- Product Definition
- Product Definition
- Setting up Accounting Details for a Product
- Identifying the Accounting Roles and Heads for a Product
1.7.1 Identifying the Accounting Roles and Heads for a Product
Before you define the accounting details for a product, you should define the various components of the contracts involving the product such as interest, charges, tax, and so on.
In the Accounting Roles screen, a list of accounting roles are automatically generated based on the components you define for the product. You should map all the accounting roles that are available with the appropriate accounting heads.
Specify the User ID and Password, and login to Homepage.
From the Homepage, navigate to Bilateral Loans Product Definition screen.
- From the Bilateral Loans Product Definition screen,
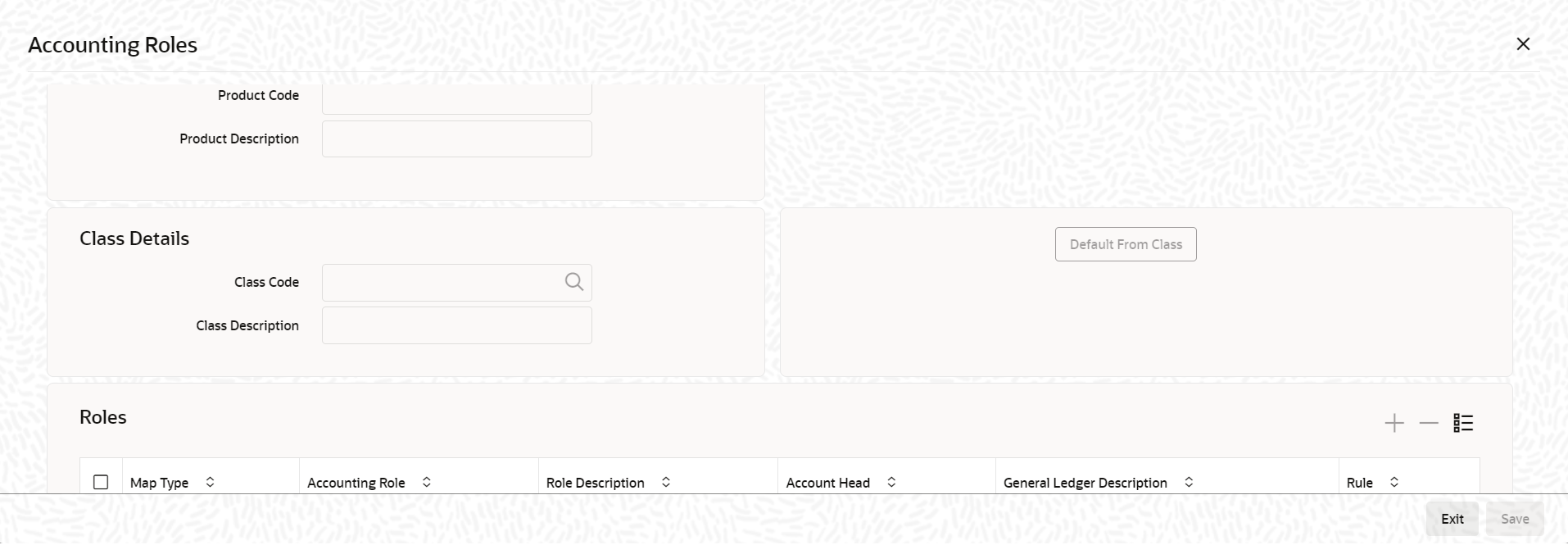
click on Accounting Roles tab.The Accounting Roles screen is displayed.
- Adopting either of the following procedures, you can specify the accounting
roles and heads for a product:
- Associating the product with an Accounting Role to Head Mapping Class. (This is possible only if you have maintained classes of Accounting Roles and Heads specifically for the module.)
- Mapping accounting roles and heads specifically for the product.
Table 1-3 Accounting Roles
Field Description Using a Class Click Default From Class in the Accounting Roles screen to associate the product you are maintaining with a class of mapped roles and heads. A list of the classes that you have defined specifically for the module is displayed. Choose a class with the requisite accounting heads and roles mapped. You can select and modify the required role to head mapping details to suit the product you are defining. You can also define new role to head mapping by clicking the + button.
The procedure for setting up an Accounting Roles to Head Mapping classes is similar to mapping accounting roles and accounting heads specifically for a product.Mapping Accounting Roles to Heads specifically for a product If you do not use a class to define accounting role and heads for a product, in this screen, you can define them specifically for the product you are creating. Map Type The mapping between an accounting role and account head can be of the following types: - Static: If the map type is static, you can link an accounting role to only one accounting/ GL head (one to one mapping).
- User Defined: For a user defined map type, you can maintain multiple linkages under different conditions using a case-result rule structure (one to many accounting).
Accounting Role and Description Accounting role is used to denote the accounting function of a GL or Account. To map an accounting role to an account head, select a valid accounting role from the option list provided. This list displays the roles available for the module. Once you choose the accounting role, the description maintained for the role is also displayed in the adjacent field. If you do not want to select a role from the option list, you can also create an accounting role for a product and specify a brief description for the same.
Account Head and Description The account head identifies the GL or Account to which the accounting entries are to be posted. Based on the type of accounting role you select (Asset, Liability so on.), the list of Account Heads (General Ledger heads) that are of the same type as that of the accounting role, becomes available in the option list provided. You can select an accounting head from this list and thus, create a role to head mapping. On selection of the Account Head, the description is also displayed in the adjacent field. Click Add icon to create subsequent mappings for the product. If you want to delete a role to head mapping, click Delete icon.
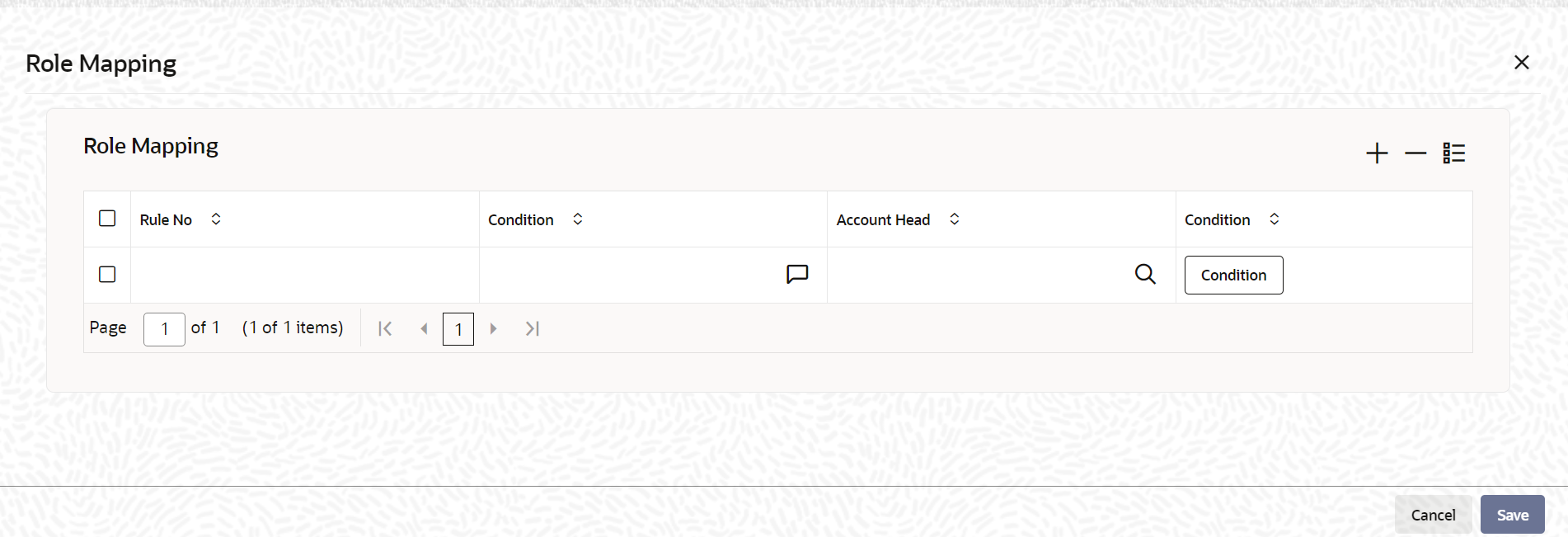
Rule If the Map Type is User Defined, you can create a case-result rule structure based on which the entries are posted to the appropriate account head. To create a rule, click Rule in the Roles section of the product screen. - You can define multiple conditions and for each condition you can specify the
resultant Account Head. This way you can maintain one to
many mappings between an accounting role and an account head. Depending on the
condition that is evaluated favourably, the corresponding account head is used
for posting the entries.To define condition you can use SDEs or UDF fields. SDEs are selected from the LOV where as UDF fields have to be manually defined using the prefix UDF@
For example, UDF@RESIDENT=YES.
To build a condition, click Condition in the Role Mapping screen. The Condition Builder is displayed. You can build the conditions using the elements (SDEs), operators and logical operators available in the screen above.
For details on building a condition using the options available in the screen, refer Defining Events and Accounting Details specifically for a Product topic.Note:
The system ensures that all accounting roles that are applicable for the product and which have been used in the definition of the accounting entries are necessarily linked to an account head. If the mapping is not complete, an error message is displayed when you attempt to save the product specifying Events and Accounting Entries. - A contract goes through different stages in its life cycle. In Oracle Lending,
the different stages a contract passes through in its life cycle are referred to
as Events.
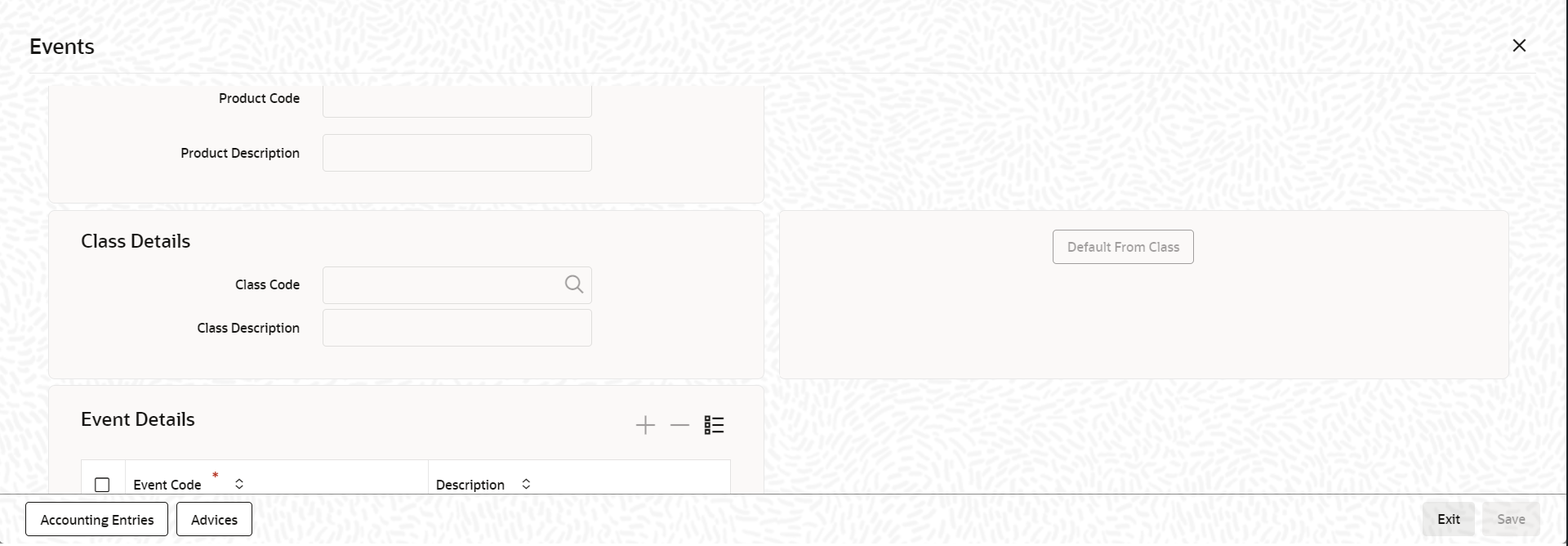
The Events screen is displayed.
- At an event, typically, if you want to post the accounting entries to the
appropriate account heads and generate the required advices. When setting up a
product, you can define the accounting entries that have to be posted and the
advices that have to be generated at the various events in the life cycle of
contracts involving the product. To do this, click Events
in the Bilateral Loans Product Definition screen.The Events screen is displayed.
- You can define the accounting entries and advices for events using either of
the following methods:
- Associating a product with an Events Class. This is possible only if you have maintained Events classes specifically for the module.
- By defining event details specifically for the product.
This topic contains following sub-topics: