
The NSSF test cases are divided into NSSF Service operations as follows:
- Availability Update: These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Update".
- Configuration: These feature files are listed with a prefix as "failure".
- Registration: These feature files are listed with a prefix as "NsSelection_Registration".
- PDU Session: These feature files are listed with a prefix as "NsSelection_PDU".
- NSSF Sanity: This feature file contains all the basic sanity cases for NSSF ATS 1.6.1.
- Subscription: These feature files are listed with a prefix as "Subscribe".
NewFeatures - Documentation
To view NSSF functionalities, go to NSSF-NewFeatures pipeline and click the Documentation link in the left navigation pane. The following screen appears:
Figure 3-40 NSSF - Documentation
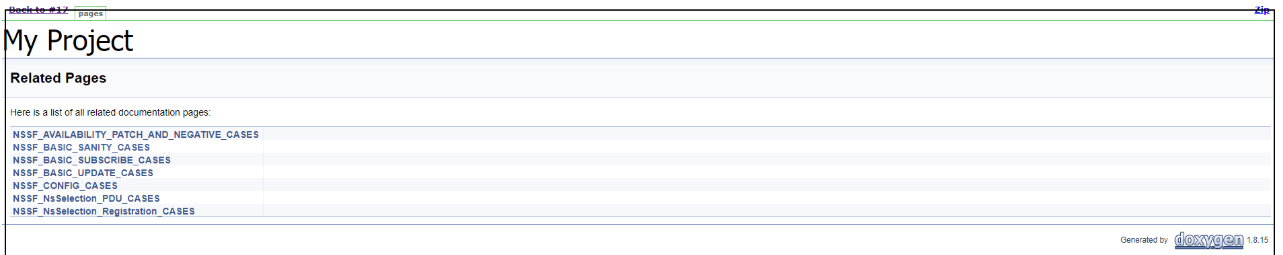
Each one of the documentation features is described below:
- NSSF_BASIC_SANITY_CASES - Lists all the sanity cases, which are useful to identify whether all the NSSF functionality works fine.
- NSSF_CONFIG_CASES - Lists all the test cases related to NSSF configuration.
- NSSF_BASIC_UPDATE_CASES - Lists all the test cases relaed to Availability Update.
- NSSF_AVAILABILITY_PATCH_AND_NEGATIVE_CASES - Lists all the test cases related to Availability Patch and other negative scenarios.
- NSSF_NsSelection_REGISTRATION_CASES - Lists all the test cases related to NsSelection registration.
- NSSF_NsSelection_PDU_CASES - Lists all the test cases related to NsSelection PDU related cases.
- NSSF_BASIC_SUBSCRIBE_CASES - Lists all the test cases related to subscription.
Figure 3-41 NSSF_BASIC_SANITY_CASES

Figure 3-42 NSSF_BASIC_SUBSCRIBE_CASES
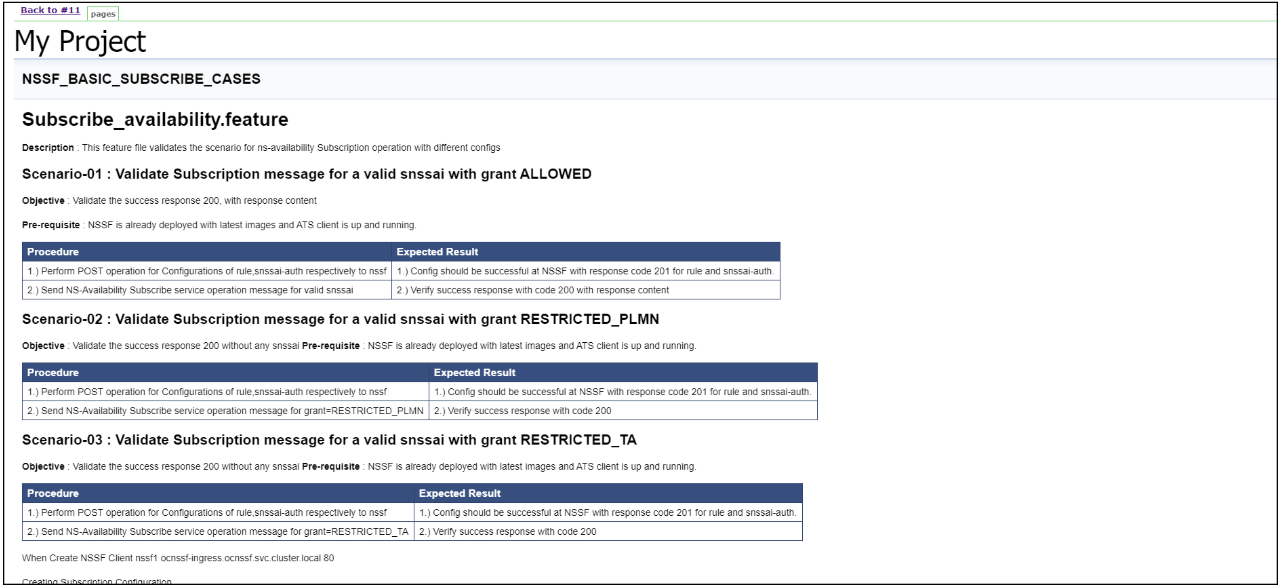
Figure 3-43 NSSF_NsSelection_Registration_CASES

Executing Policy Test Cases using ATS
This ATS-Policy release is a converged release comprising of scenarios (test cases) from PCF, CN-PCRF and Converged Policy modes. ATS 1.3.1 is compatible with Policy 1.8.1 with TLS Enabled (server side) and Disabled Mode, CN-PCRF and Converged policy.
To execute Policy test cases, you need to ensure that following prerequisites are fulfilled.
Prerequisites
- Deploy OCCNP.
- Install Go-STUB and DNS-Bind stub for PCF and Converged Policy mode.
- ATS Prometheus Metrics validation works only when the installation has a single pod for each microservice in the CN Policy deployment.
- Users can customize test cases in the custom test case folders (cust_newfeatures, cust_regression and cust_performance). They can add new test cases, remove unwanted test cases and modify existing test cases. It does not impact the original product packaged test cases available in the newfeatures, regression and performance folders. For more details, you can refer to Custom Folder Implementation.
- In the -application-config configmap, configure the following parameters with
the respective values:
primaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.<namespace_gostubs_are_deployed_in>.svc:8080Example:
primaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.ocats.svc:8080 #secondaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.ocats.svc:8080 (comment out the secondaryNrfApiRoot)- nrfClientSubscribeTypes=UDR,CHF
- #supportedDataSetId=POLICY (comment out the supportedDataSetId )
Note:
You can configure these values at the time of Policy deployment.Note:
To get all configmaps in your namespace execute:kubectl get configmaps -n <Policy_namespace>
- Configure DNS Stub for session retry feature validation. The steps are as
follows:
- Login to DNS Stub.
Note:
You can refer to the Policy ATS Installation Procedure chapter to learn the process to install DNS Stub.Example:
kubectl exec -it ocdns-ocdns-bind-86888f75cf-kv64w -n ocpcf bash - Edit the named.conf.local file present in /etc/bind location.
- Replace occne15-ocpcf-ats with cluster name where ocpcf is deployed.
- Replace ocats with the namespace where stubs are deployed.
- Replace 10.233.0.3 with the core DNS server IP address in your
deployment. If the core DNS server IP address is not known, you can
use the next available forwarder IP address. Execute the following
command inside DNS stub pod to know the next available
forwarder:
cat /etc/resolv.confFigure 3-44 Editing named.conf.local
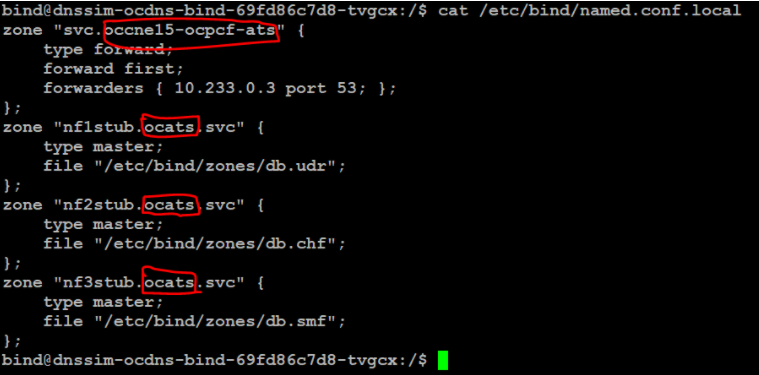
- Go to /etc/bind/zones and edit each of these files;
db.udr, db.chf and db.smf. Replace
ocats with the namespace where stubs are deployed.
Figure 3-45 Editing db.udr, db.chf and db.smf files
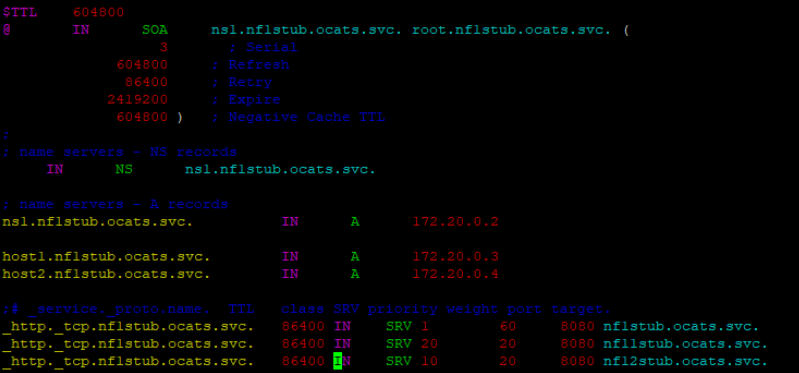
- After making all the changes, execute the following command to restart the
bind service:
/etc/init.d/bind9 restart
- Login to DNS Stub.
- Edit the Alternate Route Service deployment that points toward DNS Stub.
By default, it points to CoreDNS with following settings in deployment file:
Figure 3-46 Alternate Route Service Deployment File
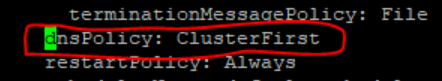
- Execute the following command to add the given content in
alternate service to query DNS stub:
kubectl edit deployment ocpcf-occnp-alternate-route -n ocpcf - Add the IP Address of the nameservers that you have recorded after installing the DNS stub (cluster IP Address of DNS Stub).
- Add the search function based on cluster name and namespace
where you have deployed PCF:
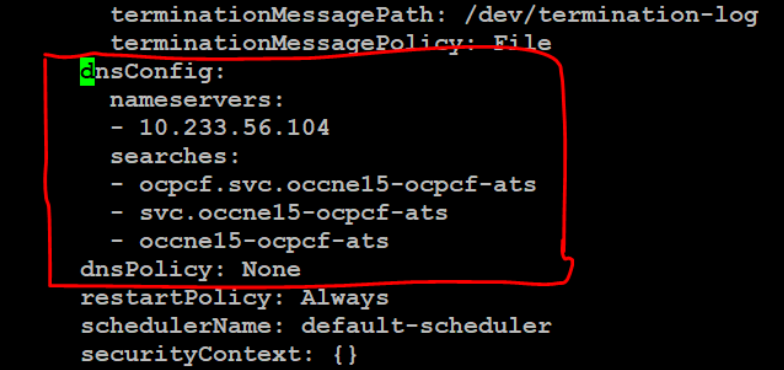
occne15-ocpcf-ats → cluster nameocpcf → namespace where pcf deployed - Set dnsPolicy to "None".
Figure 3-47 Policy Alternate Service - DNS Config Info
Once the DNS stub is configured, login to alternate service pod and execute the following commands to verify if the stubs are correctly configured:[cloud-user@pcf-occ15-vcne-bastion-1 ~]$ kubectl exec -it ocpcf-occnp-alternate-route-9cd8558c5-2vwnh -n ocpcf bash[dnssrv@ocpcf-occnp-alternate-route-9cd8558c5-2vwnh oracle]$ curl 'http://10.233.48.21:8000/lookup?fqdn=nf1stub.ocpcf.svc&scheme=http' -X GET[dnssrv@ocpcf-occnp-alternate-route-9cd8558c5-2vwnh oracle]$ curl 'http://10.233.48.21:8000/lookup?fqdn=nf2stub.ocpcf.svc&scheme=http' -X GET[dnssrv@ocpcf-occnp-alternate-route-9cd8558c5-2vwnh oracle]$ curl 'http://10.233.48.21:8000/lookup?fqdn=nf3stub.ocpcf.svc&scheme=http' -X GETwhere, 10.233.48.21 is an alternate service cluster IP.
Output of this command should be displayed as follows showing that the target information for the anchor FQDN is associated for the different stubs:
[{"target":"nf11stub.ocpcf.svc","port":8080,"ttl":86400,"type":"SRV","dclass":"IN","priority":20,"weight":20} ,{"target":"nf1stub.ocpcf.svc","port":8080,"ttl":86400,"type":"SRV","dclass":"IN","priority":1,"weight":60} ,{"target":"nf12stub.ocpcf.svc","port":8080,"ttl":86400,"type":"SRV","dclass":"IN","priority":10,"weight":20}] - Execute the following command to add the given content in
alternate service to query DNS stub:
- PCF
- PCF with TLS not available: In the PCF's custom values
file, check if the following parameters are configured with the respective
values:
ingress-gateway: enableIncomingHttps: false egress-gateway: enableOutgoingHttps: false - PCF with TLS Enabled: In the PCF's custom values file,
check if the following parameters are configured with the respective
values:
ingress-gateway: enableIncomingHttps: true egress-gateway: enableOutgoingHttps: true/falseYou also need to ensure that PCF is deployed with corresponding certificates.
This scenario has two options:- Client without TLS Enabled: In this case, PCF is deployed with TLS enabled without generating any certificate in the ATS pod.
- Client with TLS Security Enabled: In this case, PCF and ATS both have required certificates. For more details, refer to the Enabling Https support for Egress and Ingress Gateway section in this topic.
- In the -application-config configmap, configure the
following parameters with the respective values:
- primaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.<namespace_gostubs_are_deployed_in>.svc:8080
Example: primaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.ocats.svc:8080
- nrfClientSubscribeTypes=UDR,CHF
- supportedDataSetId=POLICY (Comment out the
supportedDataSetId )
Note:
You can configure these values at the time of Policy deployment also.Note:
Execute the following command to get all configmaps in your namespace.kubectl get configmaps -n <Policy_namespace>
- primaryNrfApiRoot=http://nf1stub.<namespace_gostubs_are_deployed_in>.svc:8080
- PCF with TLS not available: In the PCF's custom values
file, check if the following parameters are configured with the respective
values:
- CN-PCRF
Execute the following command to set the Log level to Debug in Diam-GW POD:
kubectl edit statefulset <diam-gw pod name> -n <namespace>Execute the following command to set the default peer in the configuration map:
kubectl edit statefulset <diam-gw pod name> -n <namespace>- name: USE_CFG_SVC
value: "false"
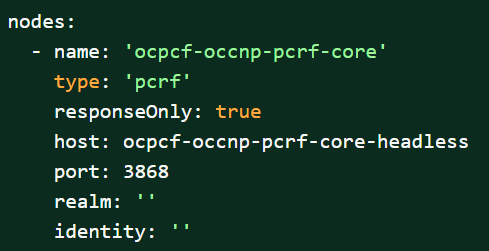
Execute the following command to edit and set the default configuration of Diameter peer in the diam configuration map and set the responseOnly parameter to true.
kubectl edit cm oc-diam-gateway-config-peers -n <namespace>Figure 3-48 Setting Diameter Log Level Configuration
- Converged Policy: It is same as PCF and CN-PCRF. You can refer to explanation given above.
- Prometheus server should be installed in cluster.
- Database cluster should be in a running state with all the required tables. You need to ensure that there are no previous entries in database before executing test cases.
- Deploy ATS in the same namespace as Policy using Helm Charts.
- User MUST NOT initiate a job in two different pipelines at the same time.
- The installation should have only one pod for each microservice related to ATS Prometheus Metrics validation to work in the CN Policy deployment.
- If you enable Service Mesh check, then you need to create a destination
rule for fetching the metrics from the Prometheus. In most of the deployments,
Prometheus is kept outside the service mesh so you need a destination rule to
communicate between TLS enabled entity (ATS) and non-TLS entity (Prometheus). You
can create a destination rule as
follows:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion:networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind:DestinationRule metadata: name:prometheus-dr namespace:ocats spec: host:oso-prometheus-server.pcf.svc.cluster.local trafficPolicy: tls: mode:DISABLE EOFIn the destination rule:- name indicates the name of destination rule.
- namespace indicates where the ATS is deployed.
- host indicates the hostname of the prometheus server.
Enabling TLS in ATS Pod
- Execute the following command to copy the caroot.cer generated while PCF
deployment to ATS pod in "cert"
directory.
kubectl cp <path_to_file>/caroot.cer <namespace>/<ATS-Pod-name>: /var/lib/jenkins/cert/ -n <namespace>Example:
kubcetl cp cert/caroot.cer ocpcf/ocpcf-ocats-pcf-56754b9568-rkj8z: /var/lib/jenkins/cert/ - Execute the following command to login to your ATS
Pod.
kubectl exec -it <ATS-Pod-name> bash -n <namespace> - Execute the following commands from cert directory to create private key and
certificates:
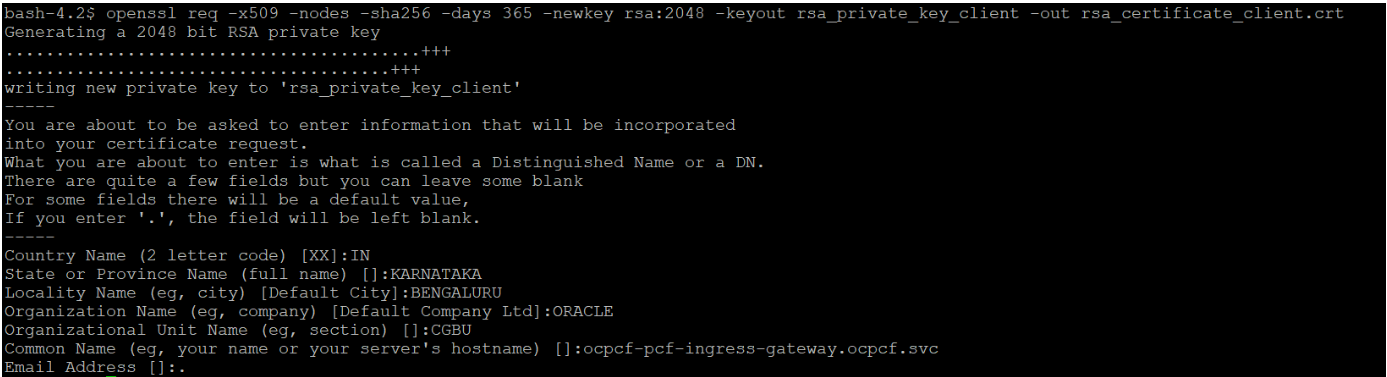
-
openssl req -x509 -nodes -sha256 -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout rsa_private_key_client -out rsa_certificate_client.crtFigure 3-49 Command 1
Note:
You need to provide appropriate values and specify fqdn of PCF Ingress Gateway service i.e. <ingress-servicename>.<pcf_namespace>.svc in Common Name. -
openssl rsa -in rsa_private_key_client -outform PEM -out rsa_private_key_pkcs1_client.pemFigure 3-50 Command 2

-
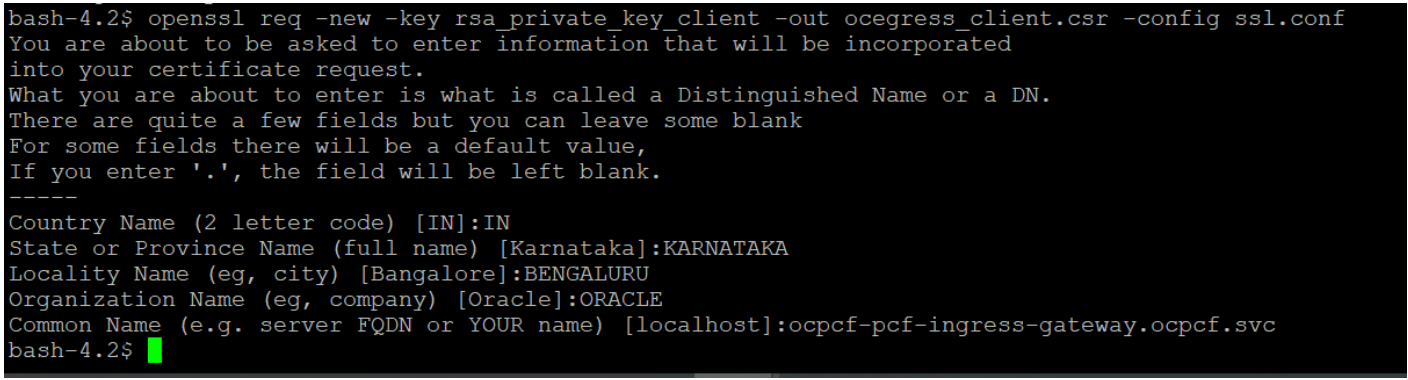
openssl req -new -key rsa_private_key_client -out ocegress_client.csr -config ssl.conf
Note:
You can either use or copy the ssl.conf file, which was used while deploying PCF to ATS pod for this step.Figure 3-51 Command 3
-
- Execute the following command to copy the ocegress_client.csr to the
bastion.
openssl x509 -CA caroot.cer -CAkey cakey.pem -CAserial serial.txt -req -in ocegress_client.csr -out ocegress_client.cer -days 365 -extfile ssl.conf -extensions req_extFigure 3-52 Copying ocegress_client.csr to bastion

- Copy the ocegress_client.cer from Bastion to the ATS Pod.
- Restart the ingress and egress gateway pods from the Bastion.
Logging into ATS
Before logging into ATS Jenkins GUI, it is important to get the nodeport of the service, 'ocats-Policy'. Execute the following command to get the nodeport:
kubectl get svc -n <Policy_namespace>
Example:
kubectl get svc -n ocpcf
Figure 3-53 Policy Nodeport
To login to Jenkins, open the Web Browser and type the URL: http://<Worker-Node-IP>:<Node-Port-of-ATS>. In the above screen, 32471 is the nodeport. Example: http://10.75.225.49:32471
Note:
For more information on ATS deployment in PCF, refer to Policy ATS Installation Procedure.Executing ATS
To execute ATS:
- Enter the username as "policyuser" and
password as
"policypasswd". Click Sign
in.
The following screen appears showing policy pre-configured pipelines:
Note:
If you want to modify your default login password, refer to Modifying Login Password- Policy-NewFeatures: This pipeline has all the test cases, which are delivered as part of Policy ATS.
- Policy-Performance: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
- Policy-Regression: This pipleine has all the test cases, which were delivered in Policy ATS - 1.7.4
Figure 3-54 Pre-Configured Pipelines
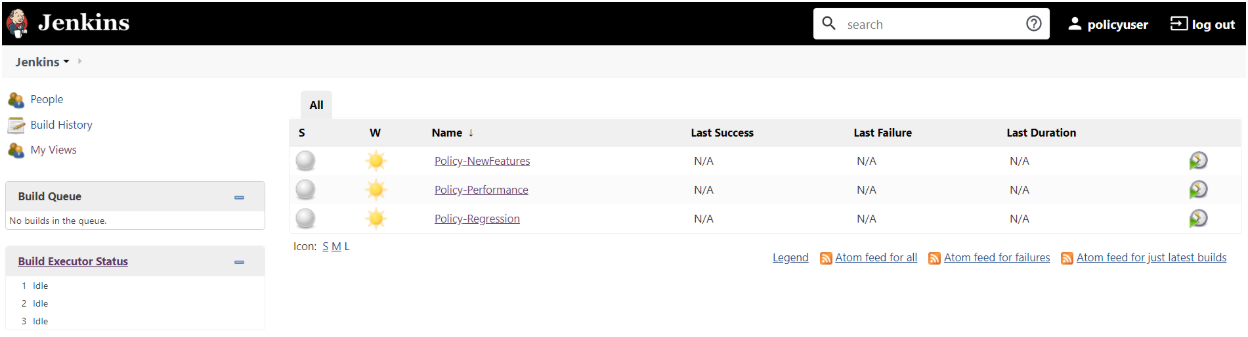
The pre-configured pipelines are explained below:
Policy-New Features Pipeline
- Click Policy-NewFeatures in the Name column and then, click
Configure in the left navigation pane as shown below:
Figure 3-55 Policy-NewFeatures Configure
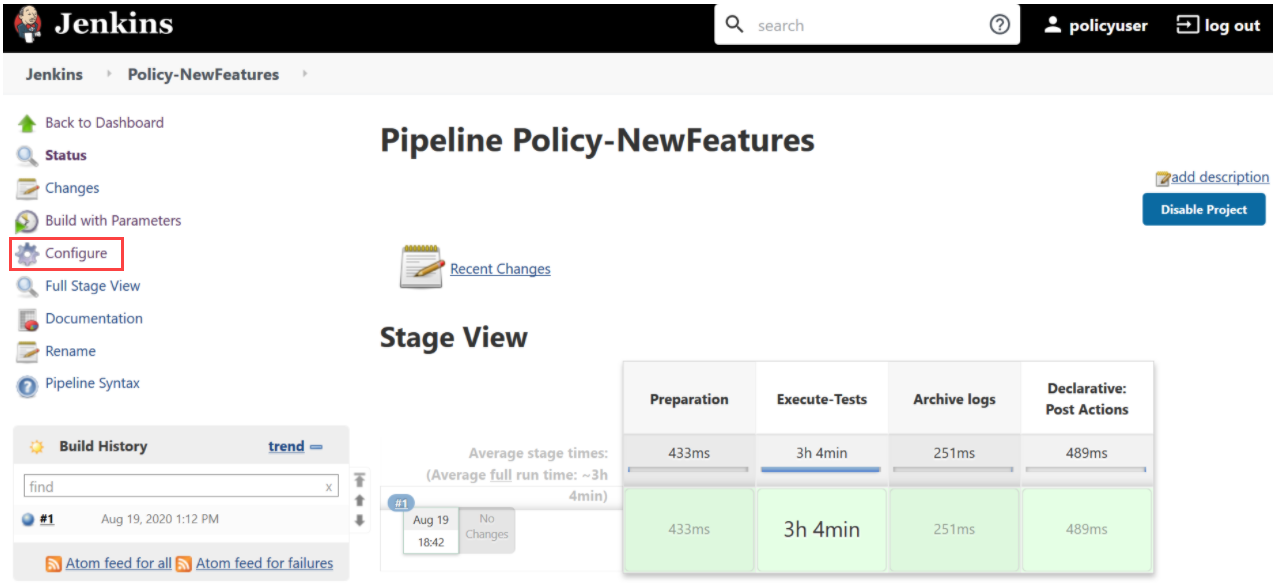
- The Policy-NewFeatures, General tab appears. Make sure that the screen loads completely.
- Scroll-down to the end. The control moves from General tab to
the Pipeline tab as shown below:
Figure 3-56 Policy - Pipeline Script
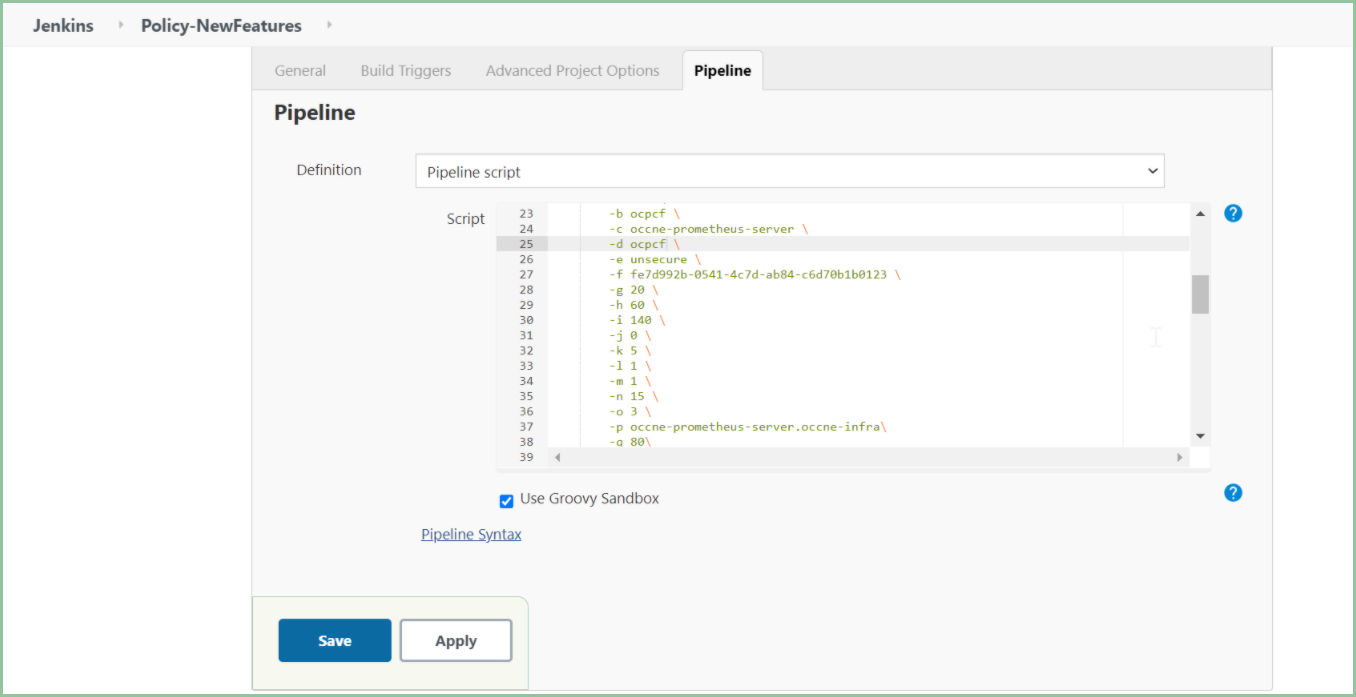 In the Script area of the Pipeline section, you can change value of the following parameters:
In the Script area of the Pipeline section, you can change value of the following parameters:- b: Change this parameter to update the namespace where Policy was deployed in your bastion.
- d: Change this parameter to update the namespace where your gostubs are deployed in your bastion.
- e: Set this parameter as 'unsecure', if you intend to run ATS in TLS disabled mode. Else, set this parameter as 'secure'.
- g: Set this parameter to more than 35 secs. The default wait time for the pod is 35 secs. Every TC requires restart of the nrf-client-management pod.
- h: Set this parameter to more than 60 secs. The default wait time to add a configured policy to the database is 60 secs.
- i: Set this parameter to more than 140 secs. The default wait time for Nf_Notification Test Cases is given as 140 secs.
- k: Use this parameter to set the waiting time to initialize Test Suite.
- l: Use this parameter to set the waiting time to get response from Stub.
- m: Use this parameter to set the waiting time after adding Policy Configuration.
- n: Use this parameter to set the waiting time after adding Policy.
- o: Use this parameter to set the waiting time before sending next message.
- p: Use this parameter to set Prometheus Server IP.
- q: Use this parameter to set Prometheus Server
Port.
Note:
DO NOT MODIFY ANYTHING OTHER THAN THESE PARAMETER VALUES. - Click Save after updating the parameters value.
The Policy-NewFeatures Pipeline screen appears.
Note:
It is advisable to save the pipeline script in your local machine that you can refer at the time of ATS pod restart.
Executing Policy Test Cases
- Click the Build with Parameters link available in the left navigation
pane of the Policy-NewFeatures Pipeline screen. The following screen
appears.
Figure 3-57 Policy - Build with Parameters
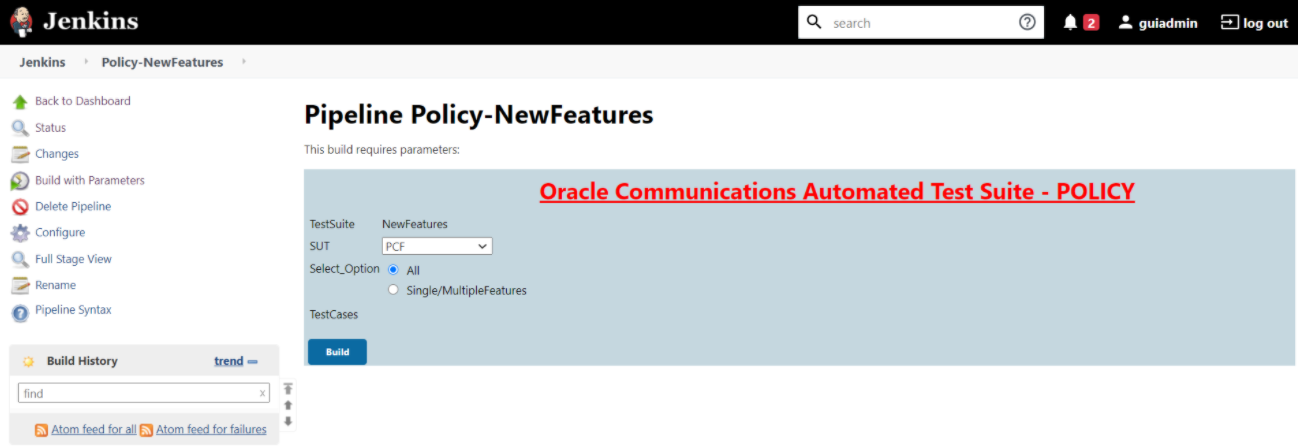
Note:
Jenkins display empty TestCases list as it is referring to the custom folder for Policy NewFeatures.Copy the required test cases that are available in the PCF/PCRF/Common folder and place them in the appropriately within custom folder for Policy-NewFeatures. Reload the Jenkins page to view the cases available in the custom NewFeatures folder.Figure 3-58 Policy - Viewing Custom test Cases
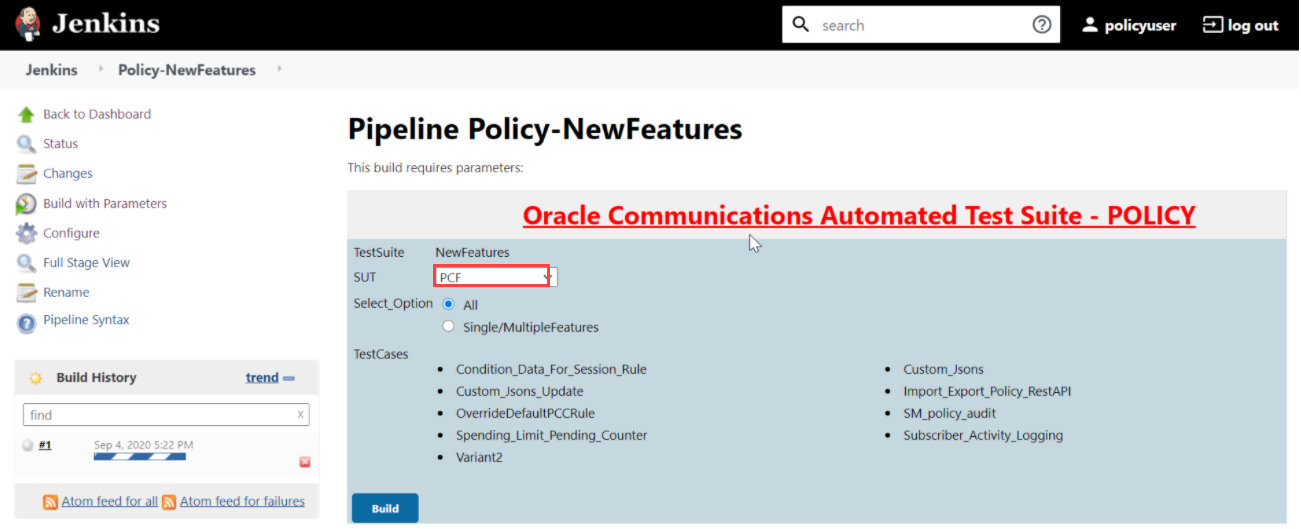 In the above screen, you can select SUT as either PCF, CN-PCRF or Converged Policy. It also has two Select_Option(s), which are:
In the above screen, you can select SUT as either PCF, CN-PCRF or Converged Policy. It also has two Select_Option(s), which are:- All: By default, all the Policy test cases are selected for execution. Scroll down and click Build to execute all the test cases.
- Single/MultipleFeatures: This option allows you to select any number of test cases that you want to execute from the list of total test cases available for execution. After selecting the test cases, scroll-down and click Build. The selected Policy test cases are executed.
Figure 3-59 SUT Options
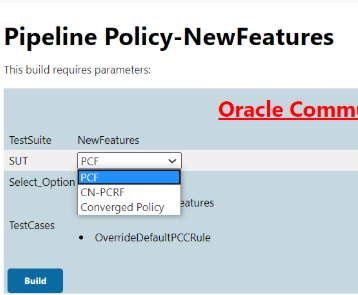 Based on your selection, related TestCases appear.
Based on your selection, related TestCases appear.Figure 3-60 Test Cases based on SUT
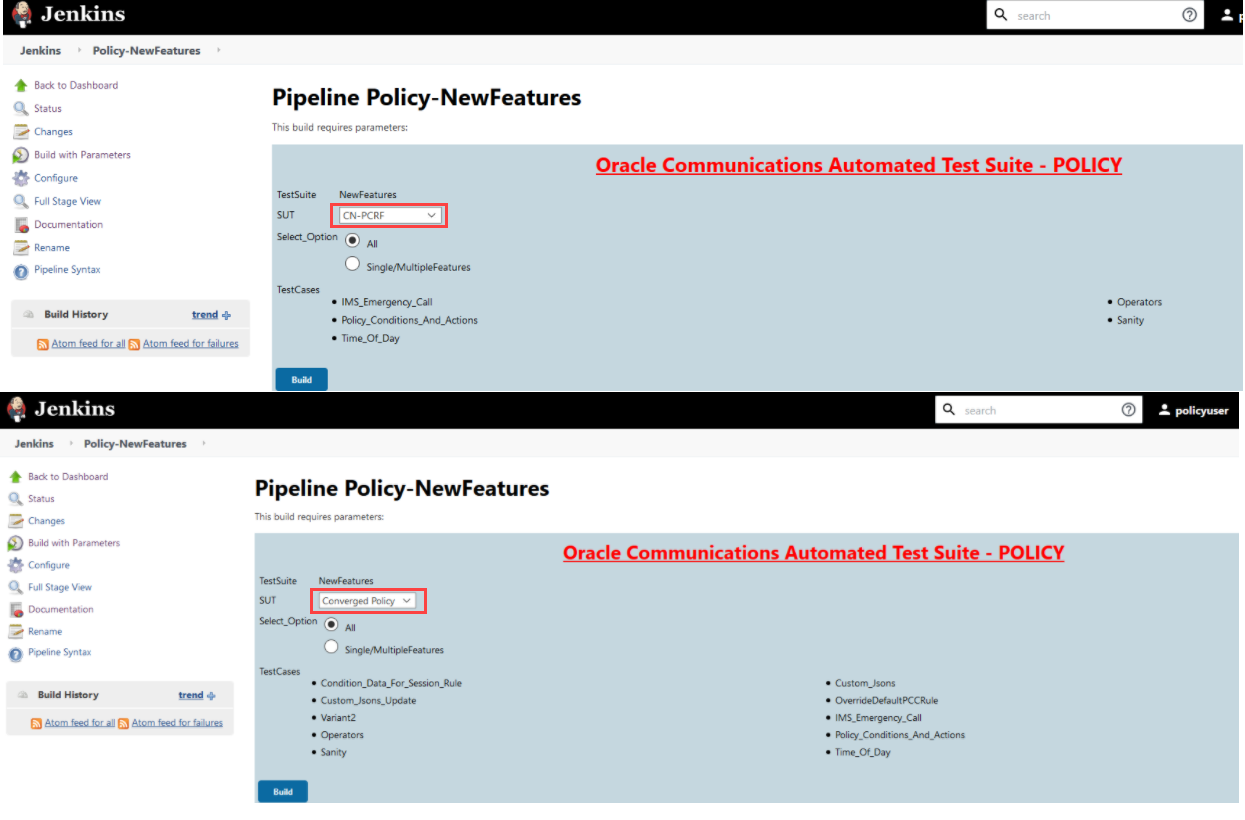
Note:
Converged Policy Test cases are combination of PCF and CN-PCRF TestCases.Go to Build → Console Output to view the test result output as shown below:
Figure 3-61 Sample: Test Result Output in Console
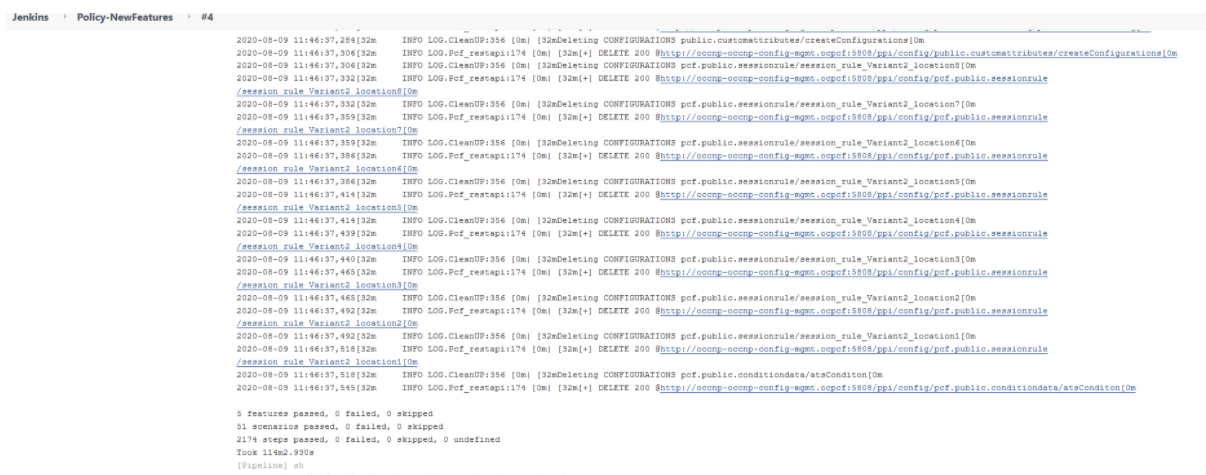
Figure 3-62 Sample Output of Build Status

NewFeatures - Documentation
Figure 3-63 Policy-NewFeatures Feature List
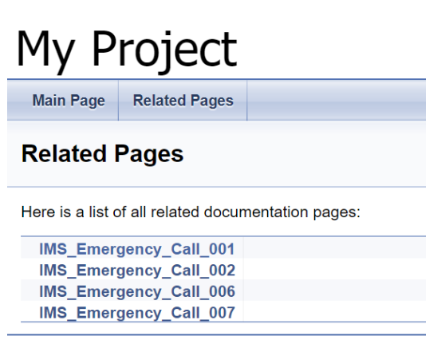
Figure 3-64 IMS_Emergency_Call_001
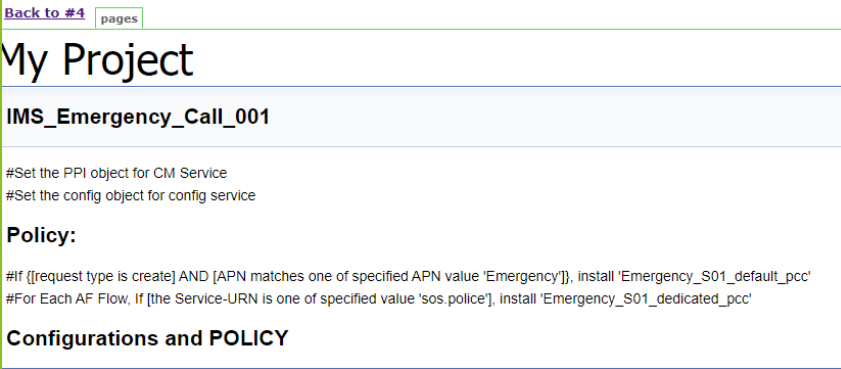
Based on the functionalities covered under Documentation, the Build Requires Parameters screen displays test cases. To navigate back to the Pipeline Policy-NewFeatures screen, click Back to Policy-NewFeatures link available on top left corner of the screen.
PCF-Regression Pipeline
This pre-configured pipeline has all the test cases of previous releases. For example, as part of Release 1.8.0, this pipeline has all the test cases that were released as part of release 1.7.4
Figure 3-65 Policy-Regression
Note:
Jenkins display empty TestCases list as it is referring to the custom folder for Policy-Regression pipeline.Figure 3-66 Policy - Regression - Viewing Custom Test Cases

Figure 3-67 Policy-Regression Build Output
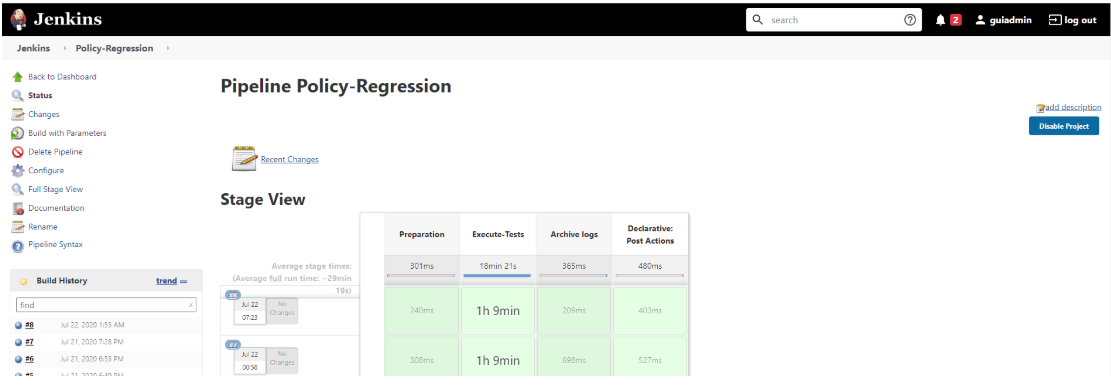
Figure 3-68 Policy-Regression Console Output

Note:
The regression pipeline does not have any sanity option. However, you should perform all the steps as performed in NewFeatures pipeline. Configure the pipeline script changes to provide environment variables.Regression - Documentation
Figure 3-69 Policy-Regression Documentation
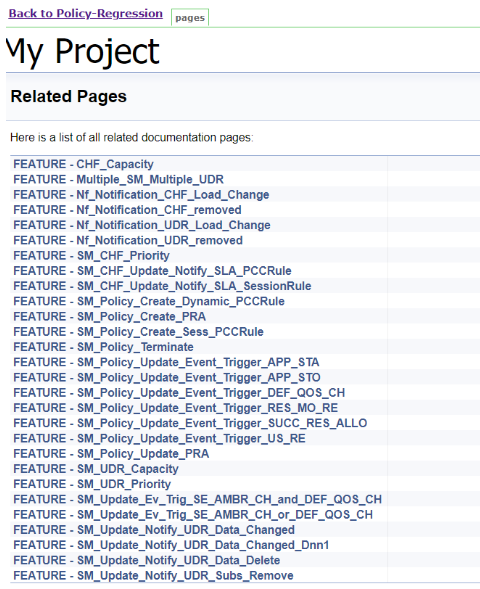
Figure 3-70 Sample: Regression Documentation - Feature

This screen shows functionalities of only those test cases that are released in previous releases.
Executing SCP Test Cases using ATS
To execute SCP Test Cases, you need to ensure that following prerequisites are fulfilled.
Prerequisites
- Deploy SCP 1.8.0 with following custom values in deployment
file.
- As you can provide NRF information only at the time of deployment, Stub NRF details like nrf1svc and nrf2svc should also be provided at the time of deployment before executing these cases. For Example: If teststub namespace is scpsvc then SCP should have been deployed with primary nrf as nrf1svc.scpsvc.svc.<clusterDomain> and secondary nrf as nrf2svc.scpsvc.svc.<clusterDomain> for NRF test cases to work.
- Deploy NRF stubs with port 8080. Thus, NRF details of SCP should specify ipEndPoints port as 8080 without any ipv4Address field. Example: ipEndPoints: [{"port": "8080"}]).
- In the SCP deployment file, servingScope should be 'Reg1', servingLocalities should have 'USEast' and 'Loc9'. In addition, the recommended auditInterval is '120' and guardTime is '10'.
- For ATS execution, you should deploy SCP with SCP-Worker replicas set to 1.
- Users can customize test cases in the custom test case folders (cust_newfeatures, cust_regression and cust_performance). They can add new test cases, remove unwanted test cases and modify existing test cases. It does not impact the original product packaged test cases available in the newfeatures, regression and performance folders. For more details, you can refer to Custom Folder Implementation.
- Deploy ATS using helm charts.
- As you can deploy default ATS with role binding, it is important to deploy ATS and test stubs in the same namespace as SCP.
Logging into ATS
Figure 3-71 Verifying ATS Deployment
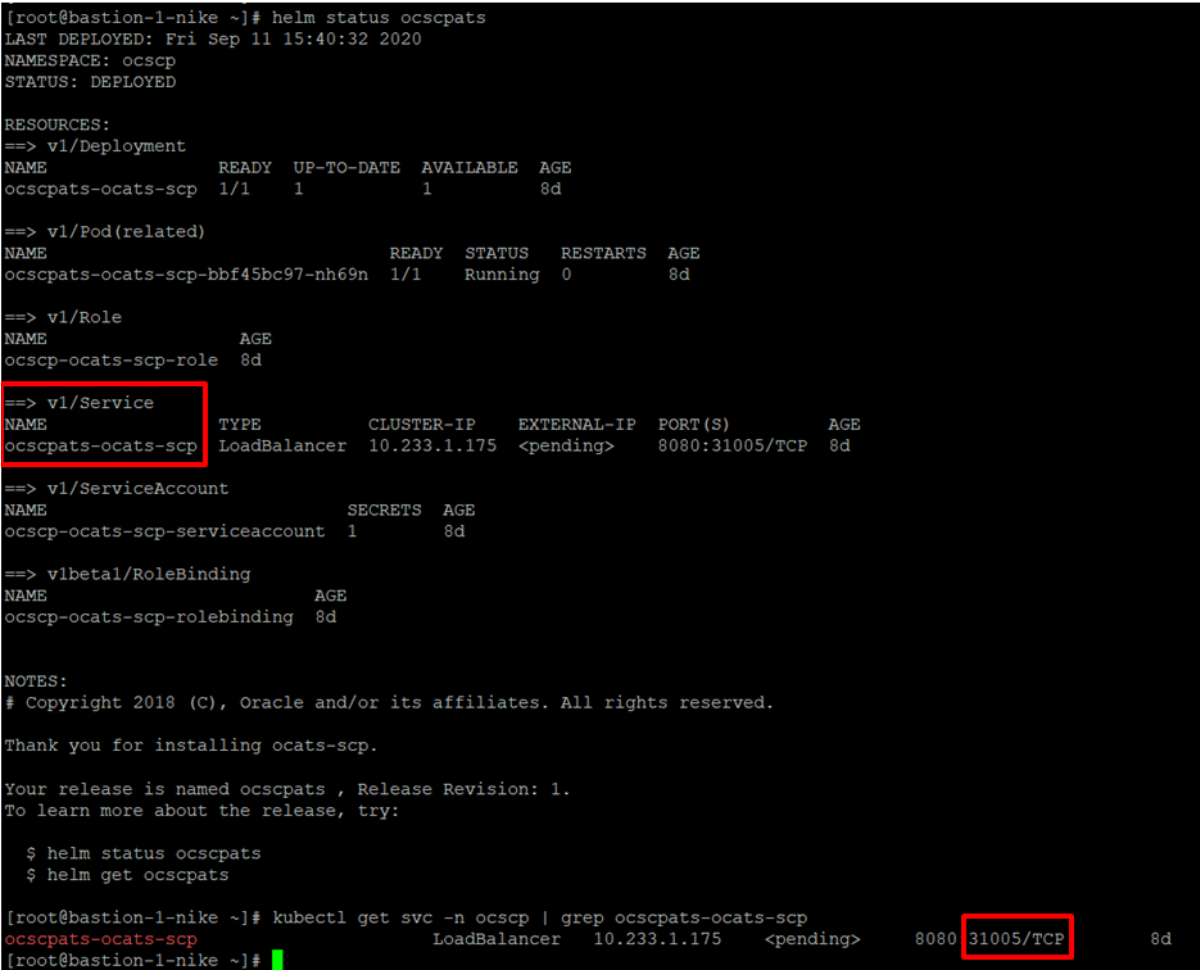
To login to ATS Jenkins GUI, open the browser and provide the external IP of
the worker node and nodeport of the ATS service as
<Worker-Node-IP>:<Node-Port-of-ATS>. The Jenkins login
screen appears.
Note:
In the Verifying ATS Deployment screen, the ATS nodeport is highlighed in red as 31005. For more details on ATS deployment, refer toSCP ATS Installation Procedure .Executing ATS
- Enter the username as "scpuser" and password as
"scppasswd". Click Sign in. A sample screen is shown below.
Figure 3-72 Logging into ATS GUI
Note:
If you want to modify your default login password, refer to Modifying Login Password - Following screen appears showing pre-configured pipelines for SCP
individually (3 Pipelines).
- SCP-New-Features: This pipeline has all the test cases, which are delivered as part of SCP ATS - 1.8.0
- SCP-Performance: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
- SCP-Regression: This pipeline covers all the test cases of the previous releases.
Figure 3-73 ATS SCP First Logged-In Screen
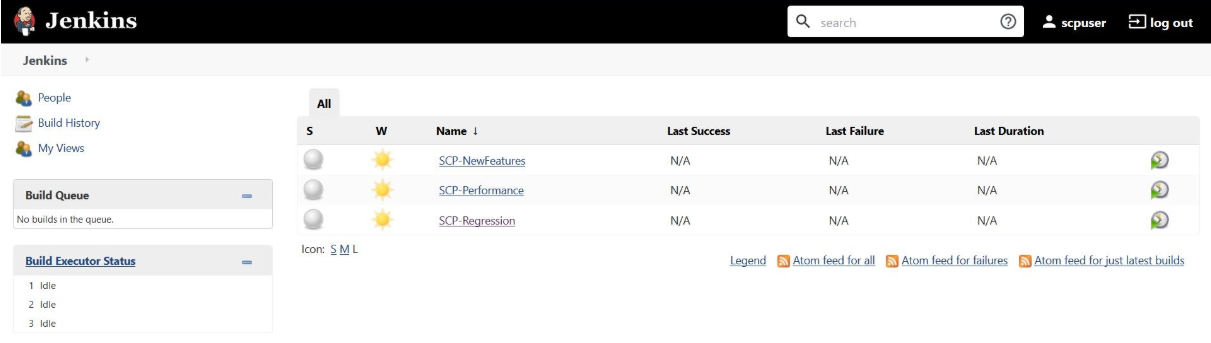
Pipeline SCP-NewFeatures
This is a pre-configured pipeline where all the SCP test cases are executed. If you are executing SCP pipeline for the first time then you have to set the Input Parameters before executing any test case. There is no need to set these parameters again unless there is any change in the configuration.
- Click SCP-NewFeatures in the Name column. The following
screen appears:
Figure 3-74 SCP-NewFeatures
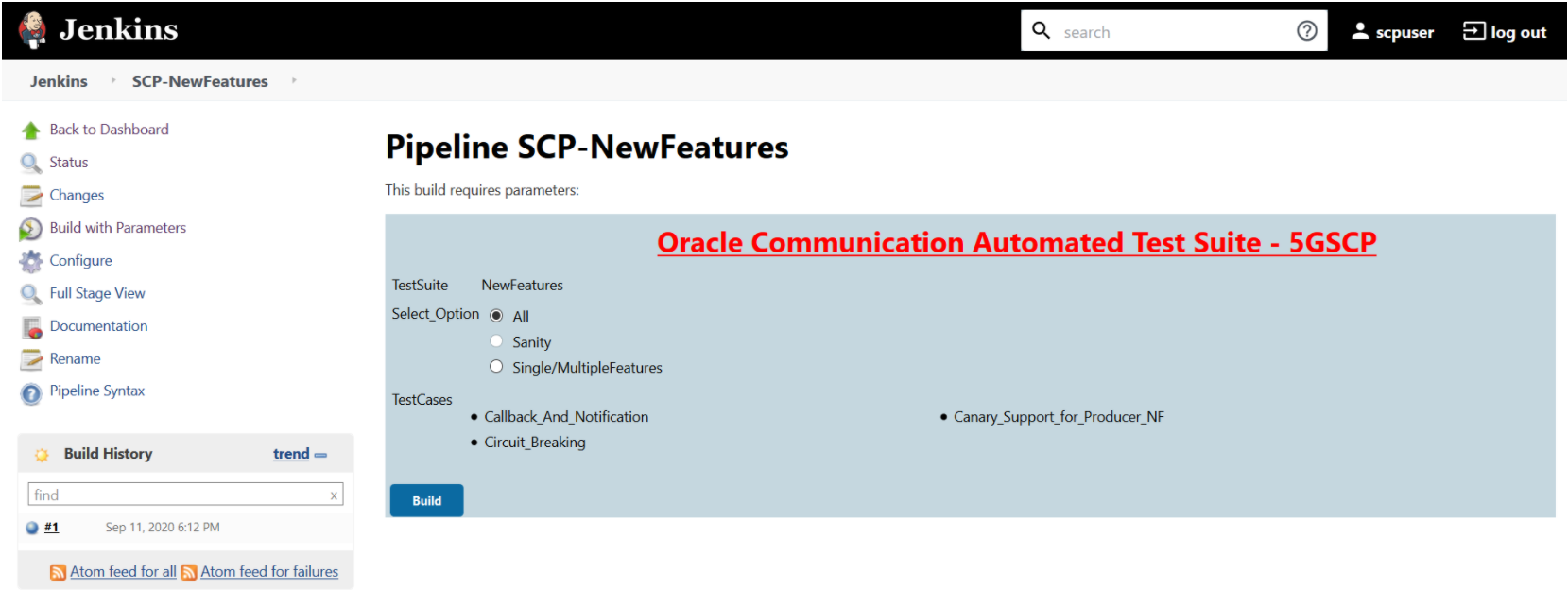
- Click Configure in the left navigation pane to provide input
parameters. The SCP-NewFeatures Configure - General tab appears.
Note:
MAKE SURE THAT THE SCREEN SHOWN BELOW LOADS COMPLETELY BEFORE YOU PERFORM ANY ACTION ON IT. ALSO, DO NOT MODIFY ANY CONFIGURATION OTHER THAN DISCUSSED BELOW. - Scroll-down to the end. The control moves from General tab to
the Pipeline tab as shown below:
Figure 3-75 Pipeline Tab
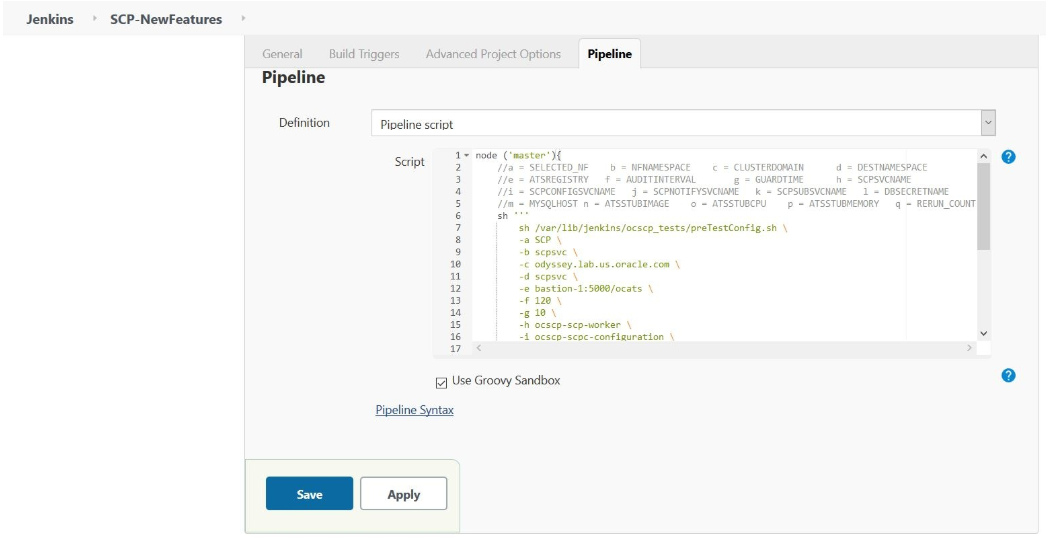 You can modify script pipeline parameters from "-b" to "-q" on the basis of your deployment environment and click Save. The content of the pipeline script is as follows:The description of these parameters is as follows:
You can modify script pipeline parameters from "-b" to "-q" on the basis of your deployment environment and click Save. The content of the pipeline script is as follows:The description of these parameters is as follows:Figure 3-76 SCP Pipeline Content

- -a - Selected NF
- -b - NameSpace in which SCP is Deployed
- -c - Kubernetes Cluster Domain where SCP is Deployed
- -d - Test Stubs NameSpace - must be same as SCP Namespace
- -e - Docker registry where test stub image is available
- -f - Audit Interval provided in SCP Deployment file
- -g - Guard Time provided SCP Deployment file
- -h - SCP-Worker microservice name as provided during deployment
- -i - SCPC-Configuration microservice name as provided during deployment
- -j - SCPC-Notification microservice name as provided during deployment
- -k - SCPC-Subscription microservice name as provided during deployment
- -l - DB Secret name as provided during deployment
- -m - Mysql Host name as provided during deployment
- -n - Test Stub Image Name with tag
- -o - Test Stub CPU requests and limit
- -p - Test Stub Memory requests and limit
- -q - re-run count
Note:
DO NOT MODIFY ANYTHING OTHER THAN THESE PARAMETERS. - Click the Build with Parameters. Following screen
appears:
Figure 3-77 Build with Parameters Options
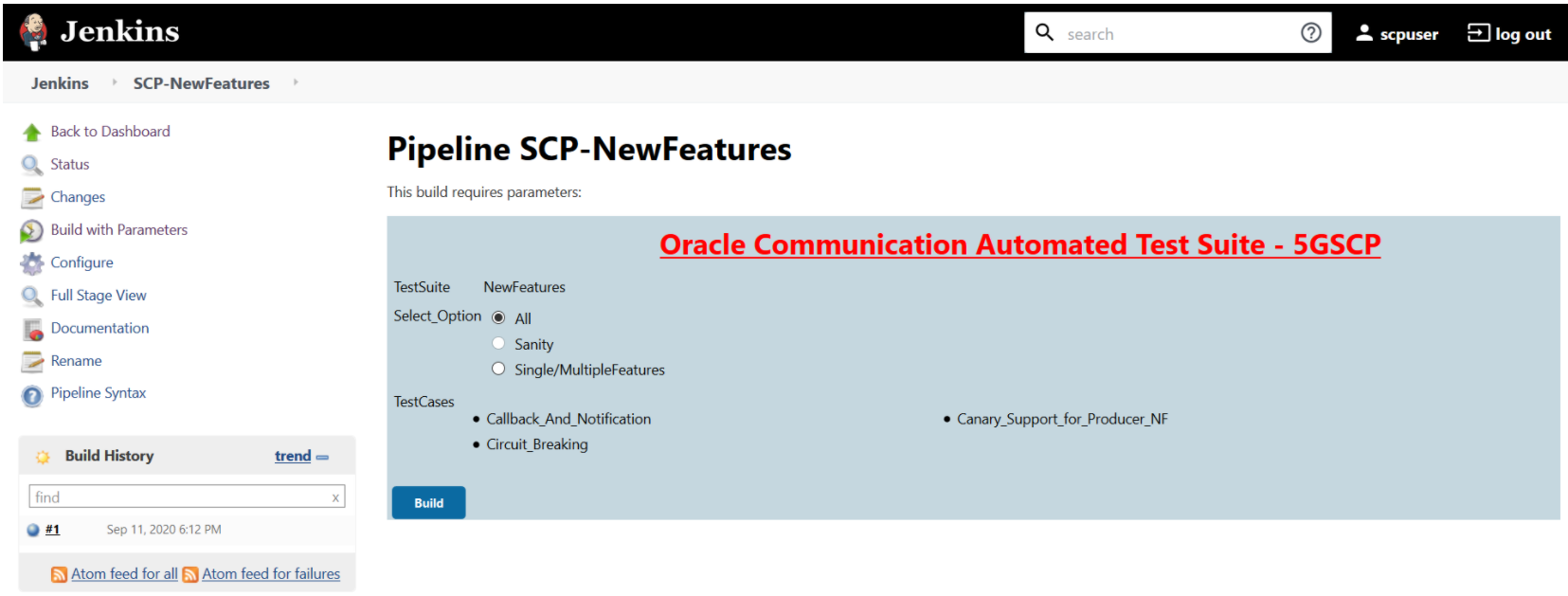 In the above screen, there are three Select_Option(s), which are:
In the above screen, there are three Select_Option(s), which are:- All: By default, all the SCP test cases are selected for execution. User just need to scroll down and click Build to execute all the test cases.
- Sanity: This option is NOT AVAILABLE for SCP.
- Single/MultipleFeatures: This option allows you to select any number of test cases that you want to execute from the list of total test cases available for execution. After selecting the test cases, scroll-down and click Build. The selected SCP test cases are executed.
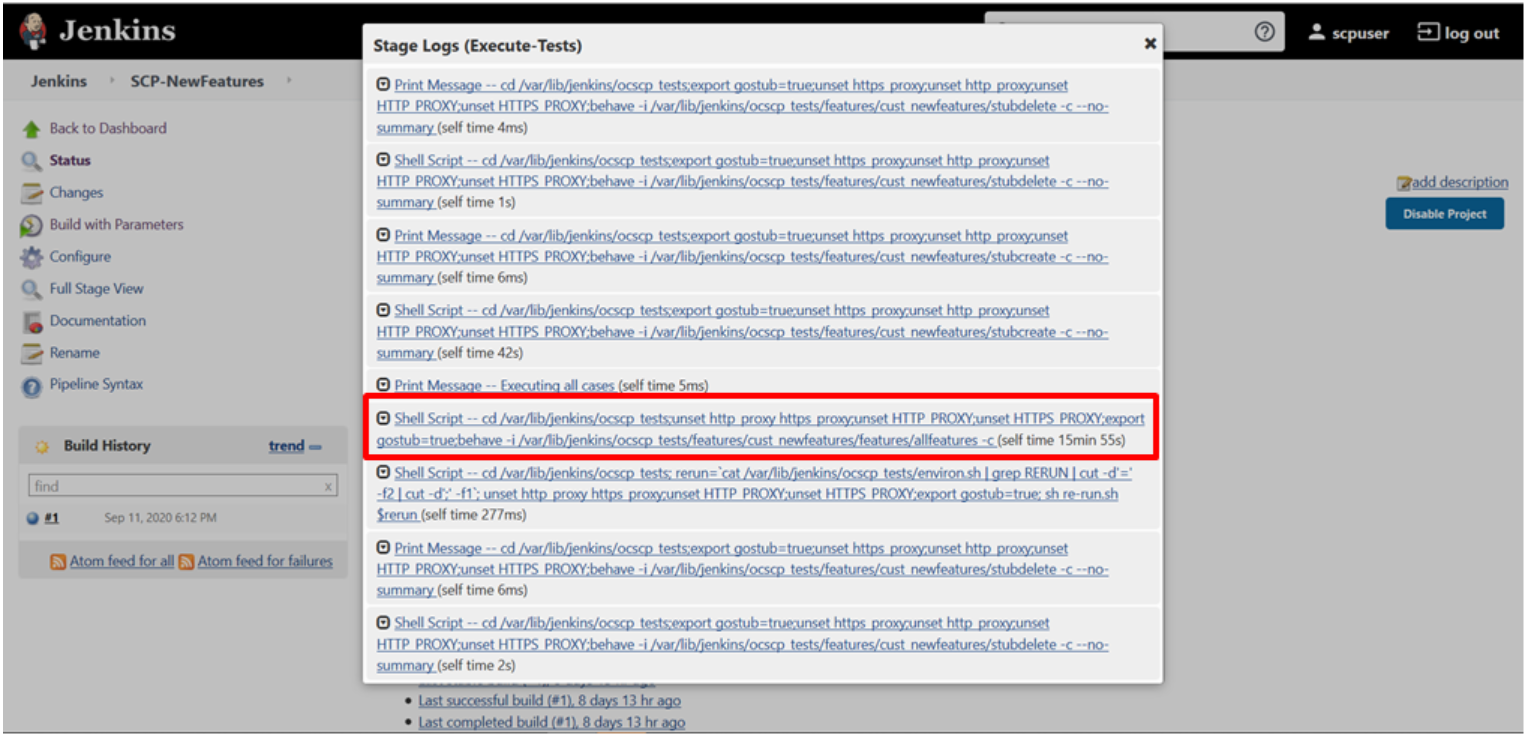
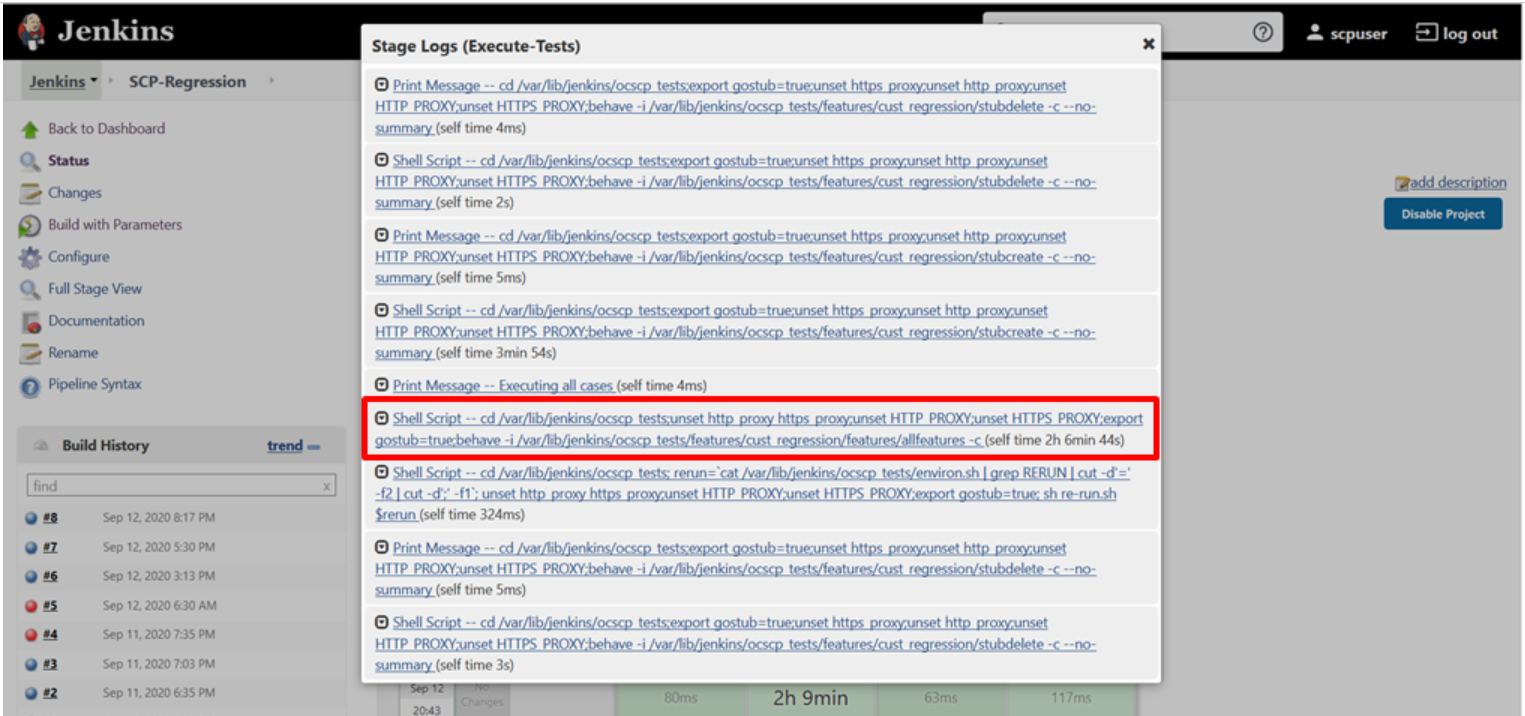
- To check execution results and logs:
- Click the execute-tests stage of pipeline and then logs.
- Select the test execution step.
- Double-click to open the execution logs console.
Figure 3-78 SCP-NewFeatures Stage Logs
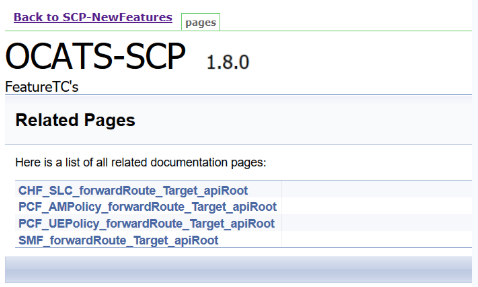
NewFeatures - Documentation
Figure 3-79 SCP-NewFeatures-Documentation
Note:
Documentation option appears only if New-Features pipeline is executed atleast once.Figure 3-80 Sample: SCP Functionality
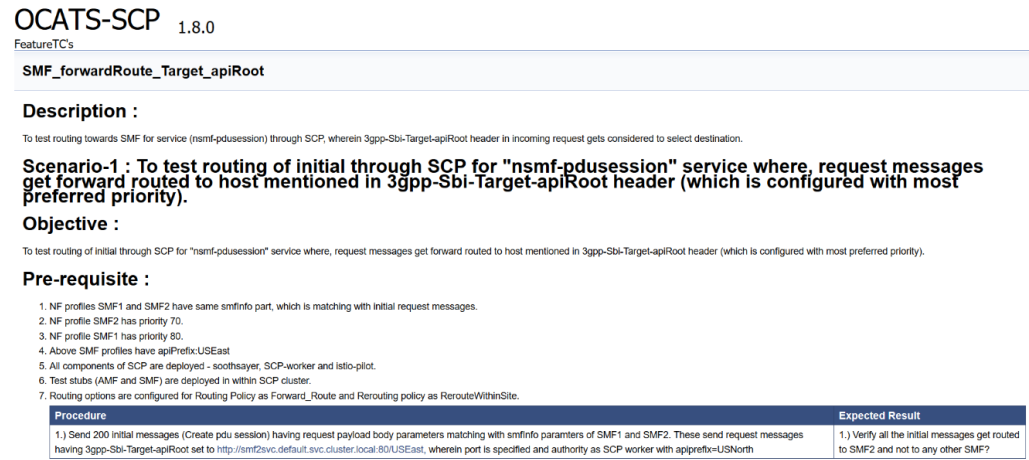
Based on the functionalities covered under Documentation, the Build Requires Parameters screen displays test cases. To navigate back to the Pipeline SCP-NewFeatures screen, click Back to SCP-NewFeatures link available on top left corner of the screen.
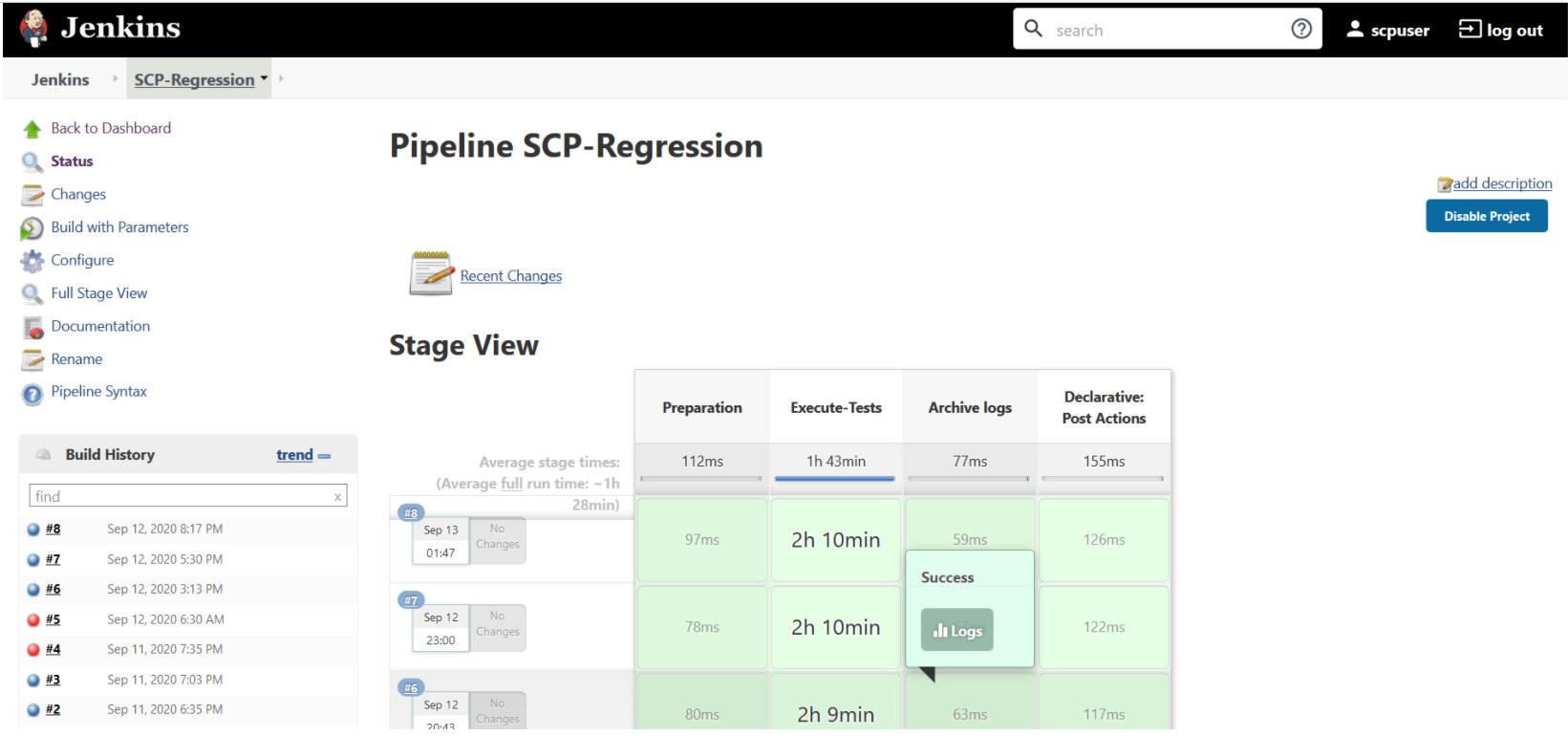
SCP-Regression Pipeline
Figure 3-81 SCP-Regression Pipeline
If you are executing SCP pipeline for the first time, you have to set the Input Parameters before execution. Subsequent execution does not require any input unless there is a need to change any configuration.
Figure 3-82 Regression - Pipeline Script
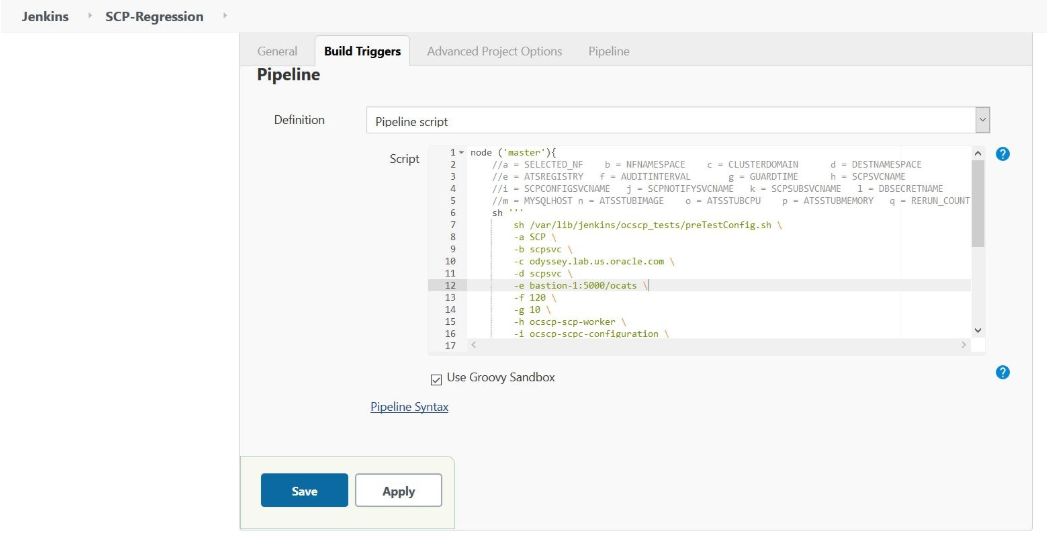
Figure 3-83 SCP-Regression Pipeline Script

-a - Selected NF
-b - NameSpace in which SCP is Deployed
-c - K8s Cluster Domain where SCP is Deployed
-d - Test Stubs NameSpace - Must be same as SCP Namespace
-e - Docker registry where test stub image is available
-f - Audit Interval provided in SCP Deployment file
-g - Guard Time provided SCP Deployment file
-h - SCP-Worker microservice name as provided during deployment
-i - SCPC-Configuration microservice name as provided during deployment
-j - SCPC-Notification microservice name as provided during deployment
-k - SCPC-Subscription microservice name as provided during deployment
-l - DB Secret name as provided during deployment
-m - Mysql Host name as provided during deployment
-n - Test Stub Image Name with tag
-o - Test Stub CPU requests and limit
-p - Test Stub Memory requests and limit
-q - re-run count
Figure 3-84 SCP-Regression Build with Parameters Option
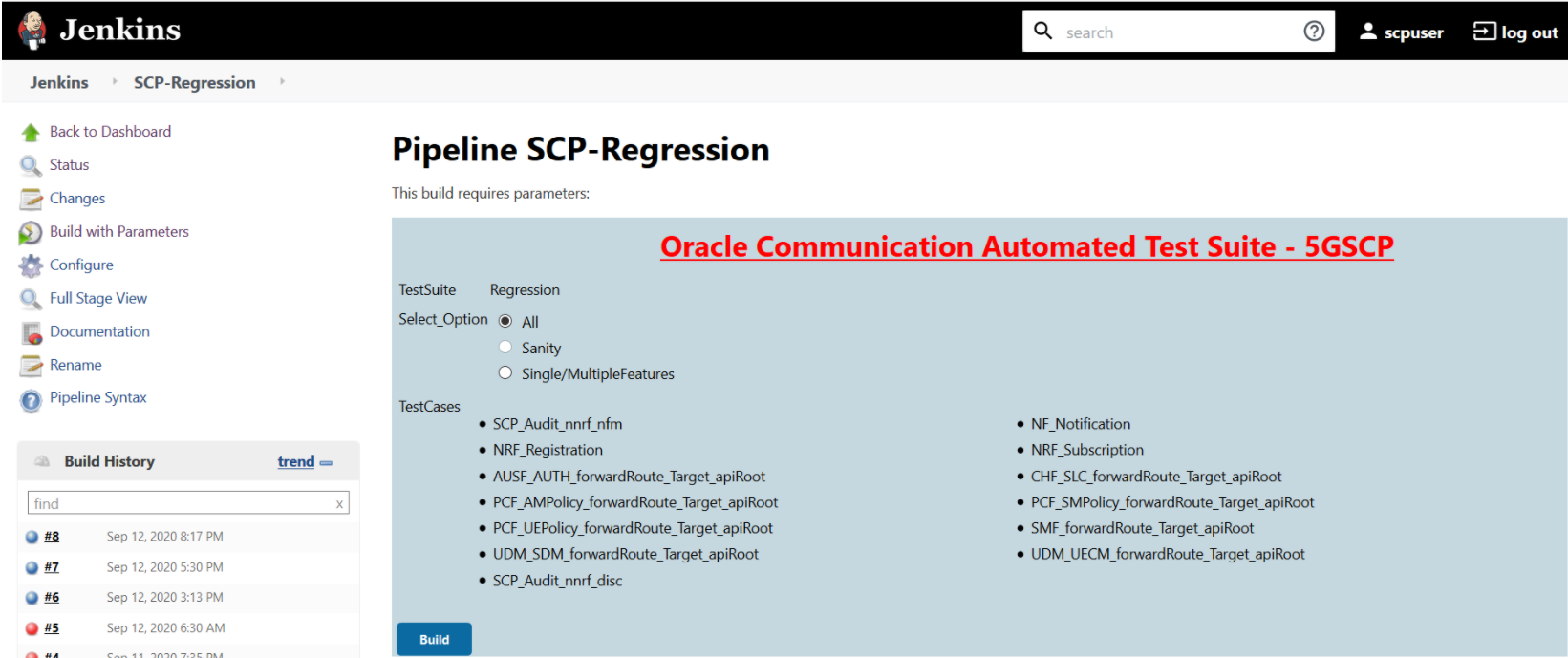
- All - To execute all the test cases except SCP_Audit_nnrf_disc. If SCP is deployed with nnrf-disc for Audit or Registration with NRF is not enabled, then you should not use the All option. Instead, use Single/MultipleFeatures option to select appropriate cases for execution.
- Sanity - This option is not available for SCP.
- Single/MultipleFeatures - To execute selected test cases. You can select one or more test cases and execute using this option.
Figure 3-85 SCP-Regression Build Option

Figure 3-86 SCP-Regression Stage Logs
Executing SEPP Test Cases using ATS
To execute SEPP Test Cases using NRF ATS 1.4, you need to ensure that following prerequisites are fulfilled.
- The user must create Kubernetes secret with certificates/keys (public and private) for both plmn and n32 gateways before deploying SEPP.
- SEPP 1.4 must be deployed with default helm configurations using helm charts.
- All micro-services of SEPP should be up and running.
- The user must create Kubernetes secret with certificates/keys (public and private) for ats client and stub server microservices before deploying SEPP ATS.
- ATS is deployed using the helm charts.
- The stub is deployed using helm charts.
- Prometheus service must be up and running.
- Users can customize test cases in the custom test case folders (cust_newfeatures, cust_regression and cust_performance). They can add new test cases, remove unwanted test cases and modify existing test cases. It does not impact the original product packaged test cases available in the newfeatures, regression and performance folders. For more details, you can refer to Custom Folder Implementation.
Logging into ATS
Before logging into ATS, you need to ensure that ATS is deployed
successfully using HELM charts. A sample screen is given below: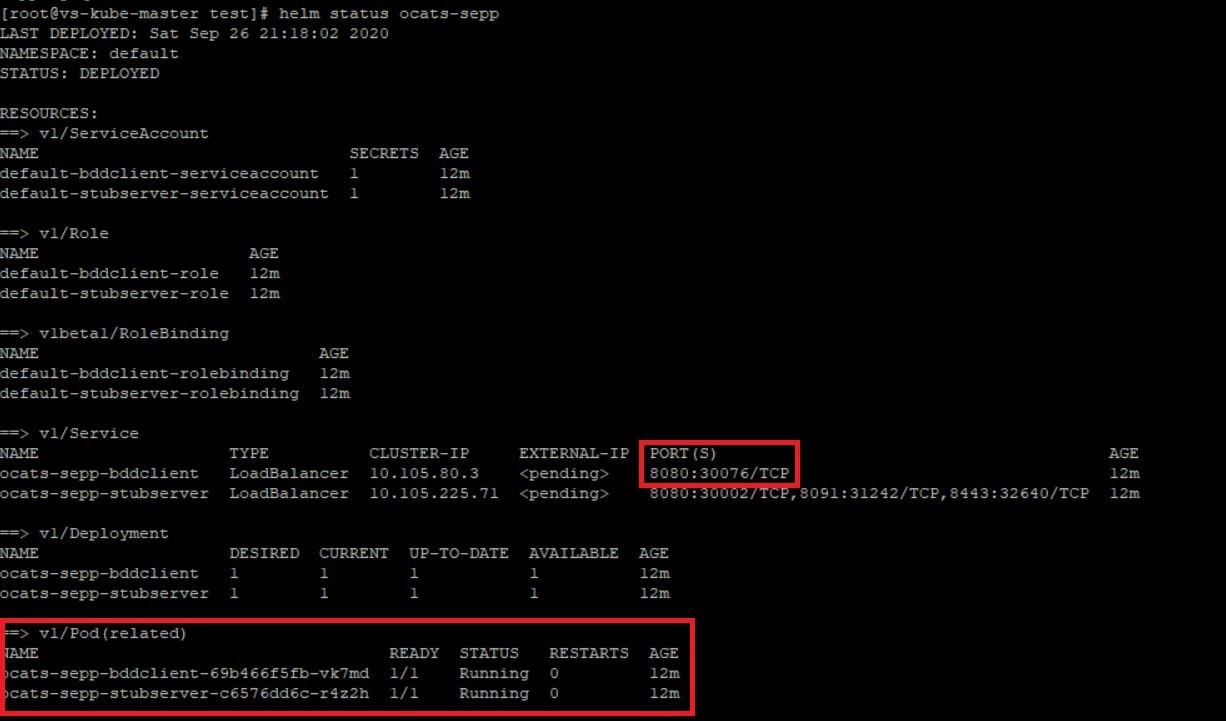
There are two ways to login to ATS Jenkins GUI.
- When an external load balancer (metalLB in case of OCCNE) is available and an external IP is provided to the ATS service, the user can login to ATS GUI using <External-IP>:8080.
- When an external IP is not provided to the ATS service, the user
can open the browser and provide the external IP of the worker node and nodeport
of the ATS service to login to ATS GUI.
<Worker-Node-IP>:<Node-Port-of-ATS>Note:
In the Verifying ATS Deployment screen, ATS nodeport is highlighted in red as 30076. For more details on ATS deployment, refer to SEPP ATS Installation Procedure.
Open a browser and provide IP and port details as <Worker-Node-IP>:<NodePort-of-ATS> (As per the above example: 10.98.101.171:32013). The ATS login screen appears.
Executing ATS
- Enter the username as 'seppuser' and password as 'sepppasswd'. Click Sign in.
Note:
If you want to modify your default login password, refer to Modifying Login Password- SEPP-NewFeatures: This pipeline has all the test cases that are delivered as part of SEPP ATS - 1.4.
- SEPP-Performance: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
- SEPP-Regression: This pipleine has all the test cases of previous releases. As this is the first release of SEPP-ATS, this pipeline does not show any previous release test cases.
Figure 3-87 Pre-Configured Pipelines
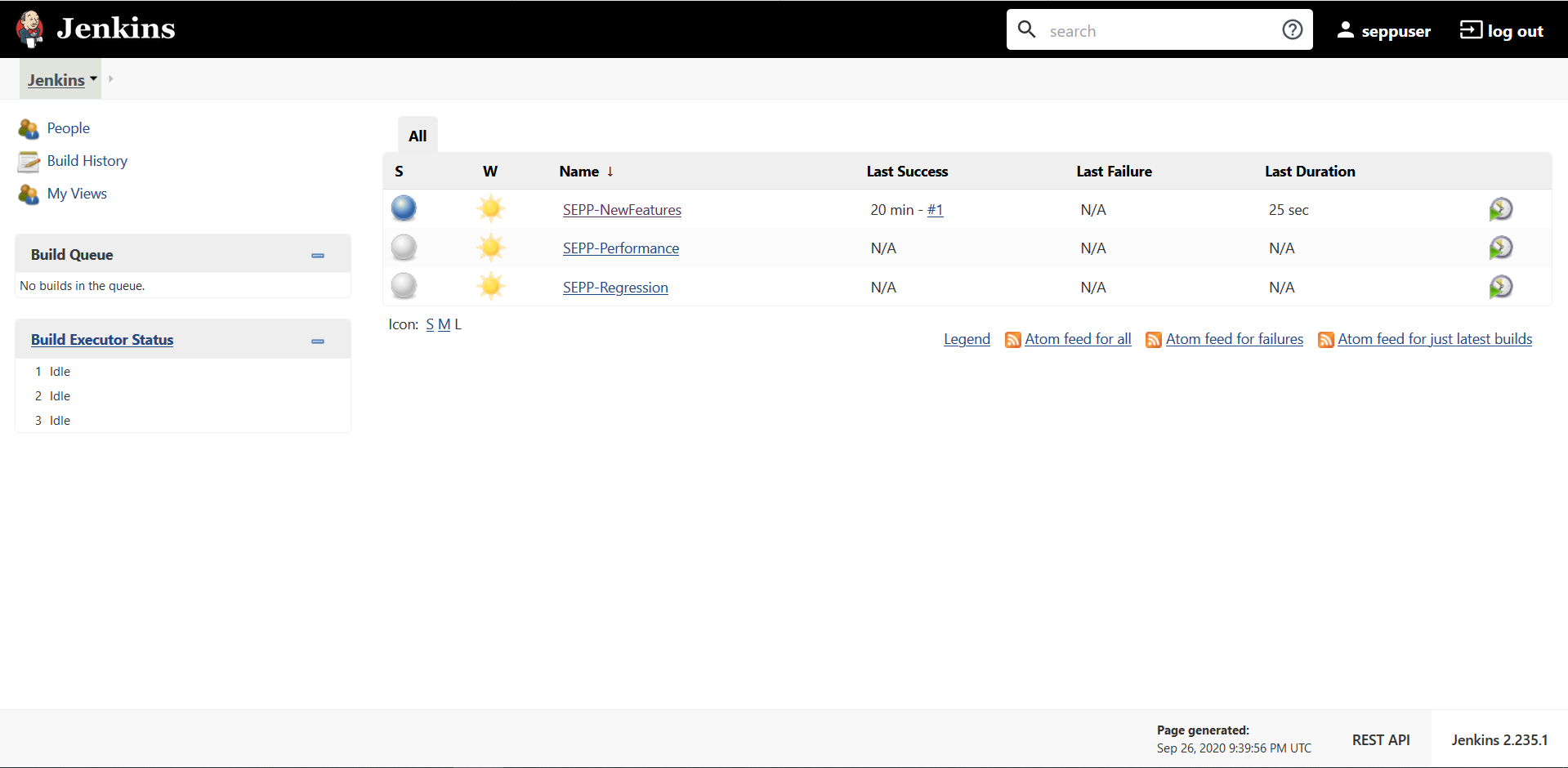
- SEPP-NewFeatures Pipeline: After identifying the SEPP pipelines, the user needs to do one-time configuration in ATS as per their SUT deployment. In this pipeline, all the new testcases related to SEPP are executed. To configure its parameters:
- Click SEPP-NewFeatures in the Name column. The following
screen appears:
Figure 3-88 SEPP-NewFeatures Pipeline
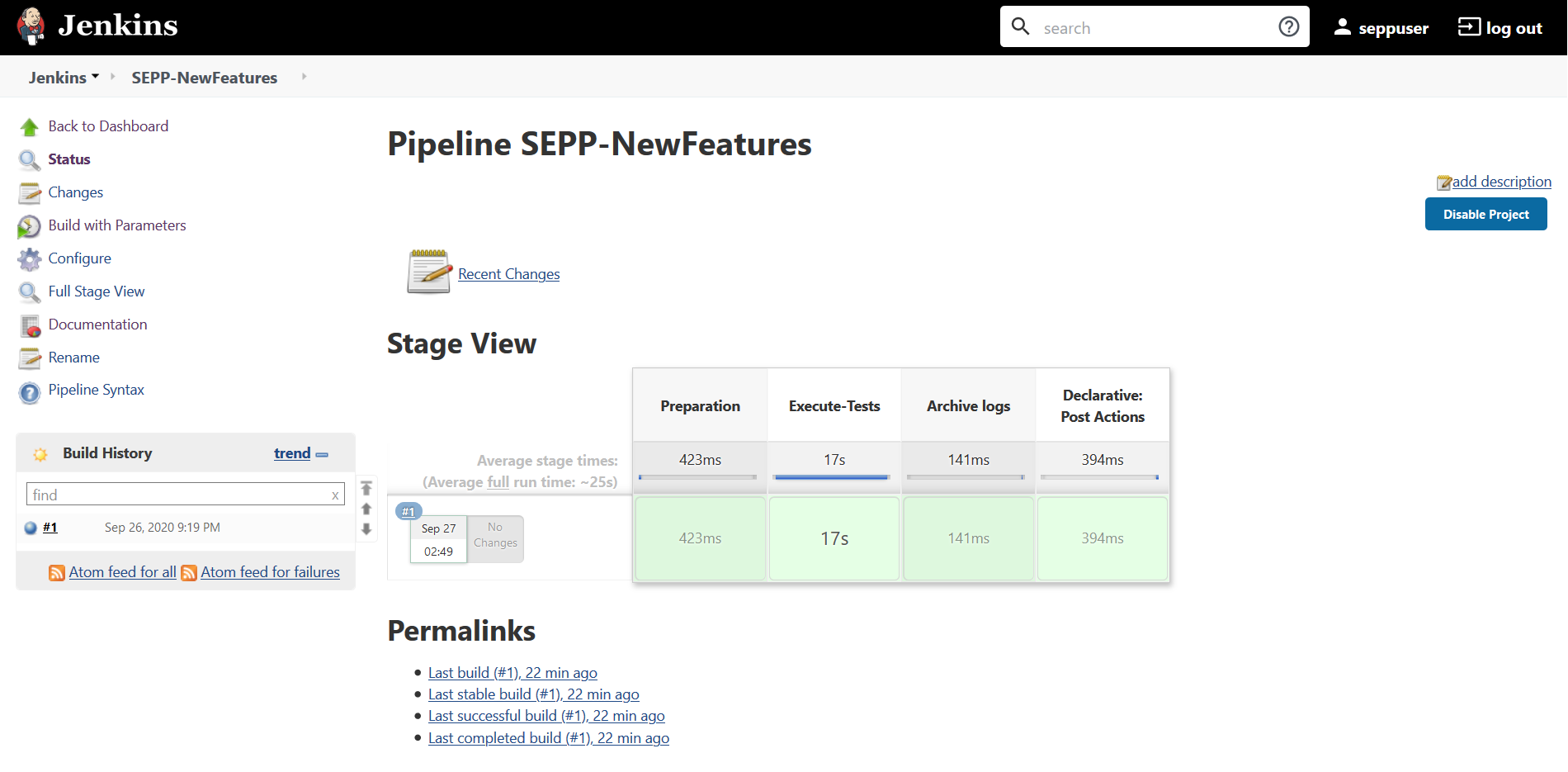
- In the above screen:
- Click Configure to navigate to a screen where configuration needs to be done.
- Click Documentation to view the documented test cases.
- Click blue dots inside Build History box to view the success console logs of the "All" and "Sanity" respectively.
- The Stage View represents already executed pipeline for the customer reference.
- Click Configure. Users MUST wait for the page to load
completely. Once the page loads completely, click the Pipeline tab to
reach the Pipeline configuration as shown below:
Note:
MAKE SURE THAT THE SCREEN SHOWN ABOVE LOADS COMPLETELY BEFORE YOU PERFORM ANY ACTION ON IT. ALSO, DO NOT MODIFY ANY CONFIGURATION OTHER THAN DISCUSSED BELOW.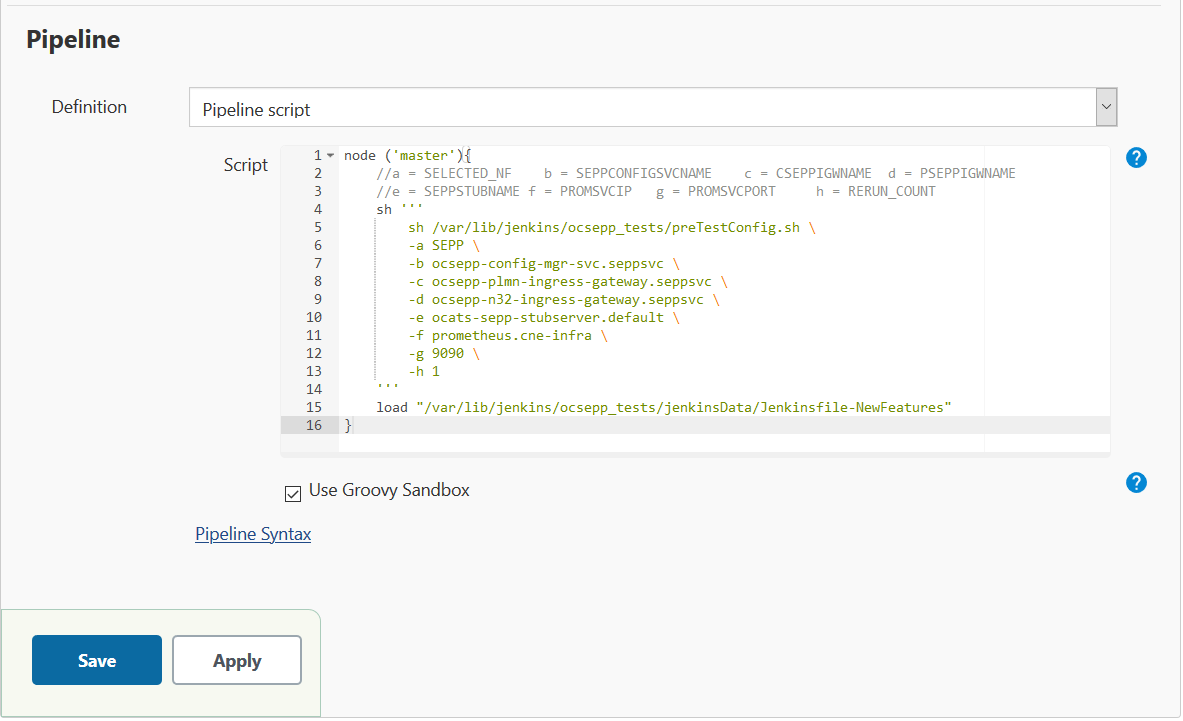
- In the above screen, the values of the 'Pipeline script' needs to
be changed. The content of the pipeline script is as
follows:
node ('master'){ //a = SELECTED_NF b = SEPPCONFIGSVCNAME c = CSEPPIGWNAME d = PSEPPIGWNAME //e = SEPPSTUBNAME f = PROMSVCIP g = PROMSVCPORT h = RERUN_COUNT sh ''' sh /var/lib/jenkins/ocsepp_tests/preTestConfig.sh \ -a SEPP \ -b ocsepp-config-mgr-svc.seppsvc \ -c ocsepp-plmn-ingress-gateway.seppsvc \ -d ocsepp-n32-ingress-gateway.seppsvc \ -e ocats-sepp-stubserver.default \ -f prometheus.cne-infra \ -g 9090 \ -h 1 ''' load "/var/lib/jenkins/ocsepp_tests/jenkinsData/Jenkinsfile-NewFeatures" }Note:
The User MUST NOT change any other value apart from line number 8 to line 20.You can change only those parameters that are marked as "a" to "h" as per your requirement.
- a - Name of the NF to be tested in capital (SEPP).
- b - SEPP Config service name including namespace
- c - cSEPP Plmn Ingress gateway service name including namespace
- d - pSEPP N32 Ingress gateway service name including namespace
- e - Stub Server service name inclding namespace
- f - Prometheus service name or IP including namespace
- g - Prometheus service port
- h - Number of times the re-run of failed case is allowed (default as 2).
Note:
You do not have to change any value if OCCNE cluster is used and SEPP, ATS and STUB are deployed in ocsepp namespace. - Click Save after making necessary changes. You are navigated back to the Pipeline SEPP-NewFeatures screen.
Executing SEPP Test Cases
- Click the Schedule a Build with parameters icon present
on the SEPP-NewFeatures screen in the extreme right column corresponding to
SEPP-NewFeatures row.The following screen appears:
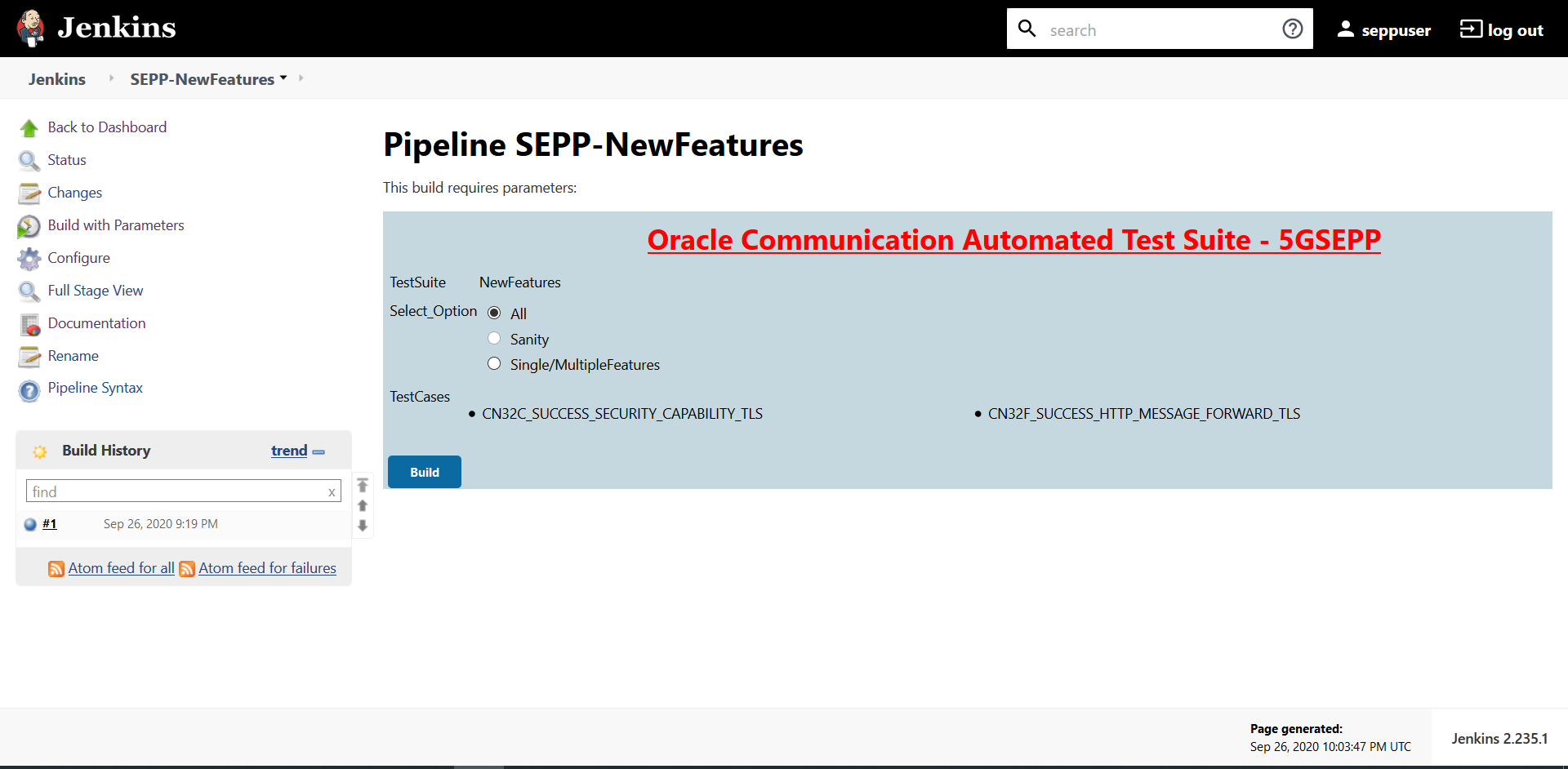
- In the above screen, there are three Select_Option(s),
which are:
- All: By default, all the SEPP test cases are selected for execution. User just needs to scroll down and click Build to execute all the test cases.
- Sanity: Currently disabled.
- Single/MultipleFeature: This option allows you to select any number of test cases that you want to execute from the list of total test cases available for execution. After selecting the test cases, scroll-down and click Build. The selected SEPP test cases are executed.
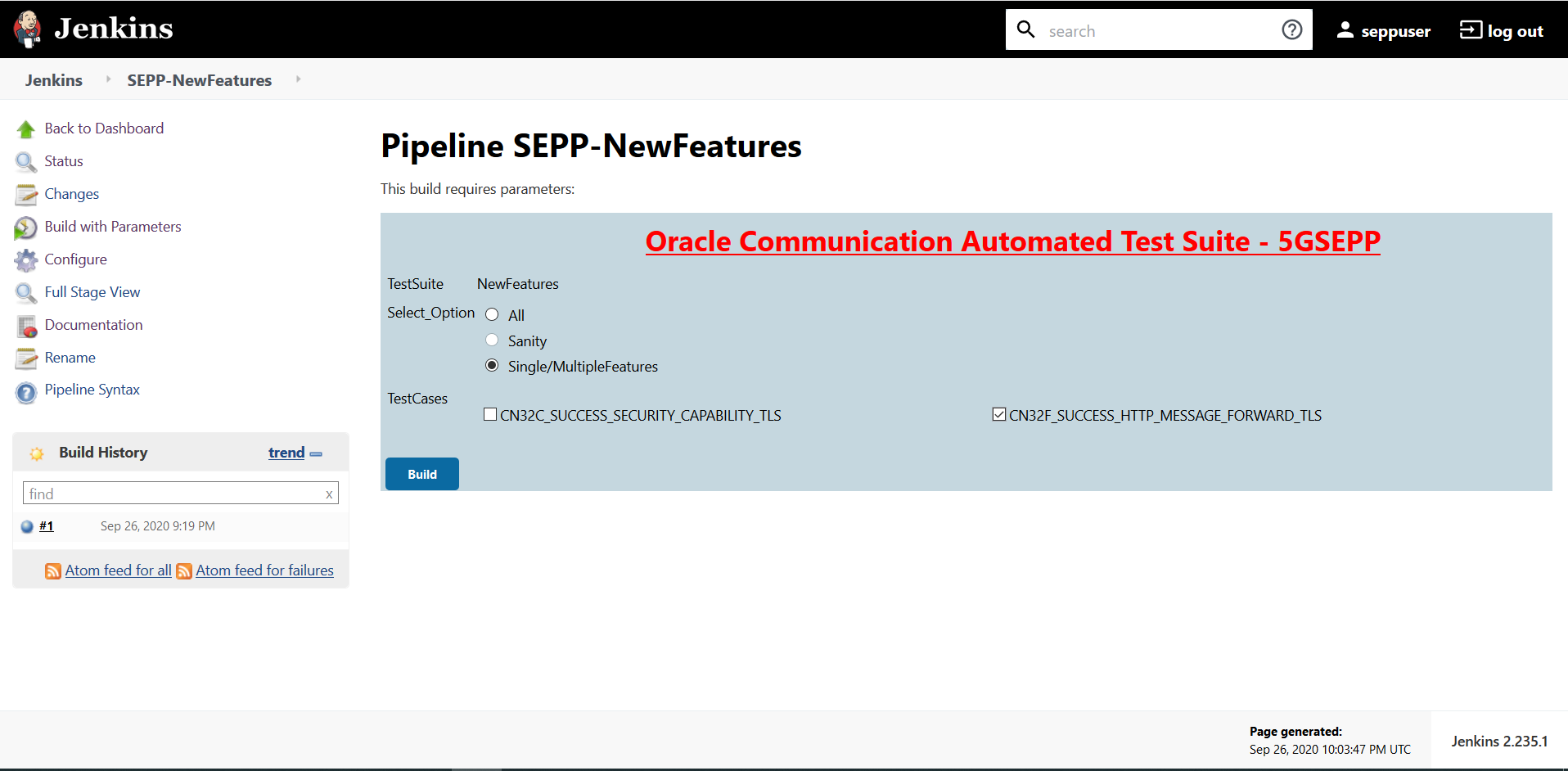
NewFeatures - Documentation
To view SEPP functionalities, go to SEPP-NewFeatures pipeline and click the Documentation link in the left navigation pane. The following screen appears:
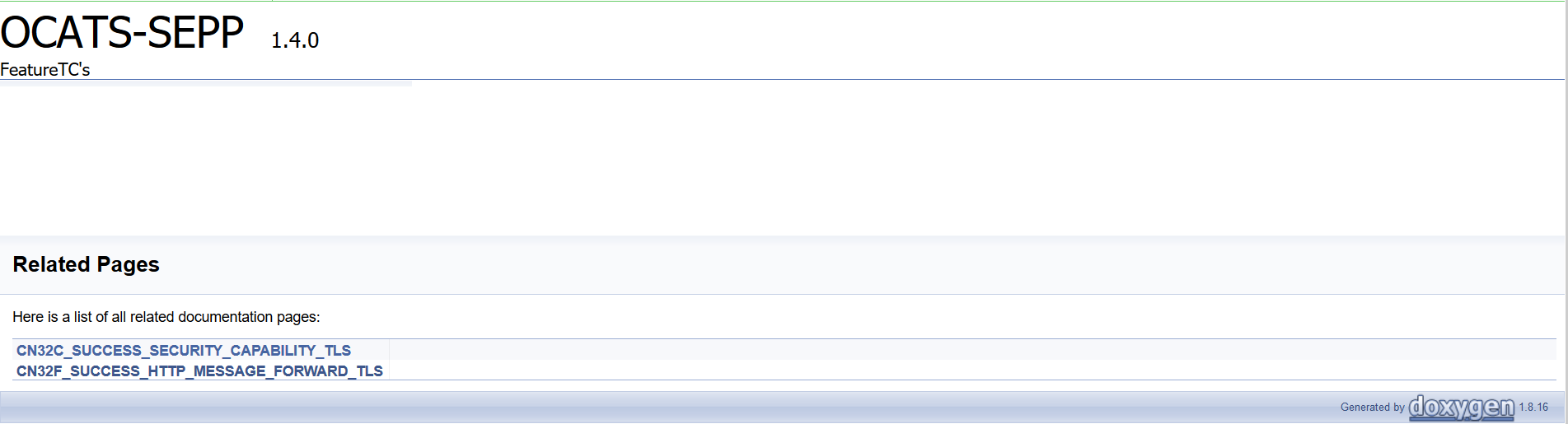
User can click any functionality to view its test cases and scenarios of each test case. A sample screen is given below:
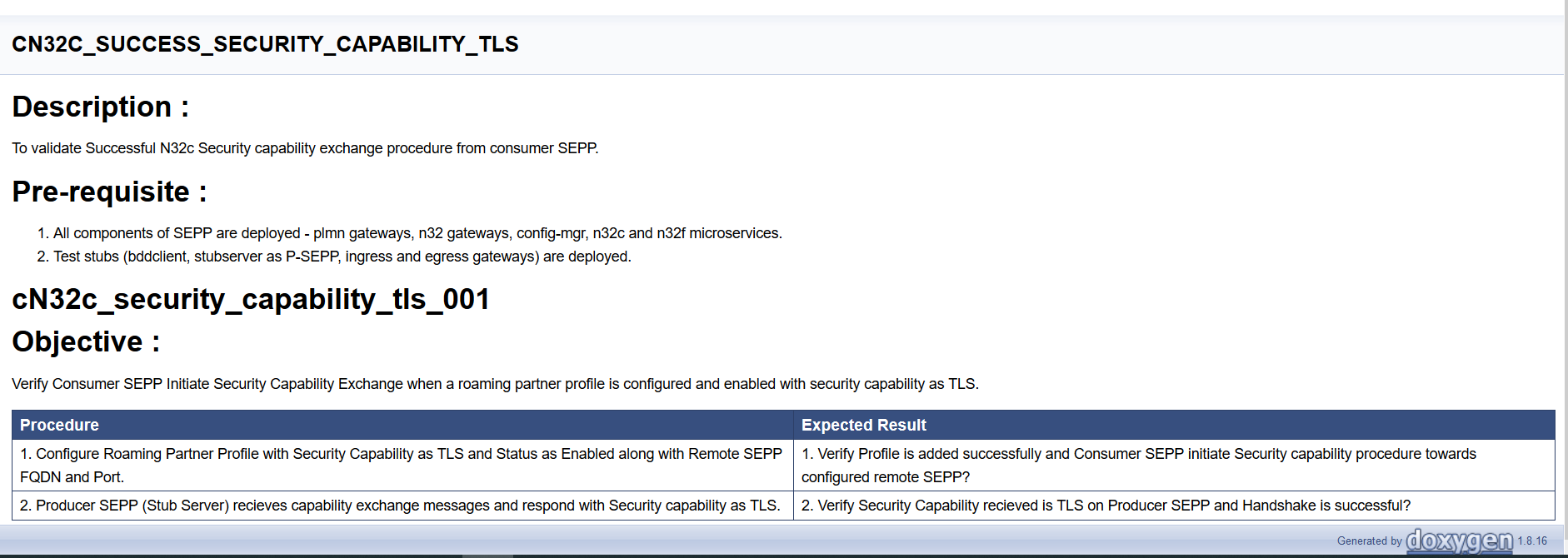
Executing SLF Test Cases using ATS
Custom Folder Implementation
Users can customize test cases in the custom test case folders (cust_newfeatures, cust_regression and cust_performance). They can add new test cases, remove unwanted test cases and modify existing test cases. It does not impact the original product packaged test cases available in the newfeatures, regression and performance folders. For more details, you can refer to Custom Folder Implementation.
Logging into ATS
Before logging into ATS, you need to know the nodeport of the "-ocats-udr-slf" service. To get the nodeport detail, execute the following command:
kubectl get svc -n <slf_namespace>
kubectl get svc -n ocatsFigure 3-89 SLF Nodeport
In the above screen, 31083 is the nodeport.
- In the web browser, type http://<Worker IP>:<port
obtained above> and press Enter.
Example: http://10.75.225.49:31083
The Login screen appears.
- Enter the username as 'udruser' and password as 'udrpasswd'.
Click Sign in. A screen with pre-configured pipelines for SLF appears
(3 pipelines).
- SLF-New-Features: This pipeline has all the test cases, which are delivered as part of SLF ATS - 1.8.0.
- SLF-Performance: This pipeline is not operational as of now. It is reserved for future releases of ATS.
- SLF-Regression: This pipeline has all the test cases of previous releases.
Note:
If you want to modify your default login password, refer to Modifying Login PasswordFigure 3-90 SLF Pre-configured Pipelines
- Click SLF-NewFeatures. The following screen appears:
Figure 3-91 SLF-NewFeatures Configure
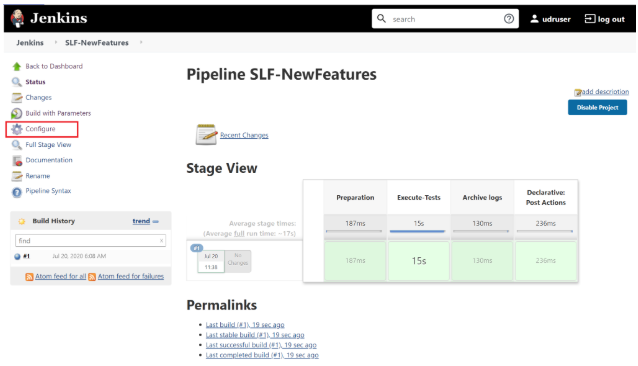
- Click Configure in the left navigation pane. The General tab appears. User MUST wait for the page to load completely.
- Once the page loads completely, click the Advanced Project
Options tab. Scroll down to reach the Pipeline configuration
as shown below:
MAKE SURE THAT THE SCREEN SHOWN BELOW LOADS COMPLETELY BEFORE YOU PERFORM ANY ACTION ON IT. ALSO, DO NOT MODIFY ANY CONFIGURATION OTHER THAN DISCUSSED BELOW.
Figure 3-92 SLF Configuration Parameters - Pipeline Tab
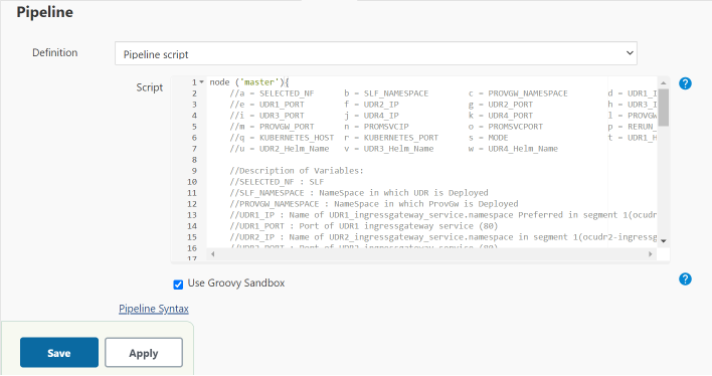 You SHOULD NOT change any other value apart from line number 36 to line 58. It means the parameters marked as "a" - to - "w" can only be changed as per user requirement. The detail about these parameters are provided as comments in line number 6 to 12. The parameters description is as follows:
You SHOULD NOT change any other value apart from line number 36 to line 58. It means the parameters marked as "a" - to - "w" can only be changed as per user requirement. The detail about these parameters are provided as comments in line number 6 to 12. The parameters description is as follows:Note:
The parameters that you should modify to execute UDR-SLF ATS SUT are: a, b, d, e, n, o and p.- a - Name of the NF to be tested in capital (SLF).
- b - Namespace in which the udr is deployed.
- c - Namespace in which ProvGw is Deployed
- d - Name of UDR1_ingressgateway_service.namespace preferred in segment 1(seg1ocudr1-ingressgateway.ocudr).
- e - Port of UDR1 ingressgateway service (80)
- f - Name of UDR2_ingressgateway_service.namespace in segment 1(seg1ocudr2-ingressgateway.ocudr)
- g - Port of UDR2 ingressgateway service (80)
- h - Name of UDR3_ingressgateway_service.namespace preferred in segment 2(seg2ocudr1-ingressgateway.ocudr)
- i - Port of UDR3 ingressgateway service (80)
- j - Name of UDR4_ingressgateway_service.namespace in segment 2(seg2ocudr2-ingressgateway.ocudr)
- k - Port of UDR4 ingressgateway service (80)
- l - Name of PROVGW_ingressgateway_service.namespace (provgw-prov-ingressgateway.ocudr)
- m- Port of PROVGW ingressgateway service (80)
- n - Name_of_Prometheus_service.namespace (occne-prometheus-server.occne-infra)
- o - Port of Prometheus service (80)
- p - Number of times the re-run of failed case is allowed (default as 2)
- q - Name of Kubernetes Host server (kubernetes.default)
- r - Port of Kubernetes Host server (80)
- s - Mode of Communication between Prov-gateway and UDR-SLF (Can be either IP or fqdn)
- t - Helm Name for UDR1 (seg1ocudr1)
- u - Helm Name for UDR2 (seg1ocudr2)
- v - Helm Name for UDR3 (seg2ocudr1)
- w- Helm Name for UDR4 (seg2ocudr2)
- Click Save after making neccesary changes. The SLF-NewFeatures screen appears.
- Click Build with Parameters. The following screen
appears:
Figure 3-93 SLF Build with Parameters
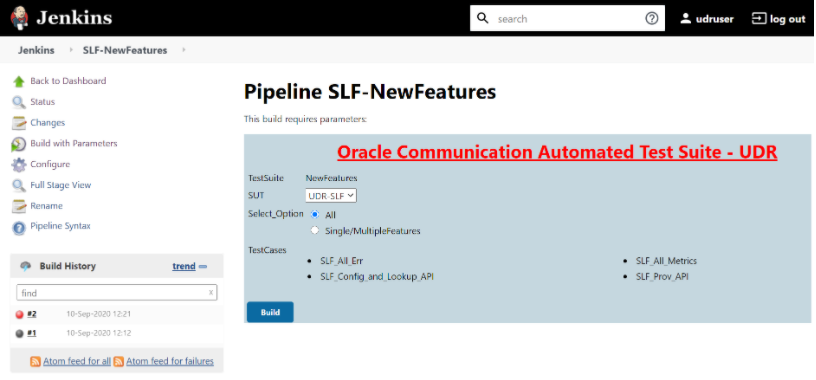
Note:
To execute UDR-SLF related test cases, select UDR-SLF from the SUT list. This is the default option.To execute ProvGw related test cases, select ProvGw from the SUT list.Note:
To execute the ProvGw test cases, it is mandatory to have 4 UDRs up and running in the same namespace as that of UDR-SLF-ATS.Figure 3-94 SUT as ProvGw
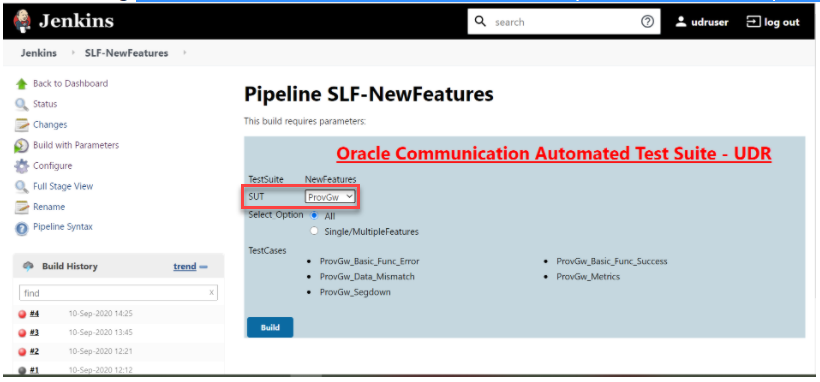 In the above screen, there are two Select_Option(s), which are:
In the above screen, there are two Select_Option(s), which are:- All: By default, all the SLF test cases are selected for execution. User just need to scroll down and click Build to execute all the test cases.
- Single/MultipleFeatures: This option allows you to select any number of test cases that you want to execute from the list of total test cases available for execution. After selecting the test cases, scroll-down and click Build. The selected SLF test cases are executed.
NewFeatures-Documentation
Figure 3-95 SLF-NewFeatures Documentation Option
Figure 3-96 SLF-NewFeatures Documentation
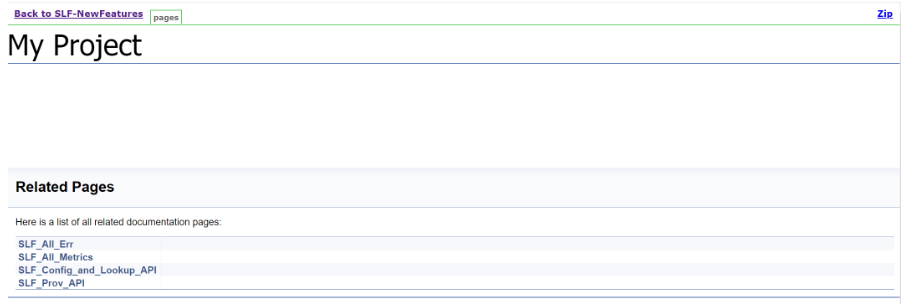
Figure 3-97 ProvGw-NewFeatures Documentation
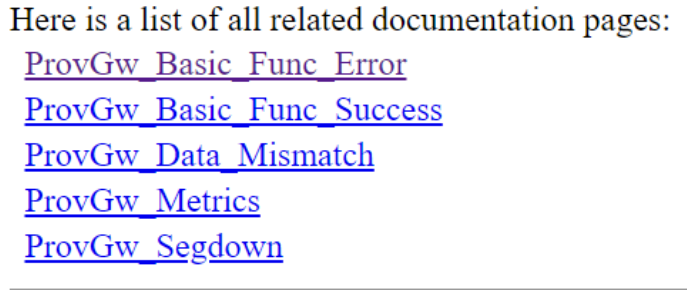
Note:
Documentation option appears only if New-Features pipeline is executed atleast once.Figure 3-98 Sample: SLF Test Case Description
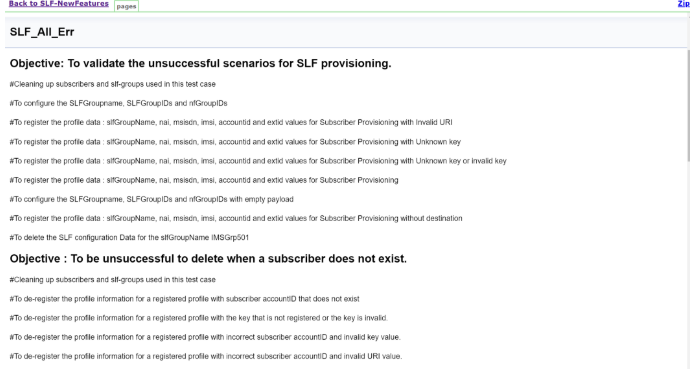
Figure 3-99 Sample: ProvGw Test Case Description

Based on the functionalities covered under Documentation, the Build Requires Parameters screen displays test cases. To navigate back to the Pipeline SLF-NewFeatures screen, click Back to SLF-NewFeatures link available on top left corner of the screen.