Grid Edge DERMS Gateway Architecture
The Grid Edge DERMS Gateway can be deployed on premise or in the cloud:
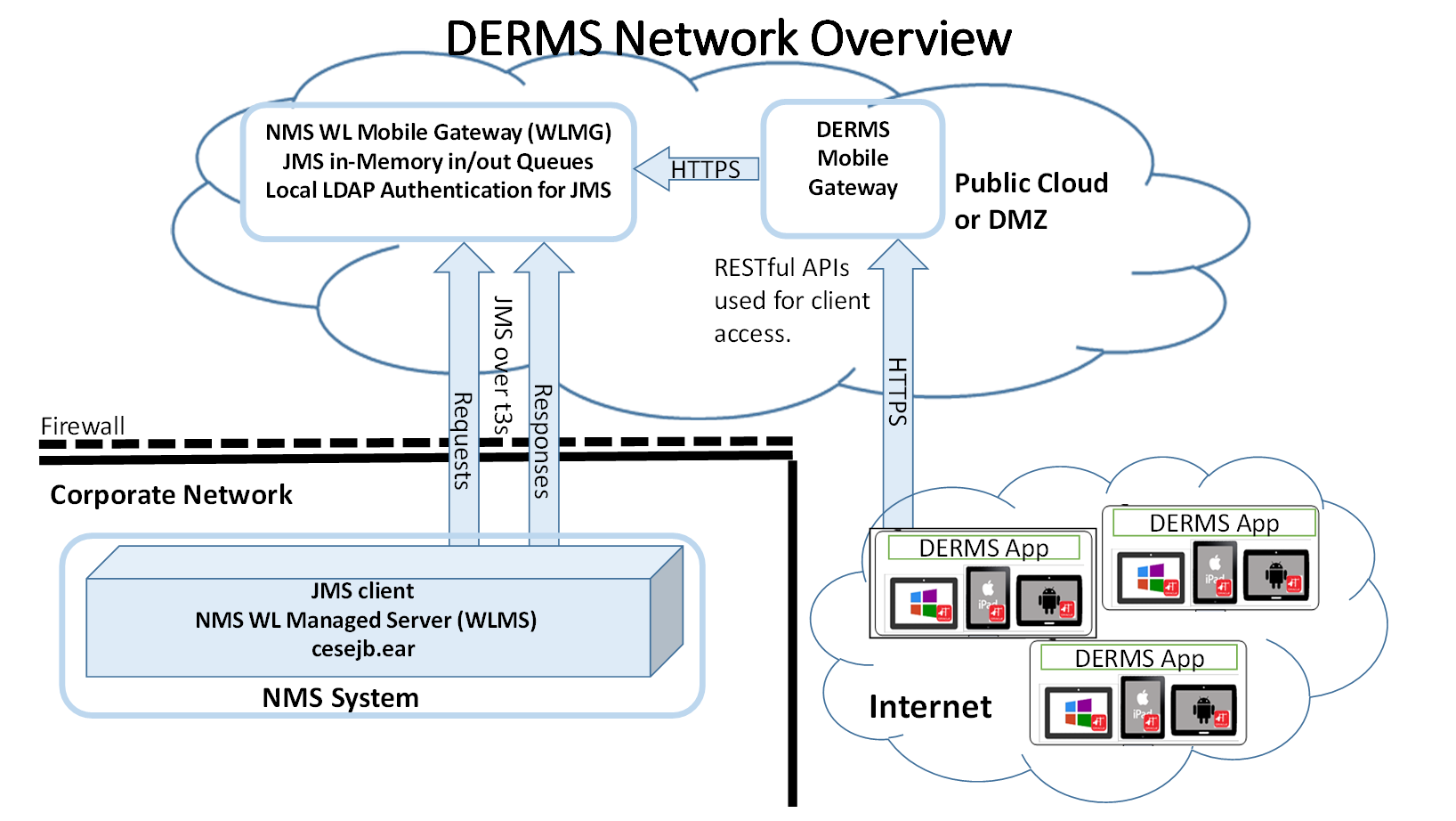
This architecture addresses many security concerns limiting the access from the Internet to the corporate network.
How Grid Edge DERMS app devices connect to the NMS instance:
1. The DERMS App client device connects to a dedicated WebLogic Managed Server, called the NMS WebLogic DERMS Gateway (WLDG), using HTTPS to make RESTful Web Service requests.
2. The WLDG places DERMS App client requests on the JMS in-memory “requests” queue.
3. The primary NMS WebLogic Managed Server (WLMS) connects to the JMS “requests” queue on the WLDG as a JMS client using the WebLogic t3s protocol and pulls requests off the “requests” queue and processes the requests via the normal channel from WLMS to NMS Services.
4. The WLMS then places responses to valid Grid Edge DERMS app client requests on the parallel JMS in-memory “responses” queue – in a similar fashion to how the “requests” queue is handled.
5. The WLDG replays to the HTTPS RESTful Web Services request with the WLMS responses.
6. The Grid Edge DERMS app client device takes the HTTPS response and processes it on the device.
Notes:
• It is recommended to have an Oracle HTTP server or other reverse proxy server to further isolate Grid Edge DERMS from the internet.
• There should be a firewall rule that allows only access to the https port from the internet (all other ports should be blocked).