2 Overview
Deployment Environment
The 5G Cloud Native Core provides a variety of possible configuration and deployment environments:
Table 2-1 Deployment Environment
| Type | Host | CNE | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bare Metal | CNE-Supported Infrastructure | CNE | In this environment, a Kubernetes Cloud Native Environment is hosted directly on the bare metal hardware, while some other elements (DB or Bastion) are hosted using virtualized servers. |
| vCNE (Virtualized CNE) | Customer Hypervisor (KVM/VMware ESXi) | CNE | In this environment, all the system elements are hosted in virtualized servers deployed on a customer provided Openstack environment. The CNE is deployed on the openstack infrastructure. |
| Cloud | Customer CNE | Customer CNE | In this environment, the customer provides the CNE and deploys the 5G NFs directly into the environment. The Oracle provided common services and cnDBTier are used; equivalent functionality is provided by the customer. |
Note:
- Oracle Communications CNE provides basic CNE environment for on-premise deployment.
- Customer CNE provides CNE environment for running not just 5G microservices but also any kind of service, not just 5G. For example- observability frameworks or 4G microservices.
- With Customer CNE, a customer is responsible for ensuring the security of a Customer CNE.
Note:
The cloud environment security recommendations and procedures focus on the CNE reference environment. Customers providing their own CNE must have security procedures already in place.2.1 Cloud Native Core Network Functions
Network Function security is prescribed by the relevant 4G and 5G standards. This document details the administrative steps required to ensure secure 5G network operations.
Table 2-2 4G and 5G Network Functions
| Network Functions | Abbreviation | Description | 3GPP Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Repository Function | NRF | NRF provides registration, discovery, and authorization services to all the Network Functions (NF) in the 5G core network. |
|
| Service Communication Proxy | SCP | SCP provides a 5G-aware service mesh. |
|
| Network Slice Selection Function | NSSF | NSSF works with the Access and Mobility Function (AMF) to select the network slice to be used by the User Equipment (UE). |
|
| Security Edge Protection Proxy | SEPP | In the roaming architecture, the home and visited networks are connected via the Security Edge Protection Proxy (SEPP) to manage the control plane of the inter-network interconnect. |
|
| Unified Data Repository | UDR/UDSF | UDR is a repository of subscriber information, and is used by various NFs (including UDR, PCF, and NEF). The UDSF is a part of the Unified Data Management Function (UDF) and is used to store state information for Network Functions (NF). |
|
| Unified Data Repository (UDR) as Subscriber Location Function (SLF). | SLF | SLF supports the storage and retrieval of subscriber information through the nudr interface. | NA |
| Network Exposure Function | NEF | Securely exposes network capabilities and events to Application Functions (AF). |
|
| Policy Control Function | PCF | Implements a unified policy framework for implementing control plane rules. |
|
| Binding Support Function | BSF | Provides PCF binding (mapping and selection) for User Equipment (UE). |
|
| Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Certificate Management | OCCM | Supports automation of certificate lifecycle management. |
|
| Cloud Native Core Console | CNC C | Configuration and Operations portal and proxy for CNC NFs and components. | NA |
Table 2-3 5G Common Services
| Network Function | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ingress Gateway, Egress Gateway, Alternative Routing Service | APIGW | Ingress and Egress Gateways for NFs |
| Automatic Test Suite | ATS | Automated Test Suite |
| Oracle Communications Certificate Manager | OCCM | Certificate Management |
| Network Repository Function - Client | NRF-Client | Product: Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core - 5G and Subcomponent: NRF-Client |
| Mediation | Mediation | Mediation modifies 5G Service Based Interface (SBI) message content, which includes HTTP2 header values and JSON message body, based on the user-defined mediation rule sets |
| Oracle Communication Cloud Native Core OCI Adapter | OCI Adaptor | Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core OCI Adapter |
| Oracle Communications DBTier | cnDBTier | Containerized deployment and automation of MySQL Cluster database technology |
2.2 Secure Development Practices
Given below are the practices followed for a secure development environment:
2.2.1 Vulnerability Handling
For details about the vulnerability handling, refer Oracle Critical Patch Update Program. The primary mechanism to backport fixes for security vulnerabilities in Oracle products is quarterly Critical Patch Update (CPU) program.
In general, the CNC Software is on a quarterly release cycle, with each release providing feature updates and fixes and updates to relevant third party software. These quarterly releases provide cumulative patch updates.
You should have procedures in place to deploy security updates for each release cycle. For more information, see Implementing Security Recommendations and Guidelines.
2.3 Trust Model
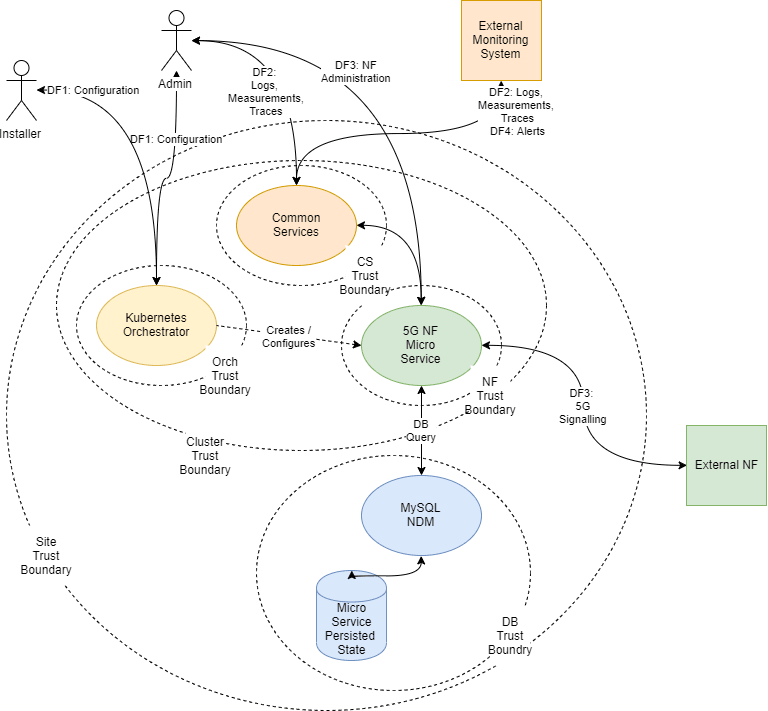
The following Trust Model depicts the reference trust model (regardless of the target environment). The model describes the critical access points and controls site deployment.
While the model shows a single 5G NF microservice deployed, several NFs are also deployed in individual clusters.
2.3.2 Key Trust Boundaries
Table 2-4 Key Trust Boundaries
| Trust Boundary | Includes | Access Control |
|---|---|---|
| Site Trust Boundary | All the NFs and other supporting elements for a given site. | Cluster Access Policies are implemented using some kind of Access Control Group (or Security Group) mechanism. |
| Cluster Trust Boundary | All the compute elements for a given cluster | Network Policies control traffic ingress and egress. Pod Security Policies manage the workloads allowed in the cluster (For example, no pods requiring privilege escalation). |
| DB Trust Boundary | All the cnDBTier elements for a given cluster | Firewall Policies control traffic ingress and egress. DB grants access and other permission mechanisms that provide authorization for users. |
| Orchestrator Trust Boundary (Orch Trust Boundary) | The orchestration interface and keys | Firewall Policies control the access to a Bastion server which provides orchestration services. Access to the Bastion host uses Secure Socket Shell (SSH) protocol. The cluster orchestration keys are stored on the Bastion host. |
| CS Trust Boundary | The common services implementing logging, tracing, and measurements. | Each of the common services provides independent Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) that are currently open. The customer may want to introduce an api-gateway, implement authentication and authorization mechanisms to protect the OAM (Operations, Administrations, and Maintenance) data. The common services can be configured to use Transport Layer Security (TLS). When TLS is used, certificates must be generated and deployed through the orchestrator. |
| NF Trust Boundaries | A collection of 5G Network Functions deployed as a service. |
5G NF microservices provide Signaling access through a TLS protected HTTP2 interface. The certificates for these interfaces are managed via the certificate manager. |
2.3.3 External Data Flows
Table 2-5 External Data Flows
| Data Flow | Protocol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DF1: Configuration | SSH | The installer or administrator accesses the orchestration system hosted on the Bastion Server. The installer or administrator must use ssh keys to access the bastion to a special orchestration account (not root). Password access is not allowed. |
| DF2: Logs, Measurements, Traces | HTTP/HTTPS | The administrator or operator interacts with the common services using web interfaces. |
| DF3: 5G Signaling | HTTP2 (w/TLS) | All signaling interaction between NFs at a site and NFs at an external site is sent through TLS protected HTTP2. |
| DF4: Alerts | SNMP (Trap) | Alerting is performed using SNMP traps. |