12 Enabling or Disabling Traffic Segregation Through CNLB in OCNADD
The section defines the procedure to enable or disable traffic segregation in the Data Director (OCNADD). These procedures are applicable only when CNLB is supported in the OCCNE. The Data Director currently supports traffic segregation and external access using CNLB for the following:
- Consumer Adapter Feeds via Egress NADs
- Ingress Adapter via Ingress NADs
- Redundancy Agent syncing via Ingress-Egress NADs
- Kafka Cluster external access using CNLB ingress NADs and external IPs
The subsequent sections define the procedures for enabling and disabling traffic segregation for the features listed above.
12.1 Enabling Traffic Segregation in OCNADD
The necessary Egress and Ingress NADs must be created for the Data Director. Ensure that the prerequisites are met before continuing further in this section.
12.1.1 Creating a CNLB Annotation Generation Job
The Data Director retrieves information about the Ingress and Egress NADs from the CNE
using the job ocnaddcnlbannotationgen. This job must be created before
enabling any type of traffic segregation for egress or ingress communication.
Caution:
The job ocnaddcnlbannotationgen requires elevated privileges, such
as cluster roles and role bindings, to fetch Egress and Ingress network attachment
definitions. These privileges are restricted to this job and should not be used by
any other Data Director microservices.
The job ocnaddcnlbannotationgen can be configured as either a
one-time job or a cron job. It must be executed whenever a new network definition is
added for the Data Director, and this definition needs to be used during feed
creation. The cron job will fetch network definitions every hour.
Users can choose between a one-time job or a cron job, keeping the following points in mind:
- Single Job: This job must be executed after adding a new network definition. It is recommended to delete the job after execution to avoid retaining elevated privileges unnecessarily.
- Cron Job: This job will run every hour to update newly added network definitions. However, it is important to note that elevated privileges will remain in place as long as the cron job is no deleted.
Step 1: Update the ocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_job.yaml or
ocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_cronjob.yaml
- Edit the file
ocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_job.yamlorocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_cronjob.yamlin the custom-templates:- Update the management namespace for the Data Director
deployment:
namespace:ocnadd-deploy # Change this management namespace as per the OCNADD deployment. - Update the OCCNE namespace used in the CNE
deployment:
namespace:occne-infra # Change this OCCNE namespace as per the CNE deployment. - Do not make any changes to the following
line:
namespace:default
- Update the management namespace for the Data Director
deployment:
- Save the file.
Step 2: Create the ocnaddcnlbannotationgen Job
The config map ocnadd-cnlbini-configmap creation requires admin or
root access. Work with the cluster administrator to arrange for the admin or root
access for creating the config map ocnadd-cnlbini-configmap.
- Create the ConfigMap
ocnadd-cnlbini-configmap:kubectl create configmap ocnadd-cnlbini-configmap -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace> --from-file=/var/occne/cluster/<cluster_name>/cnlb.iniFor example:
kubectl create configmap ocnadd-cnlbini-configmap -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace> --from-file=/var/occne/cluster/cnlb-shared/cnlb.ini - Create the Job:
- For a single-time
job:
kubectl apply -f custom-templates/ocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_job.yaml - For a cron
job:
kubectl apply -f custom-templates/ocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_cronjob.yaml
- For a single-time
job:
Step 3: Verify Job Creation
- Check Job
Status:
kubectl get jobs -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace>Sample output:
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE ocnaddcnlbannotationgen 0/1 71s 2d22h - Verify
ConfigMaps:
kubectl get cm -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace>Verify that following two ConfigMaps are listed along with others:
ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-ingresskubectl describe cm -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace> ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-ingressSample output:
Name: ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-ingress Namespace: dd-mgmt Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Data ==== ingressNaddto: ---- {"ingressCnlbNetworks":["nf-sig6-int1/10.121.44.173","nf-sig5-int1/10.121.44.167","nf-sig2-int1/10.121.44.149","nf-sig1-int1/10.121.44.143","nf-sig4-int1/10.121.44.161","nf-sig3-int3/10.121.44.157"]} BinaryData ==== Events: <none>ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-egresskubectl describe cm -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace> ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-egressSample output:
Name: ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-egress Namespace: dd-mgmt Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Data ==== egressNaddto: ---- {"egressNadResponseDto":[{"egressNadName":"nf-oam-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.110.193]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-oam-egr2","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.110.194]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig1-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.111.193]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig1-egr2","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.111.194]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig2-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.112.193]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig2-egr2","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.112.194]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig3-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.113.193]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig3-egr2","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.113.194]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig4-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.114.193]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig4-egr2","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.114.194]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig5-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.115.193]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig5-egr2","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.115.194]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig6-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.116.193]]"},{"egressNadName":"nf-sig6-egr2","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=0.0.0.0/0, gw=172.16.116.194]]"}]} BinaryData ==== Events: <none>
- Describe the ConfigMaps to verify further that egress and ingress NADs are
updated:
kubectl describe cm ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-ingress -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namesapce>kubectl describe cm ocnadd-configmap-cnlb-egress -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namesapce> - Fetch Ingress NADs:
- Run the following
command:
kubectl exec -ti -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace> ocnaddadminservice-xxxxxx -- bash - If IntraTLS is
enabled:
curl -v -k --location --cert-type P12 --cert /var/securityfiles/keystore/clientKeyStore.p12:$OCNADD_SERVER_KS_PASSWORD --request GET "https://ocnaddconfiguration:12590/ocnadd-configuration/v1/cnlb/ingress/nads" - If IntraTLS is
disabled:
curl -v -k --location --request GET "http://ocnaddconfiguration:12590/ocnadd-configuration/v1/cnlb/ingress/nads"Expected sample output:
{"ingressCnlbNetworks":["nf-sig2-int10/10.123.155.32,nf-sig1-int11/10.123.155.13,nf-sig4-int2/10.123.155.60,nf-sig3-int3/10.123.155.57"]}
- Run the following
command:
- Fetch Egress NADs:
- Run the following
command:
kubectl exec -ti -n <ocnadd-mgmt-namespace> ocnaddadminservice-xxxxxx -- bash - If IntraTLS and mtls is
enabled:
curl -v -k --location --cert-type P12 --cert /var/securityfiles/keystore/clientKeyStore.p12:$OCNADD_SERVER_KS_PASSWORD --request GET "https://ocnaddconfiguration:12590/ocnadd-configuration/v1/cnlb/egress/nads" - If IntraTLS is
disabled:
curl -v -k --location --request GET "http://ocnaddconfiguration:12590/ocnadd-configuration/v1/cnlb/egress/nads"Expected sample output:
{"egressNadResponseDto":[{"egressNadName":"nf-sig1-egr1","egressNadDstInfo":"[Route [dst=10.123.155.55/32, gw=192.168.20.193], Route [dst=10.123.155.56/32, gw=192.168.20.193]]"}]}
- Run the following
command:
Step 4: Delete the Job ocnaddcnlbannotationgen
(Optional)
- Delete Job:
- For a single-time
job:
kubectl delete -f custom-templates/ocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_job.yaml - For a cron
job:
kubectl delete -f custom-templates/ocnadd_cnlb_annotation_gen_cronjob.yaml
- For a single-time
job:
Note:
This procedure needs to be run again whenever a new Ingress or Egress NAD is added.12.1.2 Enabling Egress Traffic Segregation for Consumer Adapter Feeds
To enable Egress NAD annotation support in the consumer adapter feeds, the parameter
cnlb.consumeradapter.enabled must be set to
true.
Follow these steps to enable "cnlb" support in the consumer adapter feeds if it was not enabled during the Data Director installation:
Step 1: Update the ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file
- Enable "cnlb" in the Consumer Adapter.
- Edit the
ocnadd-custom-values.yamlfile. - Update the parameter
cnlb.consumeradapter.enabledas shown below:cnlb.consumeradapter.enabled:false ====>Change the value to "true" - Save the file.
- Edit the
Step 2: Upgrade the management namespace or the default namespace in the Data Director deployment
- Perform a Helm upgrade using the management group charts
folder.
helm upgrade <management-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<mgmt-group>.yaml --namespace <source-release-namespace> <helm_chart>For example:
helm upgrade ocnadd-mgmt -f ocnadd-custom-values-mgmt-group.yaml --namespace ocnadd-deploy ocnadd_mgmt
Step 3: Continue with new consumer feed creation or update existing feeds using the OCNADD UI
- In the "Add Destination and Distribution Plan" screen of the consumer feed, select the new Egress Network Attachment Definition (NAD).
- Verify the "dst" information according to the third-party destination endpoint.
- Submit the feed create or update request.
Step 4: Verify that all consumer adapters have respawned
- Run the following command to verify the consumer
adapters:
kubectl get po -n <ocnadd-workergroup-namespace>
12.1.3 Enabling Ingress Traffic Segregation for the Ingress Adapter
Non-Oracle NFs (Network Functions) forward traffic to the Data Director via the Ingress Adapter. If non-Oracle NFs are deployed in the same cluster as OCNADD, there is no need to enable the CNLB configuration for the Ingress Adapter, as the service name or FQDN can be used.
When non-Oracle NFs are in a separate cluster, ingress traffic segregation can be achieved by enabling CNLB support for the Ingress Adapter in the Data Director.
Note:
- In current release, a single segregation network will be attached to each Ingress Adapter configuration. If more than one non-Oracle NF wants to connect to the same Ingress Adapter Feed, ingress traffic segregation will not be possible.
- To achieve ingress traffic segregation for all non-Oracle NFs ingesting data to the Data Director, a separate Ingress Adapter Feed configuration needs to be created for each non-Oracle NF.
In this configuration, all non-Oracle NFs must share the same dedicated network to forward traffic to the Data Director. Communication between non-Oracle NFs and the Data Director will occur over a single dedicated network, using the external IP of the Ingress Adapter.
To enable the ingress NAD annotation support in the Ingress Adapters, the parameter
cnlb.ingressadapter.enabled must be set to
true.
Perform the following steps to enable CNLB support in the Ingress Adapter feeds if not already enabled during the Data Director installation:
Step 1: Update the ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file
- Edit the
ocnadd-custom-values.yamlfile. - Update the parameter
cnlb.ingressadapter.enabledas indicated below:cnlb.ingressadapter.enabled: false ====> Change the value to "true" - Save the file.
Step 2: Upgrade the management namespace or the default namespace in the Data Director deployment
helm upgrade <management-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<mgmt-group>.yaml --namespace <source-release-namespace> <helm_chart>helm upgrade ocnadd-mgmt -f ocnadd-custom-values-mgmt-group.yaml --namespace ocnadd-deploy ocnadd_mgmtStep 3: Continue with the new Ingress Adapter feed creation or updating existing feeds
In the OCNADD GUI, create or update new or existing Ingress Adapter feeds to add ingress NAD from the drop-down selection.
Step 4: Verify that all Ingress Adapters have respawned
kubectl get po -n <ocnadd-workergroup-namespace>
12.1.4 Enabling External IPs for the Redundancy Agent via CNLB
In the two-site redundancy feature, two Redundancy Agents communicate with each other to sync configuration based on the redundancy configuration. If one or both sites are deployed in a CNLB CNE environment, the Redundancy Agents must be enabled for CNLB to provide external access. In this case, network and CNLB annotations need to be configured in the Redundancy Agents as well. The Redundancy Agents use the ingress NAD with a single network for ingress communication and external access.
Refer to the following scenarios for deploying redundancy agents across two sites:
a) Both sites are deployed in the CNLB-enabled cluster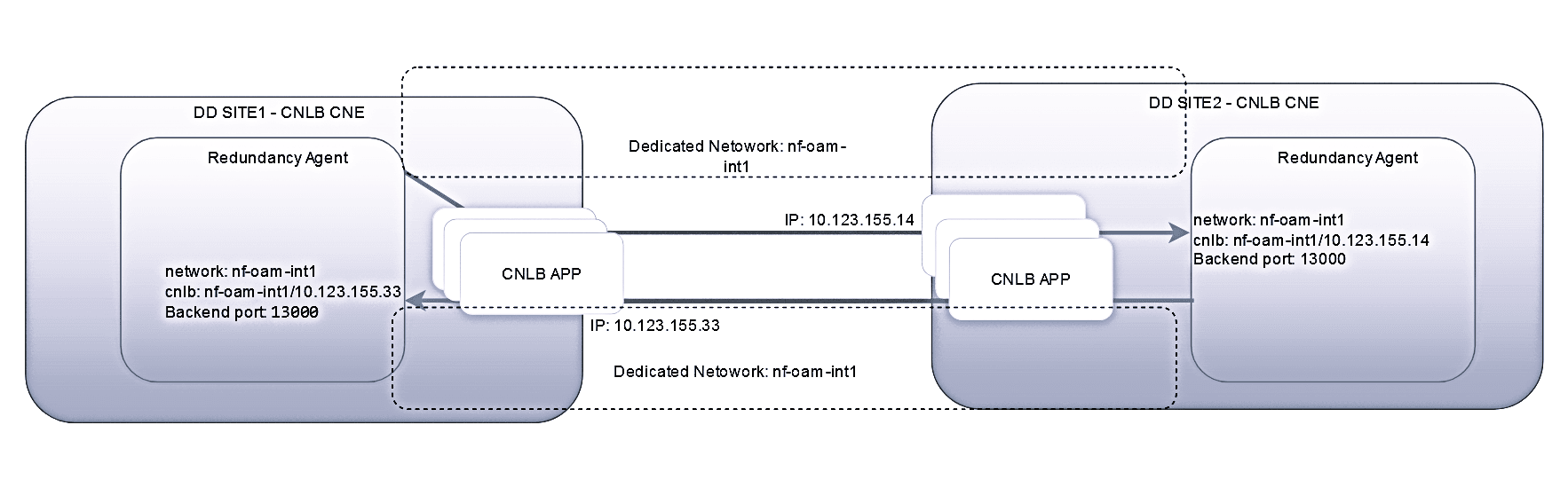
Note:
The following points should be considered:The two sites should have the same name for the egress NAD definitions, else the consumer adapter may stop processing the data if the NAD name is not present in the site.
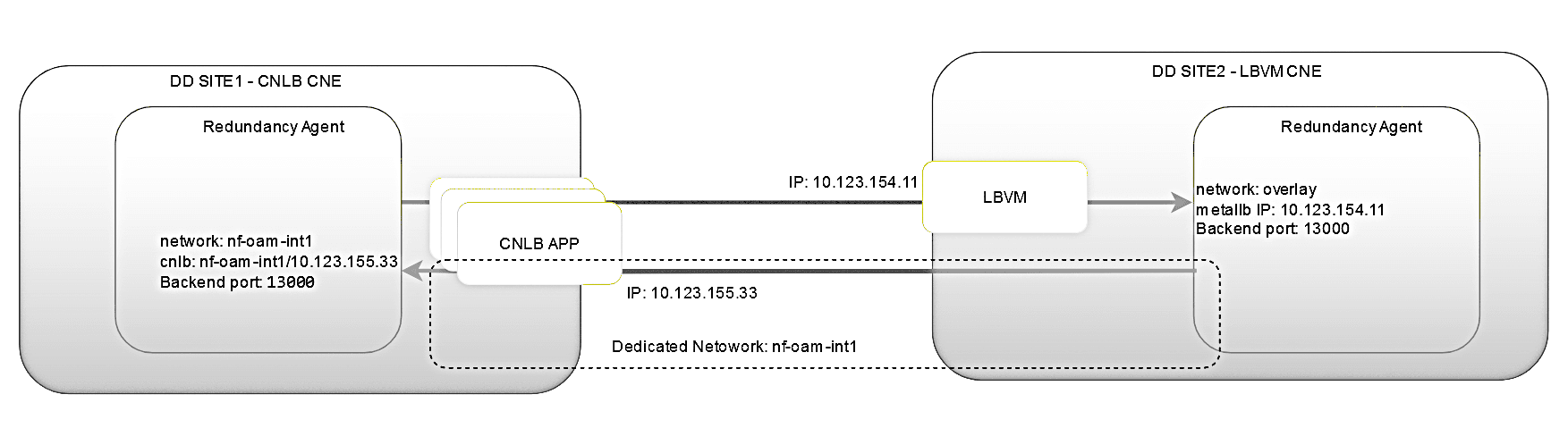
b) One site is deployed in the CNLB-enabled cluster, and the other in an LBVM-based CNE cluster
Note:
The following points should be considered:- The bi-directional configuration sync will not work if the primary site is CNLB enabled and secondary site is not CNLB enabled. In this case on the primary site, the consumer adapter feed configuration should be modified to include the NAD name in the feed.
- Discrepancy alarm is expected when the configuration sync is unidirectional and Primary site is CNLB enabled and Secondary site is non CNLB.
c) Both sites are deployed in an LBVM-based CNE cluster
Skip to the section "Enable Two-Site Redundancy Support" to continue with enabling the two-site redundancy feature in the Data Director.
12.1.4.1 Enabling CNLB in the Redundancy Agent
In the Primary Site (Site 1):
If the Redundancy Agent (RA) in the Data Director is deployed within a CNLB CNE environment, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Extract the Network and NAD Information for the Ingress-Egress NAD
Caution:
The script/var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.py
can be run by a user with admin privileges or the root user.
- Either get the necessary admin privileges from the cluster administrator before running the step below.
- Or have the command executed by an admin user and note down the output, which will be used in Step 2.
Extract NADs:
- Run the script
/var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.pyin CNE to fetch the available ingress-egress network information as per the inputs provided (Network Name: OAM, Segregation Type: INT, Network Type: SN, and Port Name: any value likehttp,8080).# python3 /var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.pyExample inputs and outputs:
# python3 /var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.py Network Names that application will use? Valid Choice example - oam OR comma seperated values - oam,sig,sig1 = oam Application pod external communication ? Valid choice - IE(Ingress/Egress) , EGR(Egress Only), INT(Ingress Only) = INT Pod ingress network type ? Valid choice - SI(Single Instance -DB tier only) , MN(Multi network ingress / egress) , SN(Single Network) = SN Provide container ingress port name for backend from pod spec , external ingress load balancing port? Valid choice - Example (http,80) = http,80 ... ... ------------------------------------------------- Pod network attachment annotation , add to application pod spec ------------------------------------------------- k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: default/nf-oam-int7@nf-oam-int7 oracle.com.cnc/cnlb: '[{"backendPortName": "http", "cnlbIp": "10.121.44.138","cnlbPort": "80"}]'
Step 2: Update the ocnadd-custom-values.yaml
- Copy the
cnlbIpandnetworksvalues from the script output and update theocnadd-custom-values.yamlfile as shown below:cnlb.redundancyagent.enabled: true cnlb.redundancyagent.network: "default/nf-oam-int7@nf-oam-int7" cnlb.redundancyagent.externalIPs: "10.121.44.138"
Step 3: Follow the procedure in the section Enable Two-Site Redundancy Support to continue enabling the two-site redundancy feature in the Data Director.
In the Secondary Site (Site 2):
Note:
If the Redundancy Agent (RA) in the Data Director is deployed in an LBVM CNE environment, skip the steps below and follow the Enable Two-Site Redundancy Support section to continue with enabling the two-site redundancy feature.If the Redundancy Agent (RA) in the Data Director is deployed within a CNLB CNE environment, follow the steps below:
Step 1: Extract the Network and NAD Information for the Ingress-Egress NADCaution:
The same script/var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.py
can be run by a user with admin privileges or the root user.
- Either obtain admin privileges from the cluster administrator before running the script.
- Or have the command executed by an admin user and note down the output for use in Step 2.
Extract NADs:
- Run the script
/var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.pyin CNE to fetch the available ingress-egress network information (similar inputs as in the primary site).# python3 /var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.py Network Names that application will use? Valid Choice example - oam OR comma separated values - oam,sig,sig1 = oam Application pod external communication ? Valid choice - IE(Ingress/Egress) , EGR(Egress Only), INT(Ingress Only) = INT Pod ingress network type ? Valid choice - SI(Single Instance -DB tier only) , MN(Multi network ingress / egress) , SN(Single Network) = SN Provide container ingress port name for backend from pod spec , external ingress load balancing port? Valid choice - Example (http,80) = http,9188 ... ... ------------------------------------------------- Pod network attachment annotation, add to application pod spec ------------------------------------------------- k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: default/nf-oam-int7@nnf-oam-int7 oracle.com.cnc/cnlb: '[{"backendPortName": "http", "cnlbIp": "10.121.44.138","cnlbPort": "9188"}]'
Step 2: Update the ocnadd-custom-values.yaml
- Copy the
cnlbIpandnetworksvalues from the script output and update theocnadd-custom-values.yamlfile as shown below:cnlb.redundancyagent.enabled: true cnlb.redundancyagent.network: "default/nf-oam-int7@nf-oam-int7" cnlb.redundancyagent.externalIPs: "10.123.155.34" global.deployment.primary_agent_ip: 10.10.10.10 ====> should be updated with ip 10.123.155.33 as extracted from CNLB on the primary site
Step 3: Follow the procedure in the section Enable Two-Site Redundancy Support to continue enabling the two-site redundancy feature in the Data Director.
12.1.5 Enabling CNLB External IPs in The Kafka Cluster
On CNLB-enabled OCCNE K8s cluster, when Kafka is deployed with external access, then Kafka brokers shall become externally accessible via external IPs exposed using ingress NADs. In this case, network and CNLB annotations should be configured in the Kafka brokers.
The section describes the procedure to extract the external IPs and ingress NADs from the configured and available CNLB network definitions and update the CNLB annotations in the Kafka brokers. This procedure is applicable to all the deployed worker groups.
OCNADD and NF sites are deployed in the CNLB-enabled clusters.
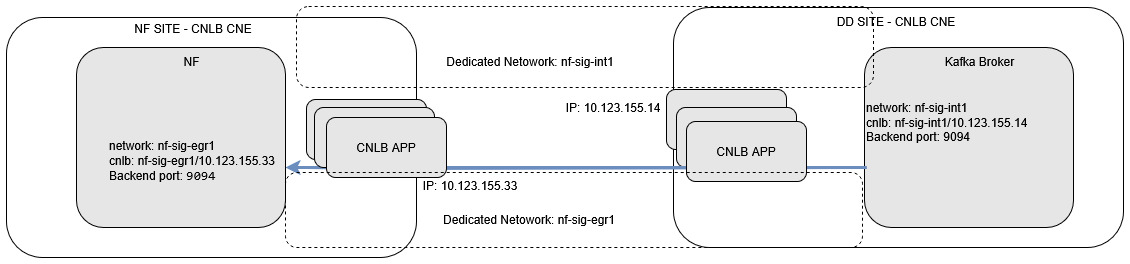
The NF can also be deployed in a non-CNLB-enabled cluster; however, the procedure remains the same on the Data Director.
Follow the procedure to enable Kafka external access on the CNLB-enabled Data Director OCCNE K8s cluster.
12.1.5.1 Enabling Kafka External Access on CNLB Enabled Cluster
- Extract the Network and NAD Information for the Ingress NAD
Caution:
The script
/var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.pyused in the following steps must be executed by a user with admin privileges or the root user.- Either obtain admin privileges (coordinate with the cluster
administrator if needed) before running the below step,
Or have the admin user run the command and share the output, which will be required in Step 2.
- Extract NADs. Run the script
/var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.pyin CNE to fetch the available ingress network information as below inputs:- Network Name: e.g.,
sigx - Segregation Type:
INT - Network Type:
SN - Port Name: Any valid value (e.g.,
http,8080)
python3 /var/occne/cluster/$OCCNE_CLUSTER/artifacts/cnlbGenAnnotations.pySample input prompts and values:
Network Names that application will use? Valid examples: oam or comma-separated values like oam,sig,sig1 Input: sig1,sig2,sig3,sig4,sig5,sig6 Application pod external communication? Valid choices: IE (Ingress/Egress), EGR (Egress Only), INT (Ingress Only) Input: INT Pod ingress network type? Valid choices: SI (Single Instance - DB tier only), MN (Multi-network ingress/egress), SN (Single Network) Input: SN Provide container ingress port name for backend from pod spec, and external ingress load balancing port: Valid example: http,80 Input: http,80Sample output:
==================================================================================================== NETWORK NAME oam AVAILABLE EXTERNAL IPS -------- ['10.148.197.139'] ==================================================================================================== NETWORK NAME sig3 AVAILABLE EXTERNAL IPS -------- ['10.148.197.158'] ==================================================================================================== NETWORK NAME sig4 AVAILABLE EXTERNAL IPS -------- ['10.148.197.161', '10.148.197.162', '10.148.197.163', '10.148.197.164'] ==================================================================================================== NETWORK NAME sig5 AVAILABLE EXTERNAL IPS -------- ['10.148.197.168', '10.148.197.169', '10.148.197.170'] ==================================================================================================== NETWORK NAME sig6 AVAILABLE EXTERNAL IPS -------- ['10.148.197.173', '10.148.197.174', '10.148.197.175', '10.148.197.176'] ==================================================================================================== AVAILABLE NETWORK ATTACHMENT NAMES: ['default/nf-oam-int1@nf-oam-int1', 'default/nf-oam-int2@nf-oam-int2', ..., 'default/nf-sig6-int4@nf-sig6-int4'] ==================================================================================================== POD NETWORK ATTACHMENT / CNLB ANNOTATION TO ADD TO POD SPEC: k8s.v1.cni.cncf.io/networks: default/nf-oam-int1@nf-oam-int1 oracle.com.cnc/cnlb: '[{"backendPortName": "http", "cnlbIp": "10.148.197.139", "cnlbPort": "80"}]' ==================================================================================================== - Network Name: e.g.,
- Either obtain admin privileges (coordinate with the cluster
administrator if needed) before running the below step,
- Update
ocnadd-custom-values_wg.yamlfor the Corresponding Worker Group- Select the available network names and external IPs.
- Copy the
cnlbIpandnetworksvalues and update theocnadd_custom_values_wg.yamlfile accordingly:
Example:cnlb.kafkabroker.enable: false =========> set it to true cnlb.kafkabroker.networks: "default/nf-sig-int7@nf-sig-int7" ===========> set the selected networks from the command output cnlb.kafkabroker.networks_extip: "nf-sig-int7/10.123.155.34" ===========> set the selected networks from the command outputThe example is provided below assuming 6 Kafka Brokers are deployed in the Kafka cluster. The user has selected the ingress
NAD nf-sig4-intXandnf-sig5-intXand corresponding available IPs from these networks. There should be one to one mapping between the network name and external IPs.cnlb.kafkabroker.enable: true cnlb.kafkabroker.networks: 'default/nf-sig4-int1@nf-sig4-int1', 'default/nf-sig4-int2@nf-sig4-int2', 'default/nf-sig4-int3@nf-sig4-int3', 'default/nf-sig4-int4@nf-sig4-int4', 'default/nf-sig5-int1@nf-sig5-int1', 'default/nf-sig5-int2@nf-sig5-int2' cnlb.kafkabroker.networks_extip: "nf-sig4-int1/10.148.197.161, nf-sig4-int2/10.148.197.162, nf-sig4-int3/10.148.197.163,nf-sig4-int4/10.148.197.164,nf-sig5-int1/10.148.197.168,nf-sig5-int2/10.148.197.169" - Update the following parameters to enable external access in Kafka, under
the Kafka section in
ocnadd_custom_values_wg.yaml:ocnaddkafka.ocnadd.kafkaBroker.externalAccess.enabled: false ======> set it to true ocnaddkafka.ocnadd.kafkaBroker.externalAccess.autoDiscovery: false ======> set it to true
- Upgrade the Corresponding Worker Group
Run the Helm upgrade using the Helm chart for the specific worker group:
helm upgrade <source-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<worker-group>.yaml --namespace <source-release-namespace> <target-release-helm-chart>Where:
<source-release-name>: Current release nameocnadd-custom-values-<worker-group>.yaml: Custom values file<source-release-namespace>: Namespace of the existing OCNADD release<target-release-helm-chart>: Path to the target Helm chart
Example:
helm upgrade ocnadd -f ocnadd-custom-values-wg.yaml --namespace ocnadd-deploy ocnadd_wg - Verify the Worker Group Upgrade
Check if the upgrade was successful:
- Monitor the pods until all return to
RUNNINGstate. - Ensure traffic stabilizes to pre-upgrade levels.
- Run the following command to view the upgrade status:
helm history <release-name> --namespace <namespace-name>Example: For worker-group, use:
helm history ocnadd --namespace ocnadd-deployExpected Output: The description should state
"upgrade complete". - Monitor the pods until all return to
12.2 Disabling Traffic Segregation in OCNADD
This section provides instructions on how to disable traffic segregation in the OCNADD (Oracle Cloud Native Application Development Director) environment.
12.2.1 Disabling Egress Traffic Segregation for Consumer Adapter Feeds
When egress traffic segregation is disabled in the consumer adapter feed, all external traffic will route through the default overlay network provided by Kubernetes, and traffic segregation will no longer be possible.
Follow these steps to disable CNLB support in the consumer adapter feeds:
ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file to disable CNLB in
the Consumer Adapter:
- Edit the
ocnadd-custom-values.yamlfile. - Update the parameter as indicated
below:
cnlb.consumeradapter.enabled:true ====> Change the value to"false" - Save the File.
Step 2: Upgrade the Management Namespace or the Default Namespace in the Data Director Deployment
Perform a Helm upgrade using the management group charts folder:
helm upgrade <management-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<mgmt-group>.yaml --namespace <source-release-namespace> <helm_chart>For example:
helm upgrade ocnadd-mgmt -f ocnadd-custom-values-mgmt-group.yaml --namespace ocnadd-deploy ocnadd_mgmtStep 3: Delete and Recreate the Consumer Adapter Feed
- Delete the existing consumer adapter feed.
- Recreate a new consumer adapter feed using the UI.
Step 4: Verify the Consumer Adapters are Respawned
Run the following command to verify that all the consumer adapters are respawned:
kubectl get po -n <ocnadd-workergroup-namespace>12.2.2 Disabling Ingress Traffic Segregation for the Ingress Adapter
When ingress traffic segregation is disabled in the ingress adapter feed, all incoming traffic will use the default overlay network provided by Kubernetes, and traffic segregation will no longer be possible.
Follow these steps to disable CNLB support in ingress adapter feeds:
Step 1: Update the ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file to disable CNLB in
the Ingress Adapter:
- Edit the
ocnadd-custom-values.yamlfile. - Update the parameter as indicated
below:
cnlb.ingressadapter.enabled:true====>Changethevalueto"false" - Save the File.
Step 2: Upgrade the Management Namespace or the Default Namespace in the Data Director Deployment
Perform a Helm upgrade using the management group charts folder:
helm upgrade <management-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<mgmt-group>.yaml --namespace <source-release-namespace> <helm_chart>For example:
helm upgrade ocnadd-mgmt -f ocnadd-custom-values-mgmt-group.yaml --namespace ocnadd-deploy ocnadd_mgmtStep 3: Delete and Recreate the Ingress Adapter Feed
- Delete the existing ingress adapter feed.
- Recreate a new ingress adapter feed using the UI.
Step 4: Verify the Ingress Adapters Are Respawned
Run the following command to verify that all the ingress adapters are respawned:
kubectl get po -n <ocnadd-workergroup-namespace>12.2.3 Disabling External IPs (Access) for the Redundancy Agent via CNLB
Caution:
The redundancy agent configuration on the CNLB-enabled CNE cluster will not function if the
cnlb.redundancyagent.enabled parameter
is set to false. External IPs will not be assigned, and the
corresponding annotations will not be set up in the redundancy agent deployment.
Follow these steps to disable external IPs (access) in the redundancy agent:
Step 1: Update the ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file
- Edit the
ocnadd-custom-values.yamlfile and update the following parameter:cnlb.redundancyagent.enabled:true ====>Changethevalueto"false" - Save the File.
Step 2: Continue to the Section Disable Two-Site Redundancy Support.
12.2.4 Disabling Kafka External Access in CNLB Enabled Cluster
- Update the following parameters in
ocnadd-custom-values_wg.yamlfor the corresponding worker group:cnlb.kafkabroker.enable: true =========> set it to false ocnaddkafka.ocnadd.kafkaBroker.externalAccess.enabled: true ======> set it to false ocnaddkafka.ocnadd.kafkaBroker.externalAccess.autoDiscovery: true ======> set it to false - Upgrade the corresponding worker group
Perform helm upgrade using helm charts folder created for the corresponding worker group:
helm upgrade <source-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<worker-group>.yaml --namespace <source-release-namespace> <target-release-helm-chart>Where,
<source-release-name>is the release name of the source release deploymentocnadd-custom-values-<worker-group>.yamlis the custom values file created for default-worker-group or the Worker Group in separate namespace<source-release-namespace>is the OCNADD namespace of the source release<target-release-helm-chart>is the location of the Helm chart of the target release
For example:helm upgrade ocnadd -f ocnadd-custom-values-wg.yaml --namespace ocnadd-deploy ocnadd_wg - Verify the Worker Group Upgrade
Check if the upgrade was successful:
- Monitor the pods until all return to
RUNNINGstate. - Ensure traffic stabilizes to pre-upgrade levels.
- Run the following command to view the upgrade status:
helm history <release_name> --namespace <namespace-name>Example: For worker-group, use:
helm history ocnadd --namespace ocnadd-deployExpected Output: The description should state
"upgrade complete". - Monitor the pods until all return to