RBT TrFO Flows
This section describes the TrFO flows when initiated by ringback tone. The flow descriptions use the OCSR as an example of an upstream or downstream service capable of HMR.
P-Acme-TrFO Call Flow
Data call identification is done via HMRs on both the ESBC and the Oracle Communications Session Router (SR).
The need for TrFO results from HMRs execution (custom logic) and translates into a private header called P-Acme-TrFO, which is included in called party 200 OK or 18x messages ingress using HMR.
The ESBC triggers TrFO feature whenever P-Acme-TrFO header is present, provided that:
- RBT triggers transcoding, based on the called party codec the ESBC selects during call establishment.
- The negotiated codec on the called party side is included within the calling party side codecs supported in the original offer and after ingress the ESBC executes the codec-policy.
TrFO for Data Calls
The need for TrFO results from HMRs execution (custom logic) and translates into a private header called P-Acme-TrFO (included in called party 200 OK ingress to ESBC - using HMR).
The ESBC triggers the TrFO feature whenever the P-Acme-TrFO header is present, provided that:
- RBT induces transcoding due to called party codec selection by the ESBC during call establishment.
- Negotiated codec on the called party side is included within the calling party side codecs supported in the original offer (after ingress codec-policy execution).
The ESBC triggers the feature when the header is inserted by HMR or when it is present in the response. The HMR logic that triggers TrFO for data calls is as follows:
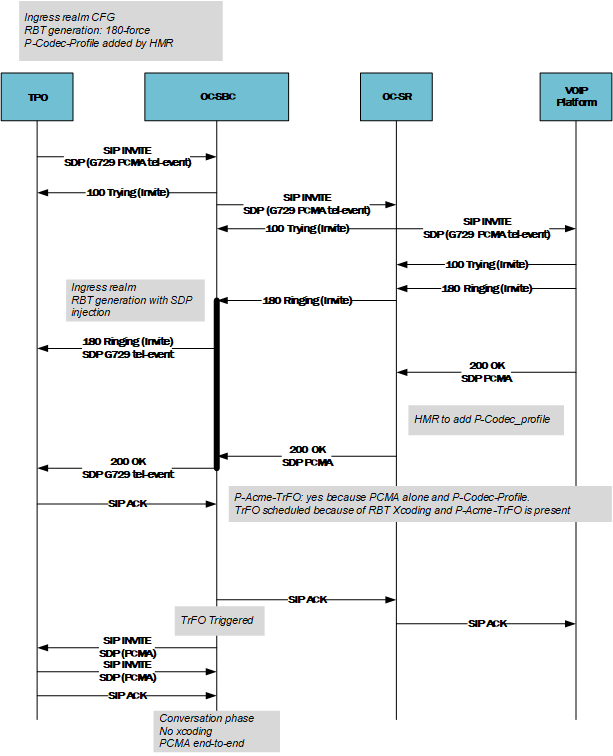
- For an Inbound call Flow:
- A known trunk that supports the data call has an Ingress HMR that adds the P-Codec-Profile Header.
- This HMR adds P-Codec-Profile: from the ESBC to the SR.
- An egress HMR on the SR adds the applicable flag based on the reception of P-Codec-Profile to the INVITE Via Header.
- Topology hiding removes the P-Codec-Profile header.
- On the reception of an answer from the distant UA, an Ingress HMR on the SR checks for the presence of the flag in the VIA, and for PCMA in the SDP.
- If the previous condition is met, the SR sends the P-Acme-Trfo Header to the ESBC, which then triggers TrFO.
- If the 4 condition is not satisfied, the SR does nothing.
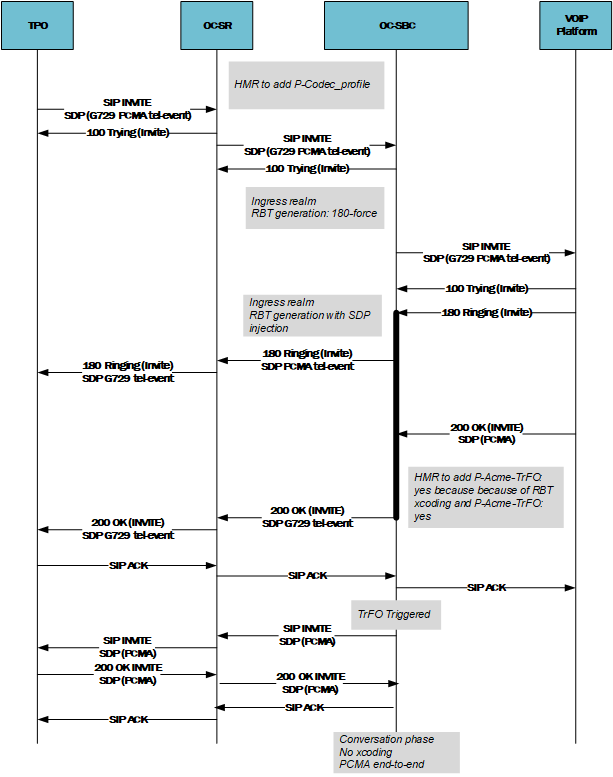
- For an Outbound Call Flow :
- A known trunk that supports the data call has an Ingress HMR that adds the P-Codec-Profile Header.
- This HMR adds P-Codec-Profile: m2m from the SR to the ESBC.
- An egress HMR on the ESBC adds the flag m2m based on the reception of P-Codec-Profile:m2m in the INVITE Via Header.
- Topology hiding removes the P-Codec-Profile header.
- On the reception of an answer from the distant UA, an Ingress HMR on the ESBC checks for the presence of the m2m flag in the VIA, and for PCMA in the SDP.
- If the previous condition is met, the ESBC adds the P-Acme-Trfo Header to the Ingress Message of the ESBC, which then triggers TrFO.
- If condition 5 is not satisfied, the ESBC does nothing.
This is an example and other logic can be used the same way to get to the same result.