1.6.1 Online Web Application
This topic describes about the online web application.
Authentication and authorization to requests to access the Online Web Application (appshell) are controlled using the below industry standard approaches:
- Standard LDAP Directory authentication
- SSO with OAM
- SSO with other External SSO Agents
- SAML with the Oracle Banking Cash Management application acting as the service provider
- SAML SSO Integration
JWT (JSON Web Tokens)
In addition to the authentication, the Oracle Banking Cash Management online web application uses JWT (JSON Web Tokens) to maintain the state for authenticated users.
JSON Web Tokens are an open, industry standard RFC 7519 method for representing claims securely between two parties. JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is used as the payload of a JSON Web Signature (JWS) structure or as the plain text of a JSON Web Encryption (JWE) structure, enabling the claims to be digitally signed.
- No Session to Manage (stateless): The JWT is a self-contained token which has authentication information, expire time information, and other user defined claims digitally signed.
- Portable: A single token can be used with multiple backend.
- No Cookies Required, So It's Very Mobile Friendly
- Good Performance: It reduces the network round trip time.
- Decoupled/Decentralized: The token can be generated anywhere. Authentication can happen on the resource server, or easily separated into its own server.
The policies for JWT are as follows:
- Token Store: To increase the security and better usability, every authentication/refresh request is secured by random unique key. The generated token and the secure key are persisted in the table, so that during the horizontal scaling of the servers, any API gateway instance can serve for the request.
- Cipher strength: Platform security module hashes the JWT footer with HS512 algorithm.
- Refresh Token: Users are allowed to get the new token any time before expiring the existing token.
- Claims: The JWT Claims Set represents a JSON object whose
members are the claims conveyed by the JWT. Platform security module validates
below claims during the process.
Table 1-2 JWT Claims set
Claim Name Description Mandatory Type Iss Issuer Yes Registered Sub Subject Yes Registered Aud Audience No Registered Exp Expiration Time Yes Registered Nbf Not Before No Registered Iat Issued At Yes Registered Jti JWT Id Yes Registered Tid Tenant Id Yes Private - Token Expiry: Platform security module invalidates the token, if the client submits after the Expiration time.
- Logout: While user calls the logout operation, platform security module clears the issued token and deletes the record from the table as well. The old token no longer will be used for any purpose.
The various security flows for the online web application are depicted are as follows:
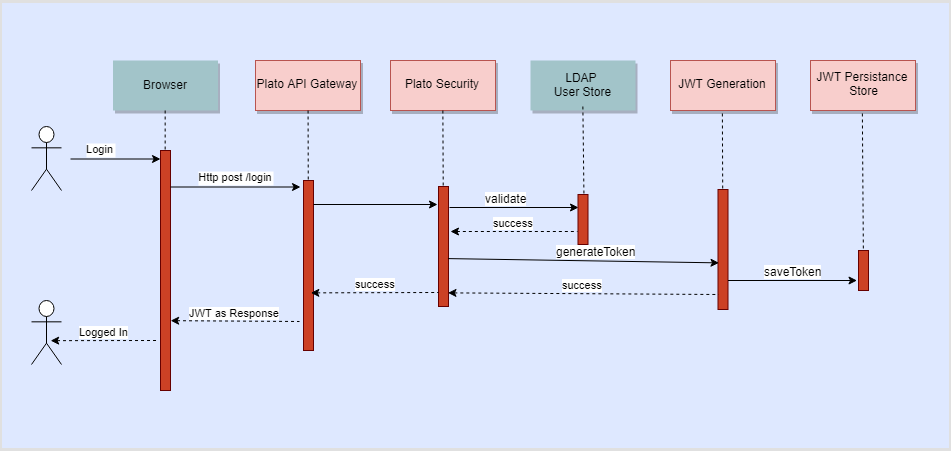
LDAP Authentication
- The user is presented the standard login page for the Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture products
- The user enters a user id and password. The credentials are validated against a standard LDAP store.
- If successful, the API Gateway generates a JWT token (Utilizing Oracle’s Security Developer Toolkit part of Oracle’s Platform Security Services), persists it in the Database and returns the same.
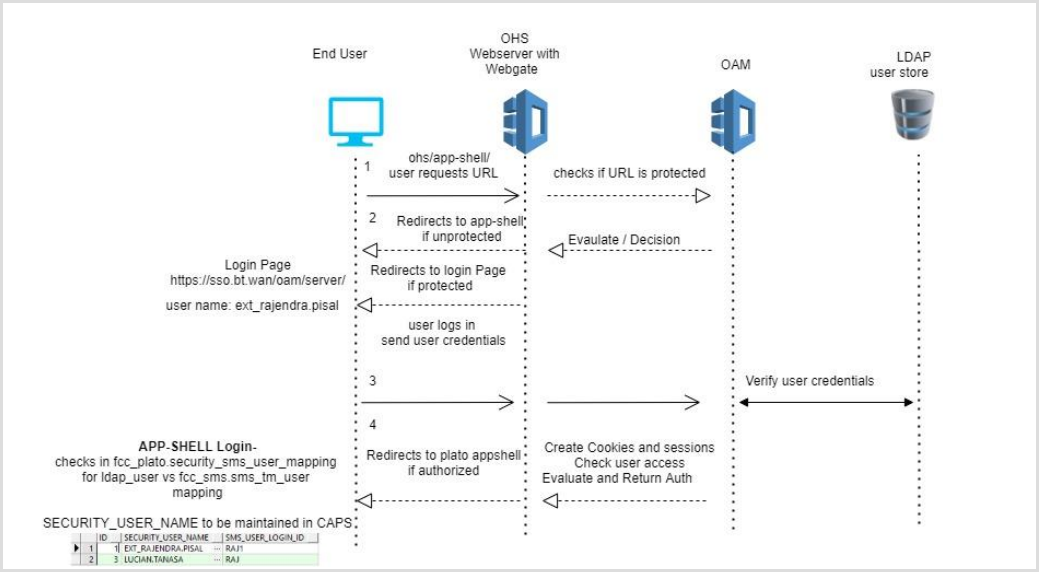
OAM Based SSO
- The online UI is protected on OAM.
- Client requests protected resource. OAM presents SSO Login screen
- Client enters a user id and password. In case of success, OAM sets the corresponding user profile details in the security context
- The request is routed to the Gateway which extracts the profile details from the security context
- The API Gateway creates a JWT token (Utilizing Oracle’s Security Developer Toolkit part of Oracle’s Platform Security Services), persists it in the Database and returns the same.
- The UI layer uses this token to maintain state and conduct subsequent invocations
Product configuration
The following parameters need to be set to enable a successful integration with OAM as SSO in Oracle Banking Cash Management products.
| ID | KEY | VALUE |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | USER_HEADER_ATTRIBUTE_KEY | userId |
| 2 | USER_HEADER_ATTRIBUTE_REQUIRED | Y |
| 3 | IS_SSO_CONFIGURED | true |
| 4 | USER_MAPPING_REQUIRED | true |
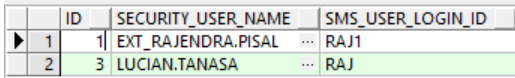
Figure 1-3 PLATO.SECURITY_SMS_USER_MAPPING table
SAML Authentication
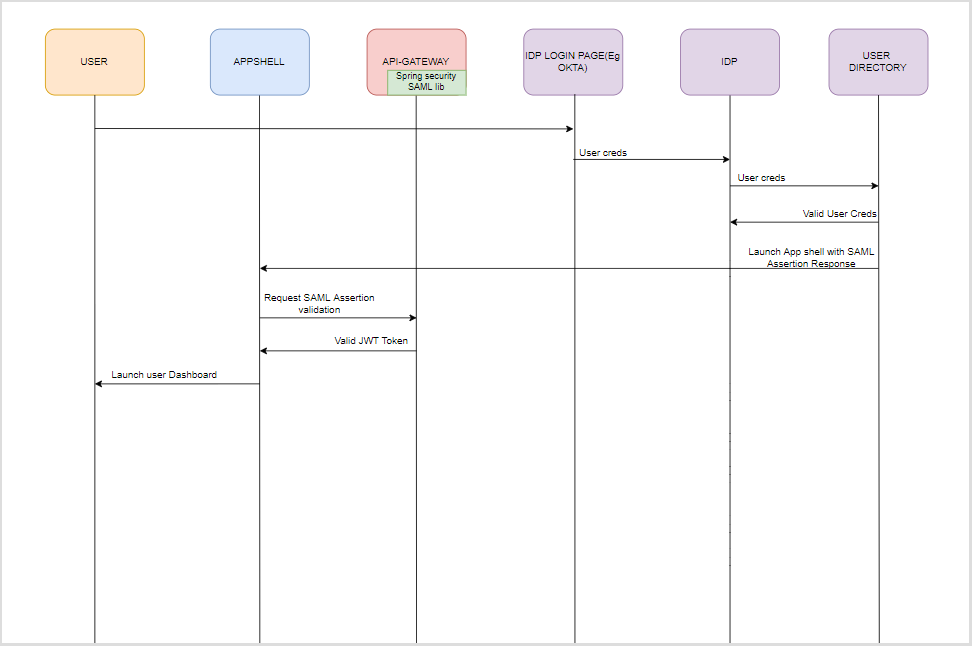
IDP Initiated SAML Authentication
Figure 1-4 IDP Initiated SAML Authentication
- The Identity Provider is external to the Oracle Banking Cash Management (e.g. OKTA) with the Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture products acting as the Service Provider.
- Client requests protected resource from Oracle Banking Cash Management. The Idp presents a configured login screen to the user.
- Client enters a user id and password. In case of success, the Idp sets the corresponding user profile details in the security context.
- The request is routed to the Gateway which extracts the profile details by decoding the SAML response.
- The API Gateway creates a JWT token (Utilizing Oracle’s Security Developer Toolkit part of Oracle’s Platform Security Services), persists it in the Database and returns the same.
- It is possible to configure an external service to do the SAML Verification instead of the API Gateway using the EXTERNAL_SSO_VALIDATION_URL parameter in the SECURITY_CONFIG table in PLATO-SECURITY schema.
SP Initiated SAML Authentication
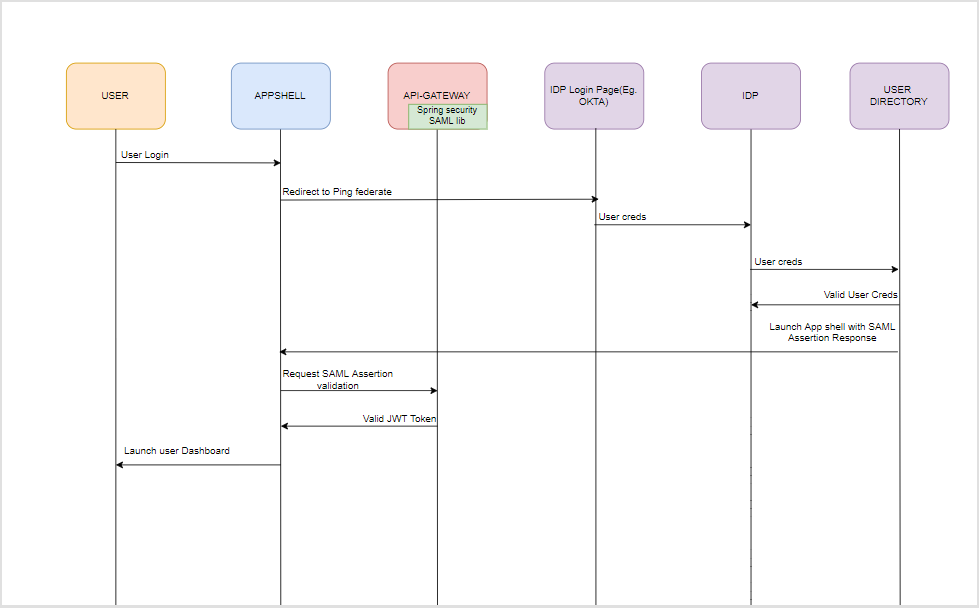
Figure 1-5 SP Initiated SAML Authentication
- The user initiates a call to the Oracle Banking Cash Management application and is redirected to the federate login page of the bank.
- The Identity Provider is external to the Oracle Banking Cash Management (e.g. OKTA) with the Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture products acting as the Service Provider
- The Idp presents a configured login screen to the user
- Client enters a user id and password. In case of success, the Idp sets the corresponding user profile details in the security context
- The request is routed to the Gateway which extracts the profile details by decoding the SAML response
- The API Gateway creates a JWT token (Utilizing Oracle’s Security Developer Toolkit part of Oracle’s Platform Security Services), persists it in the Database and returns the same.
SAML SSO Implementation
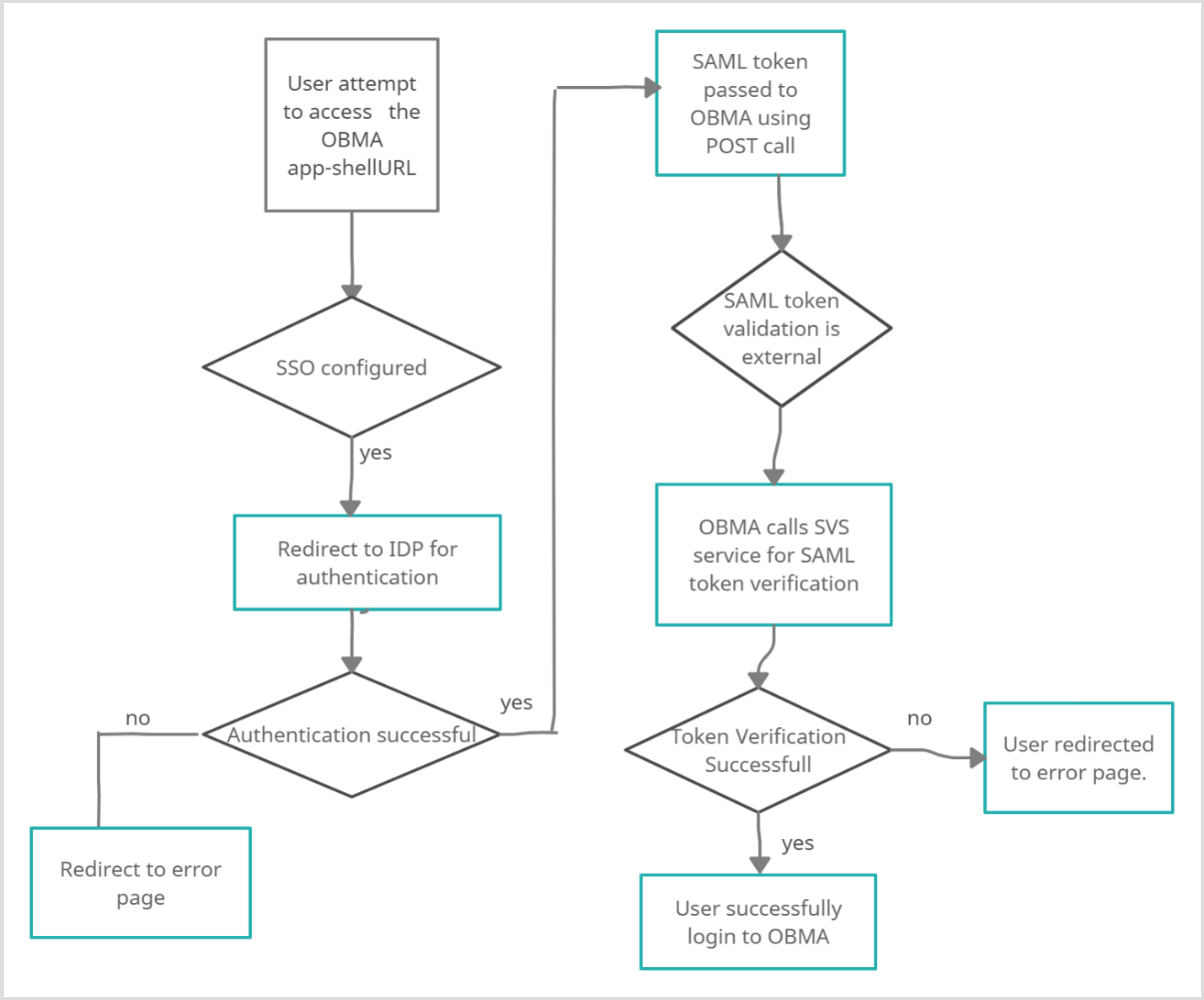
- Bank user will try to access the Oracle Banking Cash Management app-shell URL.
- Oracle Banking Cash Management will check if the IS_SSO_CONFIGURED parameter is set to true in the SECURITY_CONFIG table.
- If the IS_SSO_CONFIGURED parameter is true the user will be redirected to the IDP for authentication.
- On successful authentication IDP will generate the SAML token and pass the token to the Oracle Banking Cash Management assertion consumer service URL in the body of POST method through EXTERNAL_SSO_KEY parameter.
- Oracle Banking Cash Management will receive the token and check if the SSO_SERVICE_PROVIDER is set to EXTERNAL in the SECURITY_CONFIG table.
- If SSO_SERVICE_PROVIDER is EXTERNAL, Oracle Banking Cash Management would make a HTTP Post call to SVS using the EXTERNAL_SSO_VALIDATION_URL configured in the SECURITY_CONFIG table for SAML token validation. Oracle Banking Cash Management will pass the SAML token through EXTERNAL_SSO_TOKEN_KEY parameter in the body of the POST to SVS.
- SVS will return a XML response with IsValid tag as TRUE or FALSE. If the tag value is TRUE, Oracle Banking Cash Management would generate JWT token using the user id from the <subject> </subject> tag of SVS response and allow the user to login.
- In case of failure, Oracle Banking Cash Management would give login error to the user.
Product Configurations required:
| KEY | VALUE |
|---|---|
| IS_SSO_CONFIGURED | True |
| JWT_EXP_SECONDS | JWT expiry time |
| JWT_ALGORITHM | HS512 |
| EXTERNAL_SSO_VALIDATION_URL | SVS URL |
| EXTERNAL_SSO_KEY | Parameter in which the SAML token will be passed to Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture from IDP after user authentication. |
| SSO_SERVICE_PROVIDER | EXTERNAL |
| EXTERNAL_SSO_TOKEN_KEY | Parameter in which the SAML token will be passed to SVS URL for token validation. |
| HEADERS | Request headers for making HTTP call to SVS URL |
FCUBS integration with Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture as SSO Provider
Refer to Launching Oracle Banking Cash Management from UBS section in the Oracle Banking Cash Management Installation Guide.
Parent topic: Securing the Oracle Banking Cash Management Application