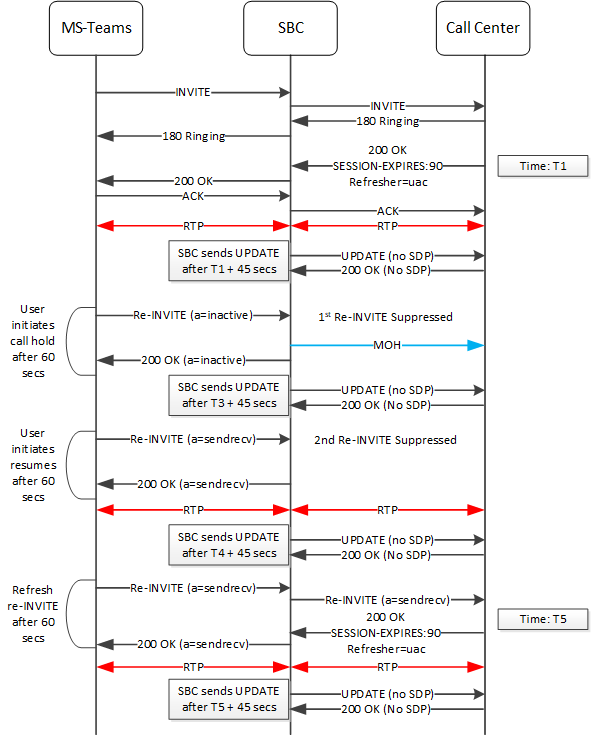
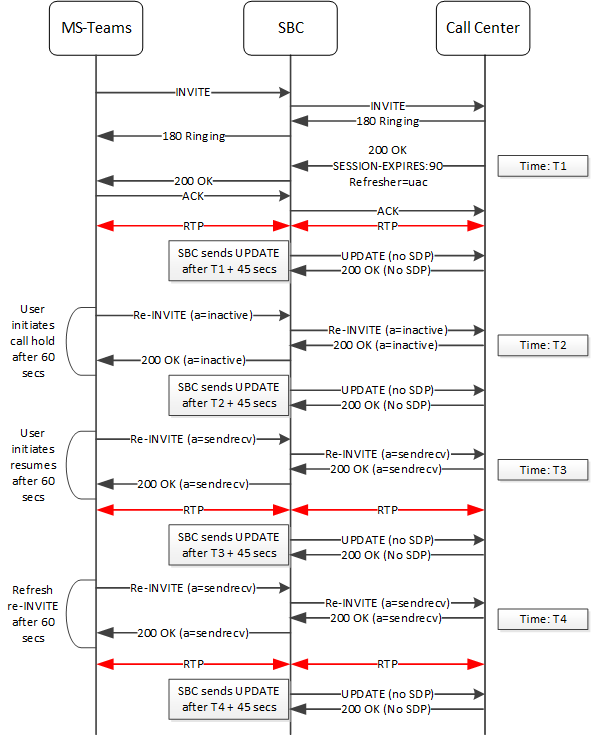
Interaction Between Session Timers and re-INVITE Suppression
When configured, the ESBC performs session timer and re-INVITE suppression operations simultaneously.
This re-INVITE suppression excludes refresh re-INVITEs. Within the context of standard SIP operation, neither an endstation nor the ESBC may necessarily be aware of a session ending, for example, without a BYE. SIP operation may use session timer mechanisms within refresh re-INVITEs and UPDATEs to convey expiration or minimal session timing information, which can confirm that a session is still active.
The ESBC distinguishes between a re-INVITE that, for example, triggers a call hold and one that performs a refresh re-INVITE triggered by the presence of the Session-Expires parameter. The Session-Expires parameter conveys the lifetime of the session. The Min-SE parameter conveys the minimum allowed value for the session timer. The ESBC forwards the latter to support session timing mechanisms unless you have also configured the session-timer-profile on the applicable sip-interface. This profile allows the ESBC to end the session by itself.
The call flow below presents the ESBC performing the functions of the session-timer-profile below. This profile has its force-reinvite parameter set to its default, enabled.
The call flow below presents the ESBC performing the functions of the session-timer-profile and the the suppress-hold-resume-reinvite on the ingress realm-config below.