Dynamic Filters
The SIP Monitor and Trace feature provides a time-saving feature of adding filters dynamically, and turning the filters ON and OFF as required. The filtering process performs on a dynamic basis dependant on the filters you specify.
Dynamic Filter Commands
You can use the ACLI to initiate the following dynamic filtering commands:
- capture start—starts the filters you specify in the filter syntax
- capture stop—stops the filters you specify in the filter syntax
Note:
Initiating these commands does not change the values set in the ACLI-configured filters on the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller (ESBC). The ESBC uses the dynamic filters until you initiate a stop command.The syntax for the dynamic filter commands are:
capture start <main filter> <subfilter(s)>
capture stop <main filter> <subfilter(s)>
You must enter a
<main
filter> and a
<subfilter(s)>
when initiating the “capture start” and capture stop commands.
The following table identifies the values you can use for each attribute in the command syntax.
| Syntax Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
| <main filter> | global - monitors and captures all
realm <realm name> - monitors and captures everything matching realm session-agent <session-agent name> - monitors and captures everything matching session agent. int-ev <short-session | local-rejection> - monitors and captures everything matching a short- session and/or local-rejection. |
| [<subfilter(s)>] | * - monitors and captures all
sessions.
user <Phone Number or User Part URI> - monitors and captures everything that matches this phone number or user part. addr-prefix <IP address or IP address and netmask> - monitors and captures everything that matches this address or address prefix. |
Examples
The following table provides examples for using the dynamic filter commands.
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| capture start global *
capture start global user USER1 capture start global addr-prefix 1.1.1.1 capture start global addr-prefix 1.1.1.1/24 capture start session-agent 172.1.1.1 addr-prefix 10.10.10.10 capture start int-ev local-rejection capture start int-ev short session |
Captures all session data.
Captures all session data for USER1. Captures all session data for IP address 1.1.1.1. Captures all session data for IP address 1.1.1.1 using netmask of 24. Captures session data for SA 172.1.1.1 at IP address 10.10.10.10. Captures session data for interesting events that occur that are of type local-rejection. Captures session data for interesting events that occur that are of type short-session. |
The following flow chart shows the dynamic filter process.
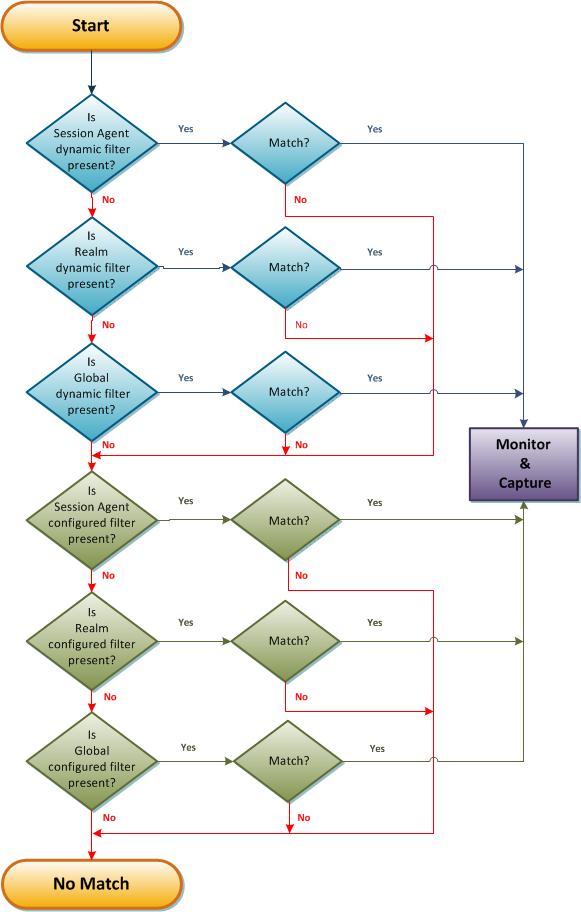
Note:
Dynamic filters are only removed after a reboot/switchover of the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller.Issuing another dynamic command may or may not affect previous dynamic commands that were already initiated. If you issue a dynamic command with a <main filter> object, and then issue another command with the same <main filter> object, the new command tasks precedence. If you issue a dynamic command with a different <main filter> object, then the Oracle® Enterprise Session Border Controller uses both <main filter> commands to monitor traffic.
ORACLE# capture start realm1 user 123ORACLE# capture start realm2 user 123To stop dynamic filter commands, you can initiate the capture stop <main filter> command. For example:
ORACLE# capture stop realm1 user 123To stop configured filters, you must manually remove them from the ACLI configuration.
Clearing all Dynamic Filters
You can clear all dynamic filters using the following command:
- reset monitoring dynamic-commands—clears all dynamic filters previously initiated
The ESBC maintains a record of all dynamically initiated active filters. When you initiate this reset command, the ESBC searches through all of the filters and resets all the dynamic filters for each main filter (realm, session-agent, session-group, interesting event).
Clearing Event Monitoring Records
You can clear all records stored in the event monitoring in-memory database using the following command:
- reset monitoring records—clears all event monitoring records from the in-memory database.
Use the following procedure to clear all event monitoring records.
To clear event monitoring records: