14 Druid Cluster Integration with OCNADD
The Druid cluster has been proposed to be deployed as a centralized storage cluster that can be shared with multiple OCNADD sites. The customer shall deploy and manage the Druid cluster, and the Data Director shall provide the necessary integration with the Druid database to store and retrieve the xDRs.
The Data Director charts shall provide parameter support to integrate with the already installed Druid cluster. The Data Director proposes the following deployment model for the Druid cluster:
14.1 Druid Cluster Deployment
- A centralized Druid cluster either in a separate K8s cluster or deployed external to a K8s cluster (VM-based) only for extended storage. It could co-locate with any of the Data Director sites.
- The deep storage can be any of the supported deep storage types.
- A Druid cluster with version 33.0.0 or later should be used.
- DD sites will share this Druid cluster amongst them.
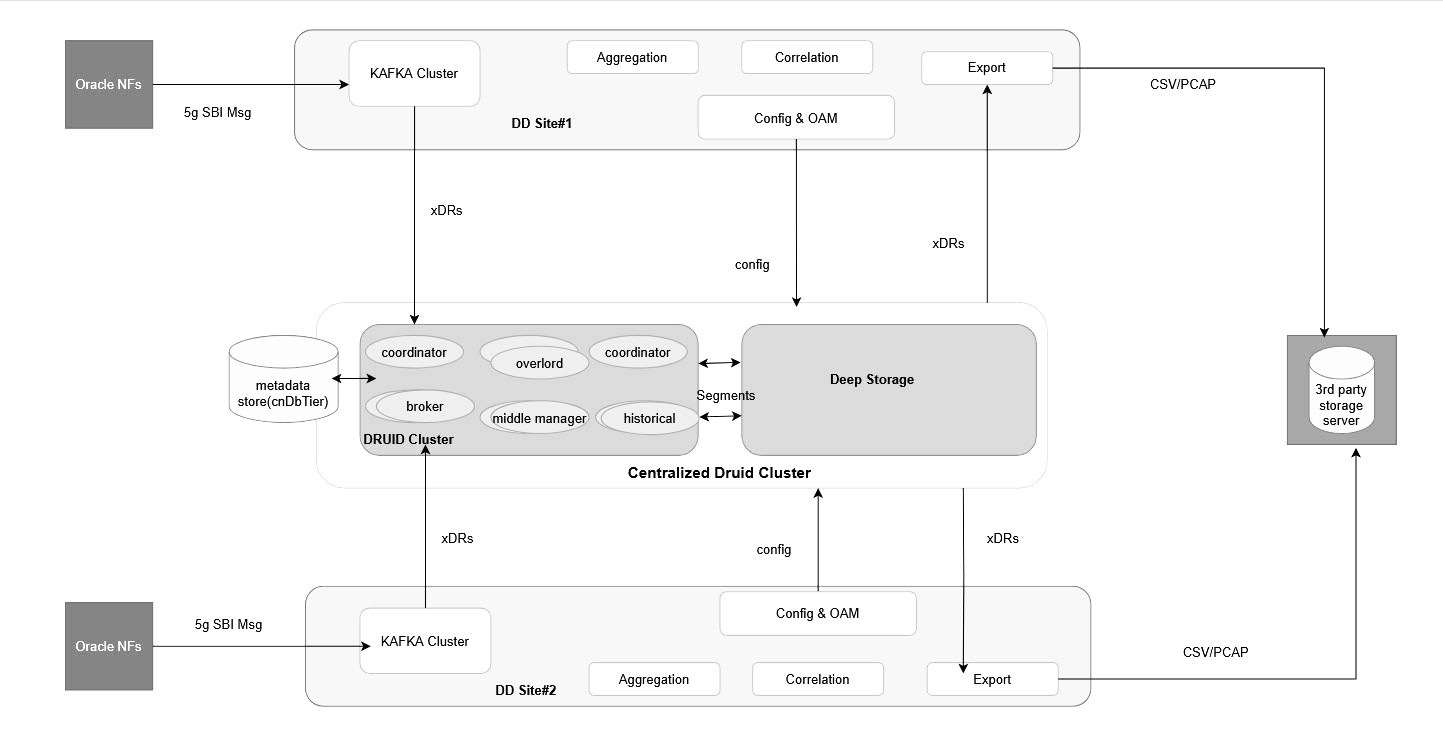
Druid also supports HDFS, S3, GCP, and Azure as deep storage. However, the Data Director has not verified the Druid integration with these options as deep storage. If the customer provides such deep storage options with the Druid cluster, then Data Director should be able to store and retrieve xDRs from the Druid database without any modifications in Data Director.
14.2 Druid Cluster Prerequisities for Integration with Data Director
Druid installation should support the following extensions, see Druid Extensions for more details.
| Extension Name | Required/Optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
| druid-kafka-indexing-service | Required |
The extension required for ingesting data from Kafka using indexing service. |
|
druid-multi-stage-query
|
Required |
Support for the multi-stage query architecture for Apache Druid and the multi-stage query task engine. |
| druid-hdfs-storage |
Required if HDFS is used as deep storage option. |
|
| druid-s3-extensions |
Required if AWS S3 is used as deep storage option. See S3 Deep Storage |
|
| druid-google-extensions |
Required if Google Cloud Storage is used as deep storage option. |
|
| druid-azure-extensions |
Required if Microsoft Azure is used as deep storage option. |
|
|
mysql-metadata-storage
|
Optional |
MySQL is used as metadata store. |
|
druid-basic-security
|
Optional | Support for Basic HTTP authentication and role-based access control. |
| druid-datasketches | Optional | Support for approximate counts and set operations with Apache Data sketches. |
| druid-stats | Optional | Statistics related module including variance and standard deviation. |
| druid-kubernetes-extensions | Optional | Druid cluster deployment on Kubernetes without Zookeeper. |
| druid-kubernetes-overlord-extensions | Optional | Support for launching tasks in Kubernetes without Middle Managers. |
| simple-client-sslcontext | Optional | It is required if the TLS communication with Druid Cluster is needed. |
- Druid Cluster must already be installed with deep storage.
- Druid Cluster must be available with sufficient deep storage to retain the xDRs for 30 days. For the xDR storage requirement, see the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Benchmarking Guide.
- The certificates for Druid, if TLS is enabled in the Druid cluster, should also be created; however, it must be noted that the same CA should be used for generating the Druid certificates as used for other Data Director services.
14.3 Druid Cluster Integration with OCNADD Site
The Druid cluster integration with the OCNADD site requires the following to be completed:
- Creation of the ocnadd user in Druid with relevant permissions
- Creation of secrets for Druid access
- Enabling Druid as extended storage in the OCNADD site
Create user for the Data Director in the Druid Cluster
Refer to the section "Druid User Management" in the Oracle Communications Network Analytics Suite Security Guide.
Create Secrets for the Data Director to access Druid Cluster
kubectl create secret generic -n <mgmt-group-namespace> <dd-druid-api-secret> \
--from-literal=username="<user_name>" --from-literal=password="<password>"Where,
- mgmt-group-namespace: the namespace where the management group is deployed
- dd-druid-api-secret: the secret name defined in custom values for
global.extendedStorage.druid.secret_name, for example,"ocnadd-druid-api-secret" - user_name: the Data Director username created in the Druid cluster (refer to the previous step)
- password: the password corresponding to the Data Director username created in the Druid cluster
kubectl create secret generic -n ocnadd-deploy ocnadd-druid-api-secret \
--from-literal=username="ocnadd" --from-literal=password="secret"
Create Secrets for the Druid Cluster to access Data Director
Create the secrets for all the available worker groups
kubectl create secret generic -n <mgmt-group-namespace> druid-sasl-<worker-group-namespace>-<ip-address-of-druid-server-without-dots> \
--from-literal=sasl-mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-256 \
--from-literal="sasl-jaas-config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"<user_name>\" password=\"<password>\";"
Where:
<mgmt-group-namespace>is the namespace where the management group is deployed (if the namespace has-, remove the hyphen in the secret name).<druid-sasl-<worker-group-namespace>-<ip-address-of-druid-server-without-dots>is the secret name generated using the worker group namespace and Druid server IP address.- Example:
druid-sasl-ocnadddeploy-10148212138, where the Druid server IP is10.148.212.138and the namespace isocnadd-deploy. - If the namespace has
-, remove the hyphen in the secret name.
- Example:
<user_name>: the external username on the Druid cluster to access the OCNADD Kafka cluster.<password>: the password for the user on the Druid cluster to access the OCNADD Kafka cluster.
ocnadd-deploy):kubectl create secret generic -n ocnadd-deploy druid-sasl-ocnadddeploy-10148212138 \
--from-literal=sasl-mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-256 \
--from-literal="sasl-jaas-config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"extuser1\" password=\"extuser1\";"
Example 2: Additional worker group
ocnadd-wg1 and management group namespace
ocnadd-deploy (if the namespace has -, remove
the hyphen in the secret
name):kubectl create secret generic -n ocnadd-deploy druid-sasl-ocnaddwg1-10148212138 \
--from-literal=sasl-mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-256 \
--from-literal="sasl-jaas-config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"extuser1\" password=\"extuser1\";"
Enable Druid as extended storage in OCNADD site
Follow the steps to enable Druid as the extended storage. The Druid cluster should already be installed and running properly.
- Update the custom values for the Data Director management group deployment.
Modify ocnadd-custom-values-mgmt-group.yaml file as mentioned below:
global: ######################### # EXTENDED XDR STORAGE-# ######################### extendedStorage: druid: enabled: false ===========> This should be set to "true " druidTlsEnabled: true ===========> This should be set to "true " if TLS is enabled in Druid cluster namespace: ocnadd-druid ===========> This should be set to the namespace where druid cluster is deployed service_ip: 1.1.1.1 ===========> This should be set to the Druid Router Service LB IP address, else leave it as is service_port: 8080 ===========> This should be set to the Druid Router Service port secret_name: "ocnadd-druid-api-secret" ===========> This should be set to the name of the secret created for the Druid services - Upgrade the OCNADD management group.
Perform helm upgrade using helm charts folder created for the management group:
helm upgrade <mgmt-group-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<mgmt-group>.yaml --namespace <mgmt-group-namespace> <mgmt-helm-chart>Where,
<mgmt-group-release-name>is the release name of the management group deploymentocnadd-custom-values-<mgmt-group>.yamlis the custom values file created for mgmt group<mgmt-group-namespace>is the OCNADD management group namespace of the release<mgmt-group-helm-chart>is the location of the Helm chart of the mgmt group
For example:helm upgrade ocnadd-mgmt -f ocnadd-custom-values-mgmt.yaml --namespace ocnadd-deploy ocnadd_mgmt - Verify that after the upgrade, the management group config and export services
have restarted.
kubectl get po -n <mgmt-namespace>It should show that the config and export pods are in the RUNNING state, and the pods that have respawned after the upgrade have the latest age (in seconds).
- Upgrade the OCNADD Worker Group(s)
- Update the custom values file for the worker group.
Modify ocnadd-custom-values-<wg-group>.yaml file as mentioned below:
global: ######################### # EXTENDED XDR STORAGE # ######################### extendedStorage: druid: enabled: false # ==========> This should be set to "true" druidTlsEnabled: true # ==========> This should be set to "true" if TLS is enabled in Druid cluster namespace: ocnadd-druid # ==========> This should be set to the namespace where Druid cluster is deployed service_ip: 1.1.1.1 # ==========> This should be set to the Druid Router Service LB IP address, else leave it as is service_port: 8080 # ==========> This should be set to the Druid Router Service port secret_name: "ocnadd-druid-api-secret" # =====> This should be set to the name of the secret created for the Druid services - Perform a Helm upgrade using the Helm charts folder created for the
corresponding worker
group:
helm upgrade <worker-group-release-name> -f ocnadd-custom-values-<wg-group>.yaml --namespace <worker-group-namespace> <worker-group-helm-chart>Where:
<worker-group-release-name>is the release name of the worker group deploymentocnadd-custom-values-<worker-group>.yamlis the custom values file created for the management group<worker-group-namespace>is the OCNADD worker group namespace of the release<worker-group-helm-chart>is the location of the Helm chart of the worker group
For example:helm upgrade ocnadd-wg1 -f ocnadd-custom-values-wg1.yaml --namespace ocnadd-wg1 ocnadd_wg1
- Update the custom values file for the worker group.
- Verify the upgrade of the worker group is successful
- Check the status of the upgrade, monitor the pods to return to the RUNNING state, and wait for the traffic rate to stabilize to the same rate as before the upgrade.
- Run the following command to check the upgrade
status:
helm history <release_name> --namespace <namespace-name>For example:helm history ocnadd-wg1 --namespace ocnadd-wg1Sample output:
The description should be "
upgrade complete".
- Continue with Correlation and Export/Trace configuration on the OCNADD.