About the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller and SIP
This section describes the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller’s support of SIP. It provides the basic information you need to understand before you configure the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller for SIP signaling.
Types of SIP Devices
There are four types of SIP devices:
- SIP user agent (UA) is an endpoint in SIP end-to-end communication. A UA is a user agent client (UAC) when it initiates a request and waits to receive a response. A UA is a user agent server (UAS) when it receives a request and generates a response. A given UA will be a UAC or a UAS depending on whether it is initiating the request or receiving the request.
- A SIP proxy (or proxy server) is an intermediary entity that acts as both a server and a client for the purpose of making requests on behalf of other clients. A proxy server’s primary role is routing. Its job is to ensure that a request is sent to another entity closer to the targeted user. A proxy interprets, and if necessary, rewrites specific parts of a request message before forwarding it.
- A SIP redirect server is a UAS that generates redirect responses to requests it receives, directing the client to contact an alternate set of targets. Unlike a proxy which forwards the request to the alternate set of targets, the redirect response tells the UAC to directly contact the alternate targets.
- A SIP registrar is a server that accepts REGISTER requests and places the information it receives in those requests into the location service for the domain it handles. Proxies and redirect servers can use the information from the location service to determine the location of the targeted user.
A redirect server and a registrar are each a special type of UA because they act as the UAS for the requests they process.
Basic Service Models
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller operates as a back-to-back user agent (B2BUA) within the following two basic service models:
- peering
- hosted IP services
About B2BUA
A B2BUA is a logical entity that receives a request and processes it as a user agent server (UAS). In order to determine how the request should be answered, it acts as a user agent client (UAC) and generates requests. It maintains dialog state and must participate in all requests sent on the dialogs it has established.
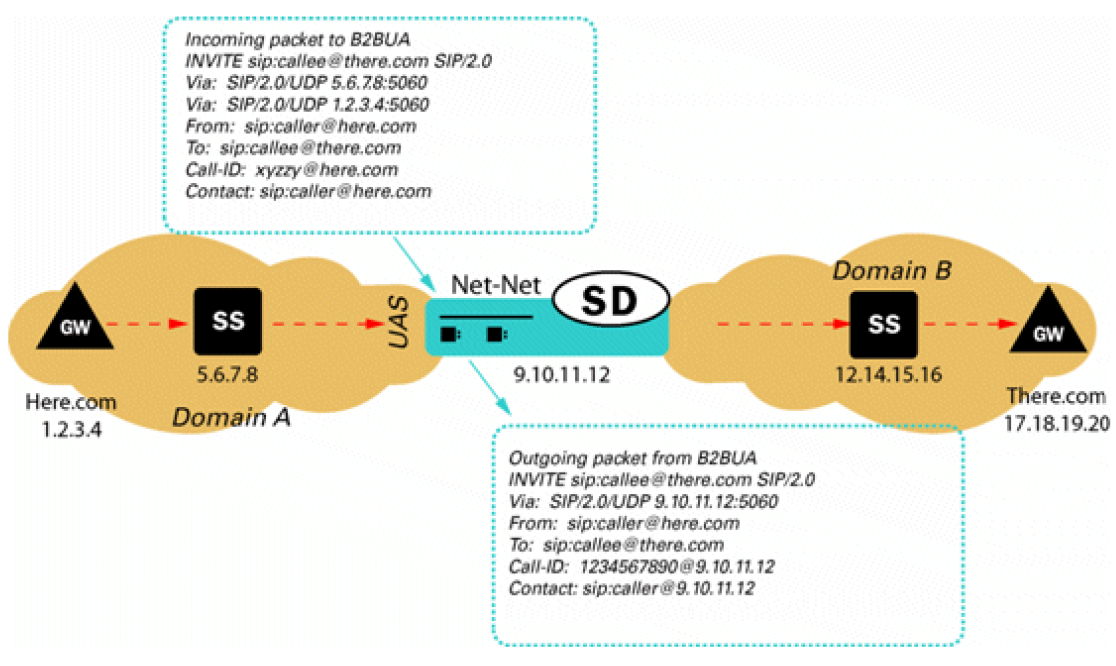
SIP B2BUA Peering
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller operates as a SIP B2BUA. It terminates SIP sessions and re-originates them as new sessions as they are routed through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. For each session, it establishes NAPT translations and re-writes SDP to allow all session related media to be routed through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. It generates new call IDs and modifies SIP headers to prevent any protected SIP addresses and route information from being transmitted to external peers. The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller supports multiple SIP interfaces that are associated with a set of media ports, thus appearing as multiple virtual SIP gateways.
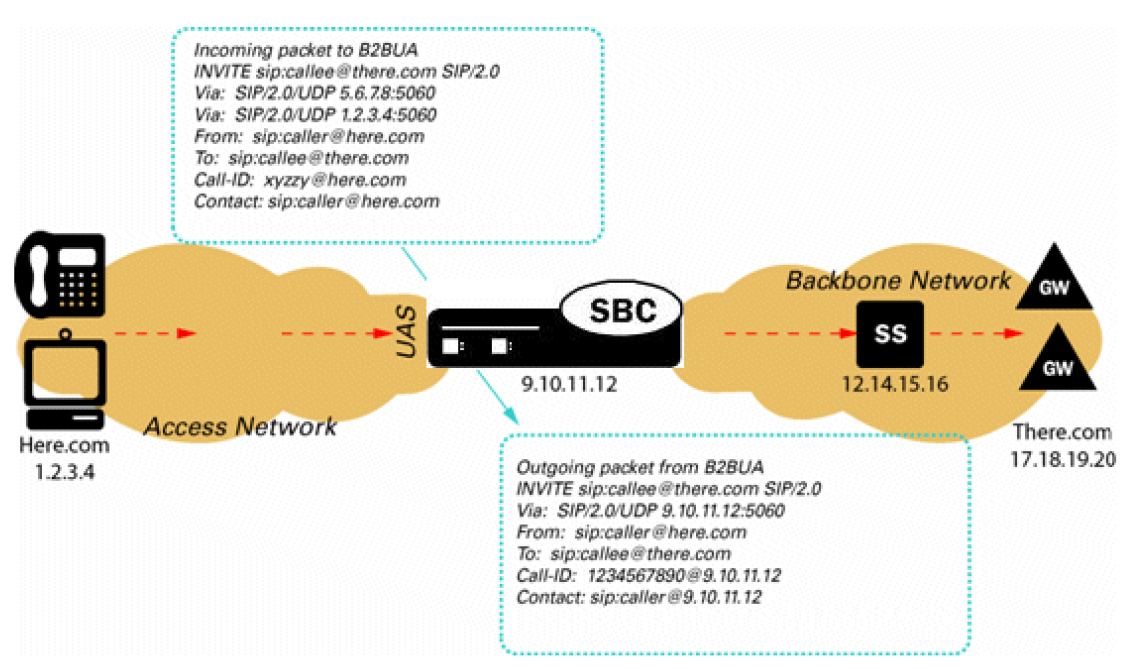
B2BUA Hosted IP Services
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller acts as an outbound proxy for SIP endpoints and performs the operations required to allow UAs behind NATs to initiate and terminate SIP sessions (Hosted NAT Traversal).
The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller caches registration requests from SIP endpoints and forwards them to the appropriate softswitch or registrar in its backbone network. All subsequent signaling between the endpoint and the backbone network is through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. Also, all calling features such as caller ID, call waiting, three-way calling, and call transfer are all supported transparently through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller.
SIP B2BUA and L3 L5 NAT
For each SIP session, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller establishes NAPT translations and re-writes SDP to route all session related media through the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller. These actions make the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller look like a SIP gateway. Also, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller support of multiple SIP interfaces associated with different network interfaces makes it appear as multiple virtual SIP gateways.
This functionality enables the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to deliver VoIP services to multiple end users, across a VPN backbone.
About SIP Interfaces
The SIP interface defines the transport addresses (IP address and port) upon which the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller receives and sends SIP messages. You can define a SIP interface for each network or realm to which the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is connected. SIP interfaces support both UDP and TCP transport, as well as multiple SIP ports (transport addresses). The SIP interface’s SIP NAT function lets Hosted NAT Traversal (HNT) be used in any realm.
SIP INVITE Message Processing
When the session agent element on the softswitch side of the message flow (ingress session agent) has the gateway contact parameter configured as an option, the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller looks for the URI parameter (as defined by the gateway contact parameter) in the Request-URI and decodes the gateway address.
Example
The following example shows a SIP INVITE message from a softswitch to a Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller.
INVITE sip:05030205555@ss-side-ext-address;gateway=encoded-gw-address
From: "Anonymous"<sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=xxxx
To: <sip:05030205555@ss-side-ext-address;user=phone>The following example shows a SIP INVITE message from a Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to a gateway.
INVITE sip:05030205555@gw-ip-address SIP/2.0
From: "Anonymous"<sip:anonymous@anonymous.invalid>;tag=SDxxxx-xxxx
To: <sip:05030205555@ hostpart;user=phone>The Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller converts the hostpart in the To header except in the following scenarios:
- when the original hostpart value received is an Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)
- when the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller is configured not to NAT the To headers.
Acme Packet recommends configuring the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller to NAT the To headers to ensure the security of protected addresses. Otherwise, the outgoing hostpart is set to the SIP NAT’s external proxy address for the SIP NAT’s external realm.