IMS Access Border Functions
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller is deployed as the access point between the core IMS network and UEs to deliver the functions defined in the TISPAN architecture as the P-CSCF, and A-BGF. These two functions can not be separated. The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller performs the following functions as the Access Oracle Communications Session Border Controller:
P-CSCF Functions
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller performs the following functions in the role of P-CSCF:
- Forwards SIP REGISTER messages and maintains a cached mapping of the user info and the UE's Address of Record (AoR), including the far-end NAT address in the case of hosted NAT traversal (HNT).
- Forwards SIP messages to a S-CSCF based on service route discovery procedures.
- Performs local emergency session handling—Local routing policy is used by the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller to identify emergency sessions and provide unique routing (e.g. can route to a dedicated S-CSCF function for emergency session handling).
- Operates as a UA (B2BUA) for generating independent SIP transactions for security purposes and handling of abnormal conditions.
- Offers current session timers which are used to monitor for media faults and abandoned calls.
- Generation of CDRs—The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller generates real-time accounting records via RADIUS.
- Authorization of bearer resources and QoS management—With integrated BGF capabilities, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller allocates bearer resources (NAPT flows) and applies QoS policies (including packet marking) based on local policies and/or policies acquired via interaction with the A-RACF (PDF).
- Interaction with the A-RACF (PDF) for session-based policy enforcement and admission control—The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller PDF interface options include COPS and SOAP/XML.
- Traffic Policing—Traffic is policed at the session and media/transport layer. At the signaling layer, the
Oracle Communications Session Border Controller polices at a number of levels including:
- Capacity—Total number of concurrent calls to/from each realm
- Session set-up rate—Maximum rate of call attempts to/from each signaling element
- Signaling message rate—Each endpoint’s signaling message rate is monitored and policed
- Signaling bandwidth—each endpoint’s signaling bandwidth is policed individually
A-BGF Functions
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller performs the following IMS BGF functions:
- Opening and closing gates/packet filtering—The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller opens and closes gates (media pinholes) on a session-by-session basis. Packet filtering rules include full source and destination IP address and port number.
- Per-session DiffServ or ToS marking—Media flows destined for the IMS core network can be explicitly marked using ToS or DiffServ. Media packets can be marked by VPN, by codec (voice, video) or by E.164 phone number prefix.
- NAPT-PT and topology hiding—The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller provides NAPT for all media flows associated with a session on a per session-basis. Double NATing, NATing both source and destination sides, is utilized to fully hide topology in each direction for RTP and RTCP. Local IP addresses and port resources are dynamically allocated from steering pools provisioned on the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller.
- Hosted NAT traversal—The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller supports HNT function that allows media flow traversal through the CPE firewall/NAT without upgrading the CPE equipment. The system interacts with the endpoints to dynamically establish and maintain bindings in the CPE firewall/NAT that allow the signaled communications to pass through. The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller's registration management and media relay functions make CPE-based NATs transparent to the service delivery elements.
- Traffic Policing—Traffic is policed at the session and media/transport layer. At the signaling layer, the
Oracle Communications Session Border Controller polices at a number of levels including:
- Policing of Media (e.g. RTP & RTCP) traffic on a per-flow basis—CBR policing is applied to each flow based on negotiated offered and negotiated media codecs.
Resource and Admission Control (RACS) Functions
The figure below illustrates the mapping of Oracle Communications Session Border Controller functions to the RACS functional model. In this model, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller incorporates the Application Function (in the case of IMS this is the P-CSCF function), the SPDF (Service Policy Decision Function) and the Core Border Gateway function.
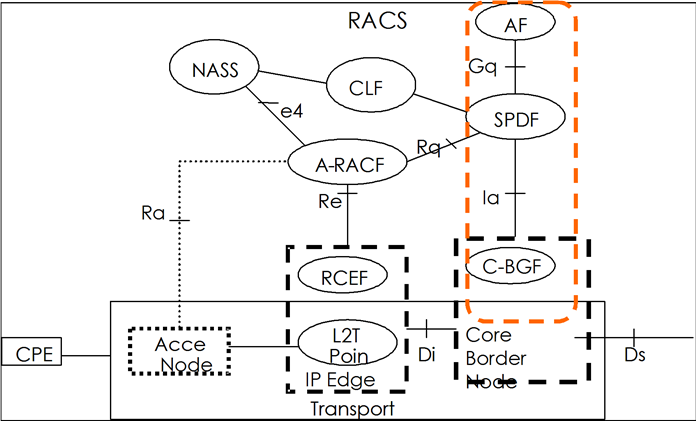
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller, acting as the SPDF, interfaces with the PDF (A-RACF policy decision function) for resource authorization and admission control on a call-by-call basis. COPS is the supported PDF interface.