2 BSF Architecture
This section provides information about Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Binding Support Function (BSF) Architecture.
2.1 BSF Architecture
The BSF network function is a cloud native application that consists of multiple microservices running in cloud native environment.
The following figure describes the component level architecture of BSF:
Figure 2-1 Architecture of Binding Support Function
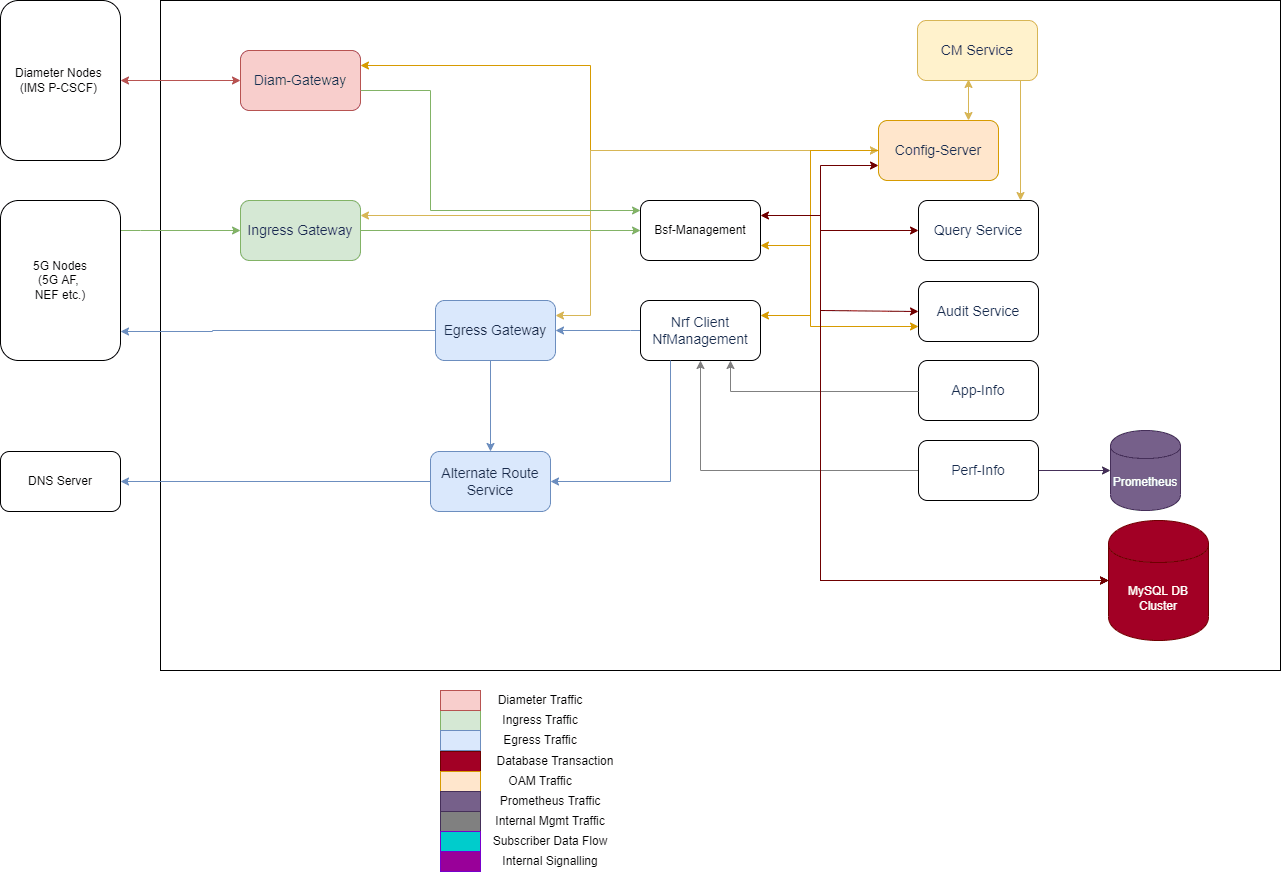
The microservices are logically categorized as following categories:
- Connectivity: It includes external entities that interact with BSF and vice-versa.
- Adaptation & Mobility: Components under this category
provide
an interface that
ensures
seamless interaction between external and internal entities. It contains the
following components:
- Diameter Gateway: Acts as a Gateway for all diameter traffic to BSF.
- Ingress Gateway: Acts as a gateway for all incoming Ingress HTTP traffic.
- Egress Gateway: Acts as a gateway for all outgoing Egress HTTP traffic.
- Alternate Route Service: Provides alternate routing
destinations for BSF (NRF-management) to re-route during failures. There
are two options for alternate routing:
- DNS (SRV) based routing - A DNS server is required to resolve SRV records having alternate destinations with higher priority.
- Static routing - Static configuration for alternate destinations with weight or priority.
- Business Logic: Components under this category can be
enabled based on deployment needs. It includes the following components:
- Bsf-Management: It implements the nbsf interface as defined in 3GPP Specification 29.521.
- Nrf-Management: It helps in the autonomous discovery of network functions.
- Operations & Maintenance: Components under this category perform
specific tasks as follows:
- Config-Mgmt: It provides GUI and REST OAM interfaces for service provisioning.
- Config Server: It abstracts the database for storage and retrieval of configuration.
- Query: It processes session viewer queries triggered from config management service.
- App-Info: It monitors application (microservice) health and status.
- Perf-Info: It monitors application (microservice) capacity and load status.
- Audit-service: It runs the Audit engine to detect and process stale
session records.
Also, Audit-service counts the maximum number of active sessions for a particular service.
- Data Management: Components under this category are responsible for storing various types of persistent data.
- Ingress and Egress Gateway Traffic Management
For more information on Ingress and Egress Gateway Traffic Management, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Environment User Guide.