IMS-AKA Change Client Port
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller is now in compliance with 3GPP TS 33.203, Access Security for IP-Based Services. Previous releases did not comply with requirements specified in Section 7.4, Authenticated re-registration, which reads in part:
Every registration that includes a user authentication attempt produces new security associations. If the authentication is successful, then these new security associations shall replace the previous ones. This clause describes how the UE and P CSCF handle this replacement and which SAs to apply to which message.
When security associations are changed in an authenticated re-registration then the protected server ports at the UE (port_us) and the P-CSCF (port_ps) shall remain unchanged, while the protected client ports at the UE (port_uc) and the P-CSCF (port_pc) shall change.
If the UE has an already active pair of security associations, then it shall use this to protect the REGISTER message. If the S-CSCF is notified by the P-CSCF that the REGISTER message from the UE was integrity-protected it may decide not to authenticate the user by means of the AKA protocol. However, the UE may send unprotected REGISTER messages at any time. In this case, the S-CSCF shall authenticate the user by means of the AKA protocol. In particular, if the UE considers the SAs no longer active at the P-CSCF, e.g., after receiving no response to several protected messages, then the UE should send an unprotected REGISTER message.”
Prior releases failed to change the protected client ports after a successful re-registration.
Protected Ports
Within IMS networks, the P-CSCF provides the network access point and serves as the outbound proxy server for user equipment -- smart phones, tablets, and similar devices. The UE must connect to the P-CSCF prior to registration and initiation of SIP sessions. Connection to the P-CSCF, which can be in the user's home network, or in a visited network if the UE is roaming, is accomplished using Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) P-CSCF discovery procedures.
After successful discovery, the P-CSCF and UE negotiate IPSec security associations (SAs) which are used to establish four protected (authenticated and encrypted using Encapsulating Security Payload protocol) ports between the UE and the P-CSCF.
The four protected ports are shown in the following illustration:
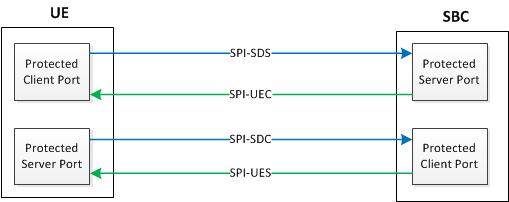
As required by Section 7.4 of 3GPP TS 33.203, the protected client ports, one on the UE and the other on the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller, must be changed after each successful re-registration.
To fulfill this requirement, this release adds a new attribute to the existing ims-aka-profile configuration object. This attribute (end-protected-client-port) works in conjunction with start-protected-client-port (protected-client-port in previous releases) to enable the identification of a pool of protected client ports, which will be used for re-registration scenarios where the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller is required to change the client port.
The Oracle Communications Session Border Controller creates new protected client ports, one on the UE and the other on the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller, after every re-registration. Old protected client ports, along with their associated SAs, are maintained for 30 seconds after re-registration to ensure correct handling or any pending responses to previously transmitted messages.
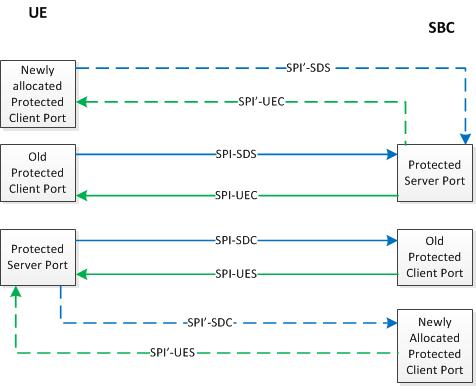
After successful re-registration, the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller updates the registration cache with updated port information and checkpoint with the HA peer, if present.
IMS-AKA Change Client Port Configuration
An IMS-AKA profile establishes the client and server ports to be protected, and it defines lists of encryption and authentication algorithms the profile supports. You can configure multiple IMS-AKA profiles, which are uniquely identified by their names.
You apply an IMS-AKA profile to a SIP port configuration using the name.
To configure an IMS-AKA profile:
Sample IMS-AKA Configuration
The following formatted extract from show running-config ACLI output shows a sample IMS-AKA profile configuration.
ims-aka-profile
name TS33.203
start-protected-client-port 4060
end-protected-client-port 4064
protected-server-port 4070
encr-alg-list aes-cbc des-ede3-cbc null
auth-alg-list hmac-sha-1-96 hmac-md5-96
last-modified-by admin@172.30.11.18
last-modified-date 2013-06-15 14:58:08