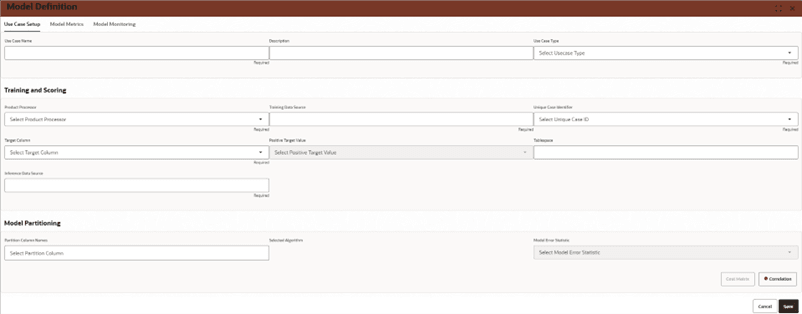
4.1 Fields
This topic provides information on Fields.
This section allows users to define basic model details.
- Use Case Name:
- Enter a unique name for the model.
- Example: "Login_Anomaly_Model" or "Payment_Fraud_Detection"
- (Required) – This field must be filled to proceed.
- Description:
- Provide a summary of the model’s purpose.
- Example: "Detects unusual login attempts based on user behaviour patterns."
- Use Case Type:
- Select the type of use case as Anomaly_Detection.
- Options may Regression & Classification, or any other specific use cases.(Required)
- Product Processor:
- Select the system or processor that will handle training.
- Example: "OBDX"
- (Required)
- Training Data Source:
- Specify the dataset used to train the anomaly detection model.
- The dataset must include the target column (i.e., the column indicating whether an instance is anomalous or normal).
- Example: A CSV file or database table containing past login records.
- (Required)
- Inference Data Source:
- Specify the dataset used when making predictions.
- Unlike the training dataset, this dataset should not include the target column.
- Example: "Live payment transaction records without labels."
- (Required)
- Unique Case Identifier:
- Select the column in the dataset that uniquely identifies each record.
- Example: "User_ID" for login data or "Transaction_ID" for payment data.
- (Required)
- Target Column:
- Select the column that defines whether a transaction/login attempt is an anomaly.
- Example: A column labelled "Anomaly_Flag" where 1 indicates an anomaly and 0 indicates normal behaviour.
- (Required)
- Positive Target Value:
- Specify the value that represents an anomaly.
- Example: If "1" indicates fraud or an unauthorized login, set "1" as the positive target value.
- Tablespace:
- Define the storage location for the model’s data within the system.
- Partition Column Names:
- Select the columns used for partitioning the dataset.
- Example: "Date" to separate records by time period.
- Selected Algorithm:
- Choose the machine learning algorithm to be used.
- Example: ALGO_SUPPORT_VECTOR_MACHINES, ALGO_NEURAL_NETWORK etc.
- Model Error Statistic:
- Select an error metric to evaluate the model’s accuracy.
- Example: F1 Score, Precision-Recall, or AUC-ROC.
- Correlation Button:
- Clicking this button will analyse relationships between features and the target variable.
- Helps in understanding the significance of different input features.
- Cost Matrix Button:
- Allows users to define cost-sensitive learning, useful for reducing false positives or false negatives.
- (Optional)
- Save Button:
- Saves the model configuration.
- Cancel Button:
- Exits without saving any changes.
Parent topic: Use Case Setup