Authorization Model
The following data model describes the security authorization model of Oracle Utilities Cloud Service.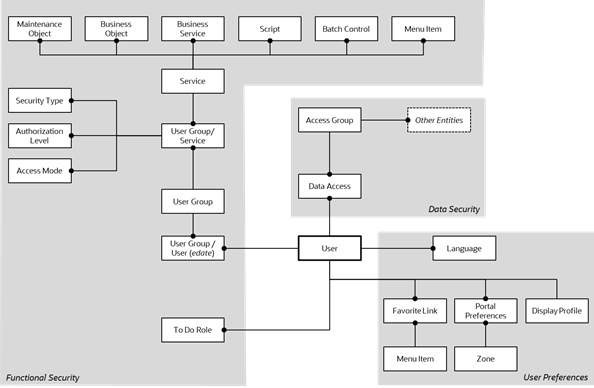

Users
A record of each user is stored in the User entity, which defines the attributes of the user including identifier, name, Portal preferences, Favorites, Display Profile (such as format of dates and so on), and Language used for screens and messages, and other attributes. Users are attached to To Do Roles that allow the user to process any error records for background processes. For example, if a particular background process produces an error, it is possible to define the users that will process and address the error.
Note: To maintain consistency, it is recommended to maintain user records in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access Management (IAM) and perform a synchronization from that service rather than altering users in the User entity.
It is now possible to configure a default template user on the F1-OIMUSR algorithm definition.
User Groups
Users are also attached to User Groups. This relationship is effective dated, which means that the date period it is active across is also defined. This can be useful for temporary employees such as contractors or for people who change roles regularly.
User Groups are mechanisms for grouping users, usually around job roles. Each user group is then attached to the Application Services that the group is authorized to access. The Application Services are the functions within Oracle Utilities Cloud Service. Loosely, these correspond to each of the screens accessible in Oracle Utilities Cloud Service. In this attachment, the Access Mode is also defined with standards being Add, Modify, Read, and Delete. With this combination, it is possible to define what functions and what access can those functions for user groups (and hence users).
Additionally, it is possible to define the authorization level of the User Group to that function. For example, you may find that a certain group of users can only approve payments of a certain level unless authorization is obtained. The Authorization Level is associated with a Security Type that defines the rules for the Application Service.
Note: To use security types, the implementation must develop server side or client-side user exits to implement code necessary to implement the security level.
Services can be attached to individual menus, batch controls, maintenance objects, business objects, business services, and scripts to denote the service to be used to link user groups to access these objects. In this case, business object security overrides and maintenance object security. The same applies to business services security overriding that Application Service it is based on.
The Oracle Utilities Cloud Service allows you to limit user access to specific data entities to prevent users without the appropriate rights from accessing specific data. By granting a user access rights to an account, you are granting the user access rights to the account’s bills, payments, adjustments, orders, and so on.
Access Groups
Access Groups define a group of accounts that have the same type of security restrictions. Data Access Roles define a group of users that have the same access rights (in relation to access to entities that include access roles). When you grant a data access role with rights to an access group, you are giving all users in the data access role rights to all entities in the access group.
The following summarizes the data relationships involved with data security:
• Entities reference a single access group. An access group may be linked to an unlimited number of relevant entities.
• A data access role has one or more users associated with it. A user may belong to many data access roles.
• A data access role may be linked to one or more access groups. An access group may be linked to one or more data access roles.