MSRP and Middlebox Traversal Using the CEMA Extension and Session-ID
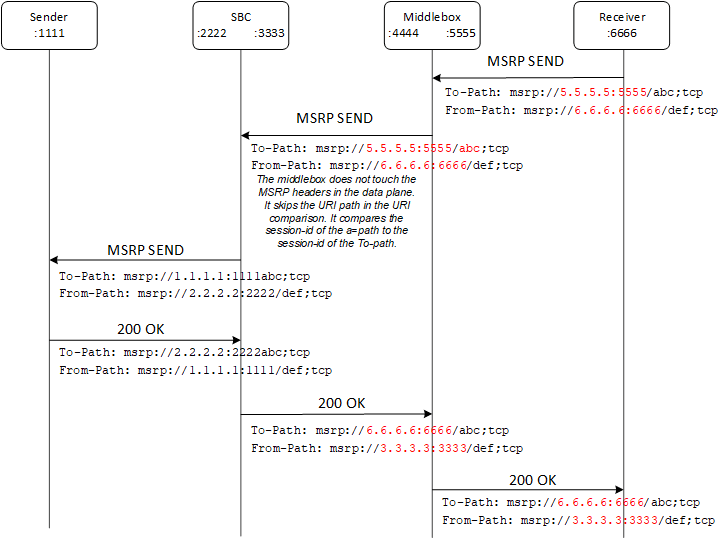
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (Enterprise SBC) requires the Connection Establishment for Media Anchoring (CEMA) extension (RFC6714) and the session-id matching mechanism to allow the Enterprise SBC to exchange Message Session Relay Protocol (MSRP) messages through middleboxes that do not act as MSRP Back to Back User Agents (B2BUA). When such a middlebox passes the MSRP messages through without updating the SDP a=path attribute, the Enterprise SBC cannot establish a TCP connection through the middlebox. The CEMA mechanism makes the connection possible. In a scenario where the middlebox does update the SDP a=path attribute, the MSRP messages will not pass validation and will be dropped. The Session-id matching mechanism prevents that situation. The Enterprise SBC supports this functionality only on Virtual Machines.
With the CEMA extension enabled, the Enterprise SBC detects the presence of a middlebox that anchors the media and does not update the SDP a=path attribute by comparing the SDP c and m lines to the SDP a=path attribute. When the CEMA-enabled Enterprise SBC plays the active role in establishing the TCP connection it establishes the connection to the endpoint identified by the c and m lines instead of the a=path.
Figure 22-2 Signaling Flow with a Middlebox and CEMA Enabled
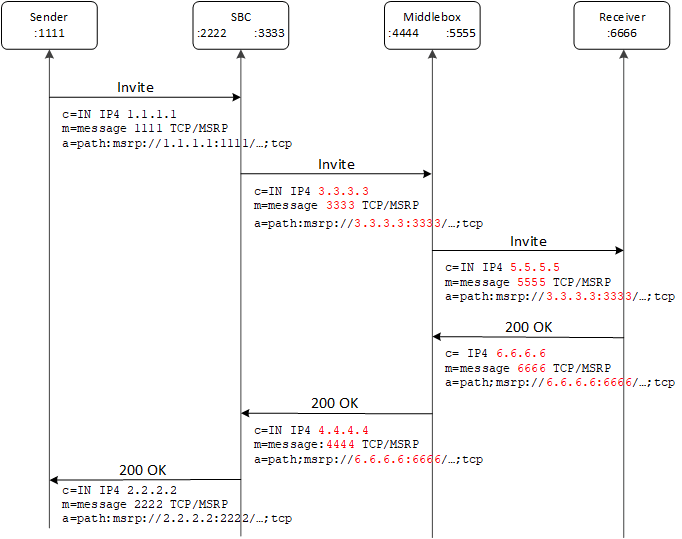
Figure 22-3 MSRP Flow with a Middlebox and CEMA Enabled
- Disabled (default)-When playing the active role, the Enterprise SBC establishes the TCP connection to the IP address and port number specified in the SDP a=path attribute of the peer. If the SDP a=path attribute contains a DNS name, the Enterprise SBC attempts to use the c line. If the c line also contains a DNS name, the Enterprise SBC rejects the session.
- Enabled-When the Enterprise SBC detects the presence of a middlebox, it tries to negotiate the CEMA support by including the a=msrp-cema-support media attribute. When playing the active role, the Enterprise SBC establishes a TCP connection to the IP address and port number indicated in the peer's SDP c and m lines rather than the a=path media attribute. If you enable msrp-cema-support, you must disable msrp-sessmatch.
Note:
The Enterprise SBC does not perform DNS name resolution for either the SDP a=path or the c and m lines.To-path Authority Validation
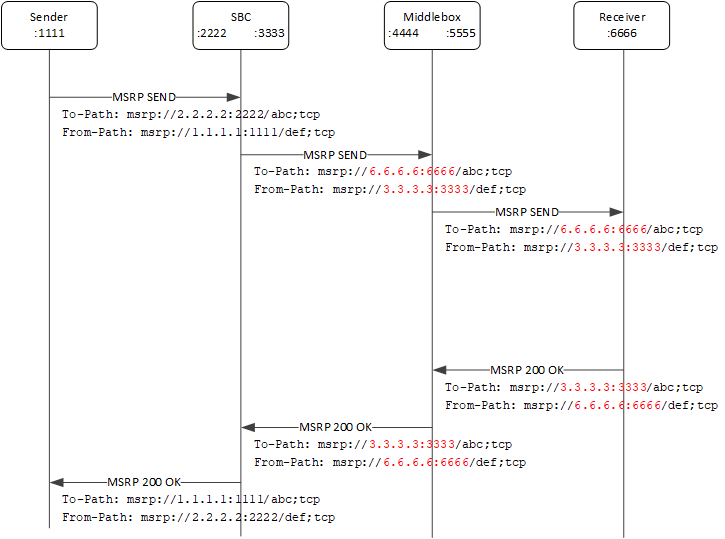
The presence of middleboxes that anchor the media and update the SDP a=path attribute to match the updated SDP c and m lines cannot be detected in the signaling plane. An MSRP B2BUA that is not enabled for CEMA correctly sets up TCP connections to the middlebox because the SDP a=path attribute points to the middlebox. Because the middleboxes do not accordingly update the MSRP message To-Path headers, MSRP messages passing through such a middlebox cannot validate because the authority part of the To-Path header does not match the authority part of the SDP a=path attribute. In such scenarios the validation of the MSRP URI is based only on the session-id part of the MSRP URI, the MSRP scheme, and transport (Session-Id matching).
- Disabled (default)-The MSRP URI comparison between the SDP a=path attribute and the To-Path header in the MSRP messages received from a realm includes the MSRP URI scheme, authority IP address, port number, session-id, and transport. If the comparison is unsuccessful and the sender requires a report, the Enterprise SBC returns an MSRP 481 error response to the sender.
- Enabled-The MSRP URI comparison between the SDP a=path attribute and the To-Path header in the MSRP messages received from a realm includes only the MSRP URI scheme, session-id, and transport. If the comparison is unsuccessful and the sender requires a response, the Enterprise SBC sends an MSRP 481 error response to the sender. If you enable msrp-sessmatch, you must disable msrp-cema-support.
Figure 22-4 Signaling Flow with Session Matching Enabled
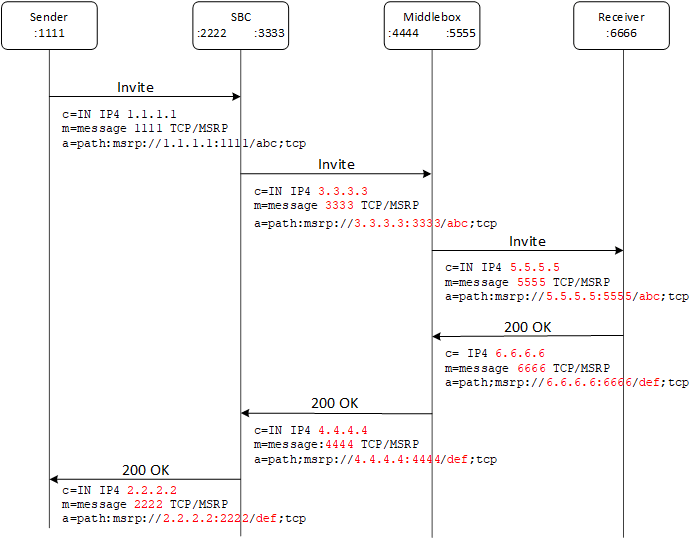
Figure 22-5 MSRP Flow with Session Matching Enabled