The ESBC as an ALG for HTTP and HTTPS
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC) functions as an HTTP Application Layer Gateway (ALG) for HTTP/HTTPS traffic that originates on Avaya endpoints and terminates on the Avaya Session Manager (ASM) as follows:
- The E-SBC receives HTTP requests from Avaya endpoints on a user-configurable IP address and port.
- The E-SBC forwards the requests to a user-configurable destination, which is the IP address and port of the ASM.
- The ASM sends the response
to the HTTP request to the
E-SBC.
The E-SBC parses the HTTP response and searches for getHomeServerResponse and getHomeCapabilitiesResponse messages. If the getHomeServerResponse message is found, the E-SBC replaces any text between the <PpmServer> or <SipServer> tags with the IP address of the public interface on which the HTTP-ALG is configured. If the getHomeCapabilitesResponse is found, the E-SBC replaces any text contained between the <ServiceURI> tags with the IP address of the public interface on which the HTTP-ALG is configured.
- After the E-SBC processes the response, it forwards the response to the originating Avaya endpoint. The following illustration shows how the E-SBC sends and receives HTTP requests and responses to the Avaya Session Manager.
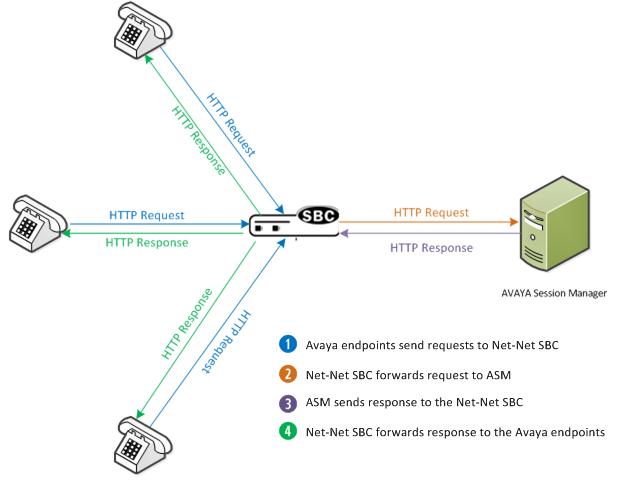
The following is the call flow that occurs as the HTTP/HTTPS requests and responses are passed between the Avaya endpoints, the E-SBC, and the ASM.
