Understanding Data
In the data model, any object that stores associated attribute data is called a point. A point's attribute data (called facts) depend on the object's categorization. For example, if an electric meter has an electric meter point type, the meter's facts might include service status, returned readings, and manufacturer. When a meter is in service, it is related to other objects in the model, such as service point location, premise, the transformer that supplies the premise, the feeder that supplies the transformer, and the substation that supplies the feeder. All consumption data is based on information coming from the meter and is aggregated upward to the related parent points.
On this page:
Parent-Child Relationships
Oracle Utilities Analytics Insights allows data points to have a hierarchical association known as a parent-child relationship. For example, a transformer can have a relationship with the meters that it supplies. Therefore, the transformer is the parent, and its associated meters are considered children.
Sibling Relationships
Two points that share the same parent are considered siblings. For example, an electric meter and a gas meter at the same premise and transformers on the same feeder are siblings. Parent-child and sibling associations are configurable.
Understanding Facts
Any attribute stored for a point is stored as a fact. Facts are grouped into three types:
- Standing / Non Time Series: Data that does not change often. Normally, this data has a start date, and an end date that will be in the future when a change occurs, such as for example, tenant move out or meter exchange. Examples of a standing/ non time series are Relation, Attribute, Numeric Attributes.
- Time Series: Consistent recurring time-based data such as daily register read or an event. Metric, Event, List, Segment, Text, Count are examples of a time series.
- Interval (IV): Time series where intervals are shorter than daily, such as for example, 15- minute interval reads.
Facts are auto-generated in the metadata layer as they are loaded and defined in the relational fact table.
Note: Data Types should not be confused with Point Types. Point Types are the categories for objects in the data model.
| Fact Data Type | Grouping of Data Types | Fact Example |
|---|---|---|
| Metric | Time series | kWh |
| Event | Time series | Register Gap |
| List | Time series | No Gas Con |
| Segment | Time series | Read Collection |
| Text | Time series | kWh Peak Date |
| Relation | Standing non-time series | Status |
| Attribute | Standing non-time series | Address |
| Numeric Attribute | Standing non-time series | Amps Rating |
| Interval Metric | Interval | kWh |
| Interval Text | Interval | Voltage Quality |
| Count | Time series | Power Out Count |
Understanding Point Types
The following table describes the default point types.
|
Point Type |
Description |
Parent Points |
|---|---|---|
|
Account |
Accounts are utility customer accounts in the database. |
Bill Cycle, Zip Code |
|
Bill Cycle |
Bill cycles are the billing cycles that correspond to the day of the month when the bill is prepared. |
Not Applicable |
|
Electric Meter |
Electric meters are all of the electric meters in the database. |
Account, Bill Cycle, Line Transformer, Premise, Service Point, Zip Code |
|
Feeder |
Contains the feeders that are associated with meters. |
Substation |
|
Gas Meter |
Gas meters in the system. |
Account, Bill Cycle, Premise, Service Point, Zip Code |
|
Line Transformer |
Contains the transformers that provide service connections for electric meters. |
Feeder |
|
Load Profile Class |
Contains load profile classes that may be associated with a meter. |
Not Applicable |
|
Premise |
The address associated with a meter. |
Account |
|
Rate |
The billing rate charged for consumption of electricity, gas, etc. The rate may vary depending on customer type, time of use, etc. |
Not Applicable |
|
Rate Class |
Rate class (or customer type) that applies to an account (e.g., residential, commercial, etc.). |
Not Applicable |
|
Route |
Contains meter reading routes. |
Not Applicable |
|
Service Order Agreement |
Contains service order agreements for accounts. |
Not Applicable |
|
Service Point |
Service connection points. |
Premise |
|
Utility or Supplier |
Contains utilities or suppliers that provide service. |
Not Applicable |
|
Zip Code |
Contains zip codes in the service area where meters are located. |
Not Applicable |
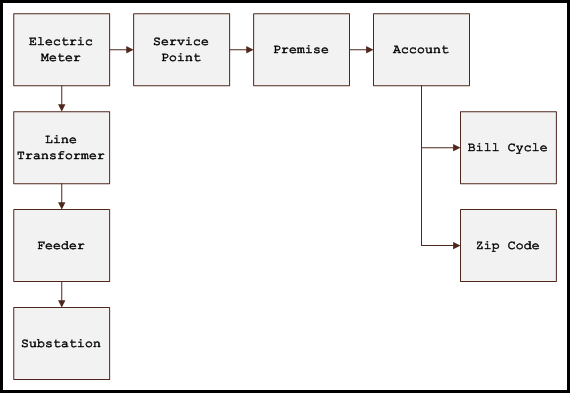
For example, data aggregates from an electric meter on two paths:
- Meter to line transformer, line transformer to feeder, then feeder to substation.
- Meter to service point, service point to premise, premise to account, and then account to either bill cycle or zip code.
Consumption Data Type
Consumption data is represented according to how it originated. Data origin can refer to both data sources and calculations. All types of consumption data are displayed at the meter level; consumption data aggregated to other points (for example, transformers or rate classes) is represented as two consolidated data types: Metered and Estimated.
The table below lists the data types.
Note: The following sections on Oracle Utilities Analytics Insights data types are based on the default configuration. Your data types may be configured differently by your project manager based on your available data and requirements.
Metered Data Types
| Metered Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Loaded |
Consumption data received in engineering units and not transformed by Oracle Utilities Analytics Insights. No multiplier or other derivation has been applied. |
| Calculated | Calculated data is derived as the difference between the current and previous day's midnight read. |
| Aggregated |
Aggregated data is the summation of consumption data from a shorter time-basis to a longer time-basis. For example, a 15-minute interval to hourly. Note: This aggregated data does not mean aggregating to a parent point. For example, this would not refer to aggregating from meters to transformers.
|
| Interpolated |
Interpolated data is a fixed amount of consumption allocated to a normalized time basis such as calculated from register reads that are not received at the anticipated time. |
Estimated Data Types
| Estimated Data Type Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Estimated |
Estimated data is calculated based on a meter's historic Usage Factor and Load Profile. |
| Estimated (Agg) | Estimated (Agg) data is estimated data aggregated to another time-basis. For example, hourly Estimated data is aggregated to daily Estimated (Agg). |