1 Introduction
Oracle Communications Certificate Management (OCCM) is an automated solution for managing the certificates needed for Oracle 5G Network Functions (NFs). OCCM constantly monitors and renews the certificates based on their validity or expiry period. As 3GPP recommends using separate certificates based on the client or server mode and the type of workflow, automated certificate management eliminates any possibilities of network disruption due to expired certificates. In SBA network deployments, the Network Functions (NFs) are required to support multiple operator certificates for different purposes and interfaces. This amounts to hundreds of certificates in the network with varying validity periods and unwieldy to monitor and renew the certificates manually. Hence, automation of certificate management becomes important to avoid network disruptions due to expired certificates.
Note:
This guide covers the installation instructions when Podman is the container platform with Helm as the Packaging Manager. For any other container platform, the operator must use the commands based on their deployed container runtime environment.1.1 Overview
OCCM integrates with the Certificate Authority(s) using Certificate Management Protocol Version 2 (CMPv2) and RFC4210 to facilitate these certificate management operations:
- Operator-initiated certificate creation
- Operator-initiated certificate recreation
- Automatic certificate monitoring and renewal
Figure 1-1 OCCM Integration with CA
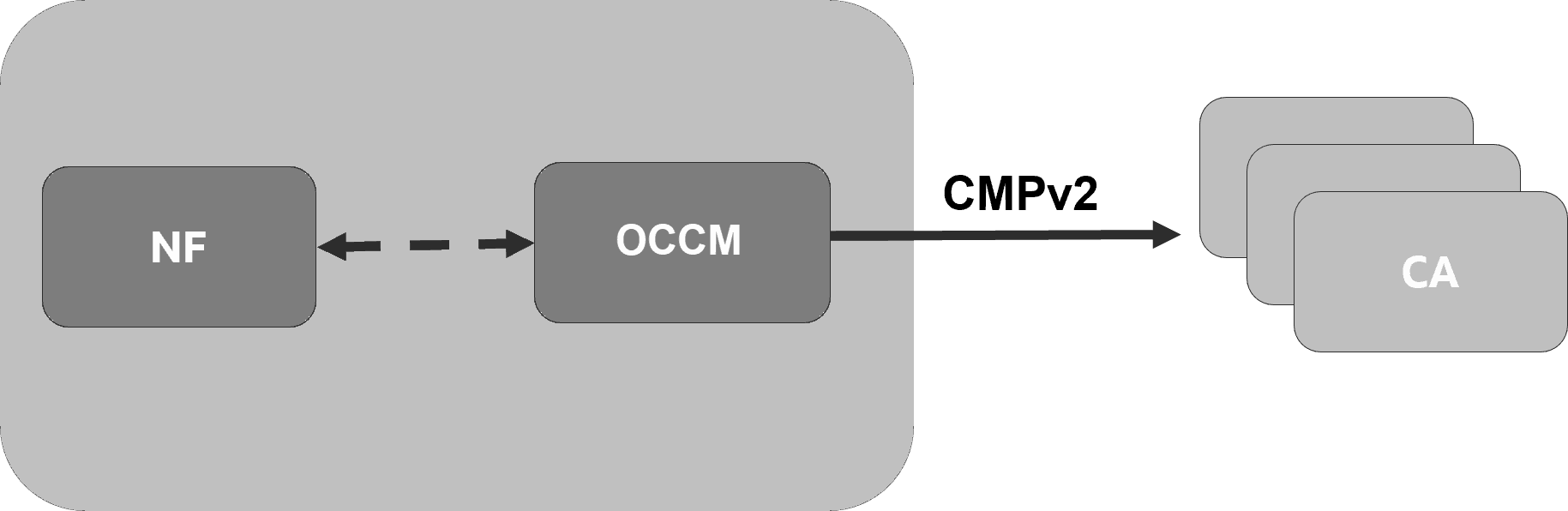
OCCM supports transport of CMPv2 messages using HTTP-based protocol.
- Certificate-based message signing
- Pre-shared key or MAC based authentication
All the subsequent CMPv2 procedures are authenticated using the certificate-based mechanism in compliance with 3GPP TS 33.310.
The keys and X.509 certificates are managed using Kubernetes secrets.
1.2 OCCM Architecture
OCCM is a Cloud Native application consisting of a single microservice. OCCM is packaged and delivered as a CSAR or Helm chart.
Figure 1-2 OCCM Architecture

Architecture Description
OCCM is deployed as a single Kubernetes Pod and has a small resource footprint. The OCCM application uses a set of OpenSSL Certificate Management Protocol (CMP) CLI commands based on the provided configuration and the certificate management procedure that needs to be carried out at a point in time. The Output – Key and Certificate – is stored in configuration defined Kubernetes secret.
Operator provides the desired key and certificate configuration through Console. OCCM contacts the CA for certificate signing. After successful Certificate creation, OCCM writes the key and certificate in Kubernetes secrets.
- Dedicated deployment model - OCCM resides in the same Kubernetes namespace as the NF or Components.
- Shared deployment model - OCCM is deployed in a separate Kubernetes namespace and can manage certificates of multiple NFs or components deployed in other Kubernetes namespaces.
Appropriate permissions must be assigned to OCCM using Kubernetes Service Account, Role and Role Binding, based on the selected deployment model.
1.3 OCCM Deployment Models
- Dedicated deployment model - OCCM resides in the same Kubernetes namespace as the NF or components.
- Shared deployment model - OCCM is deployed in a separate Kubernetes namespace and can manage certificates of multiple NFs or components deployed in other Kubernetes namespaces.
Figure 1-3 Deployment Model-1: Dedicated OCCM Deployment – Single Namespace Management

In the dedicated OCCM deployment model, OCCM is deployed in the same namespace as the component(s) managed by it.
Figure 1-4 Deployment Model-2: Shared OCCM Deployment - Multiple Namespaces Management
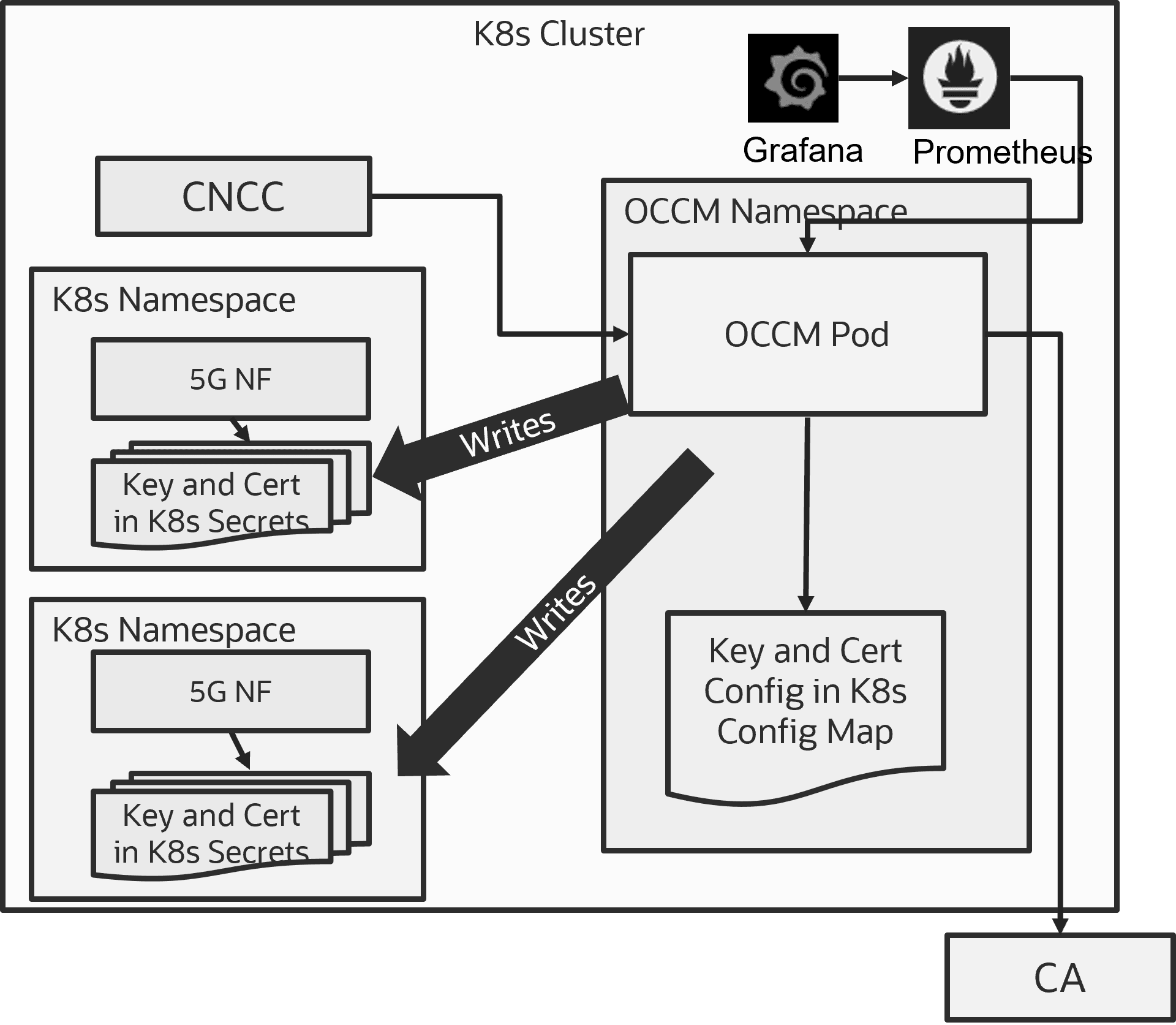
In the shared deployment model, OCCM is deployed in a separate Kubernetes namespace and can manage certificates of multiple NFs or components deployed in other Kubernetes namespaces. OCCM provides Key and certificate for NFs running in multiple namespaces. OCCM needs privileges to be able to create or write Kubernetes secrets in multiple namespaces. Care must be taken to not provide Kubernetes Cluster Role access as it provides access to all namespaces in the cluster. Multiple namespace specific roles are created and then bind to OCCM service account using role binding. OCCM is deployed in a dedicated namespace different from the components’ namespace managed by it. For more information, see Creating Service Account, Role, and Rolebinding.