- Securities User Guide
- General Maintenance
- Branch Parameters
- Maintain Market Details
3.5.8 Maintain Market Details
It is necessary to maintain certain standard details, relating to the markets where securities are traded. The information relates to issues such as the interest calculation method, the relevant spot, ex-dates, and the default safekeeping location.
Only the Head Office of your bank can define, and maintain market place related details. The other branches of your bank can refer to these details, every time a security is processed.
The advantage of defining market place details is that at the time of defining security, you only need to specify the code assigned to the market. All the details maintained for the particular market is automatically picked up.
- On the Home page, type SEDXMTCD in the text box, and click next arrow.
If you are maintaining details of a new market place, choose New from the Actions menu or click on a new icon to open the Definition detailed screen.
If you are calling a market place maintenance record that has already been defined, choose the Summary option under Market Codes. From the Summary, screen double clicks a record of your choice to open it.
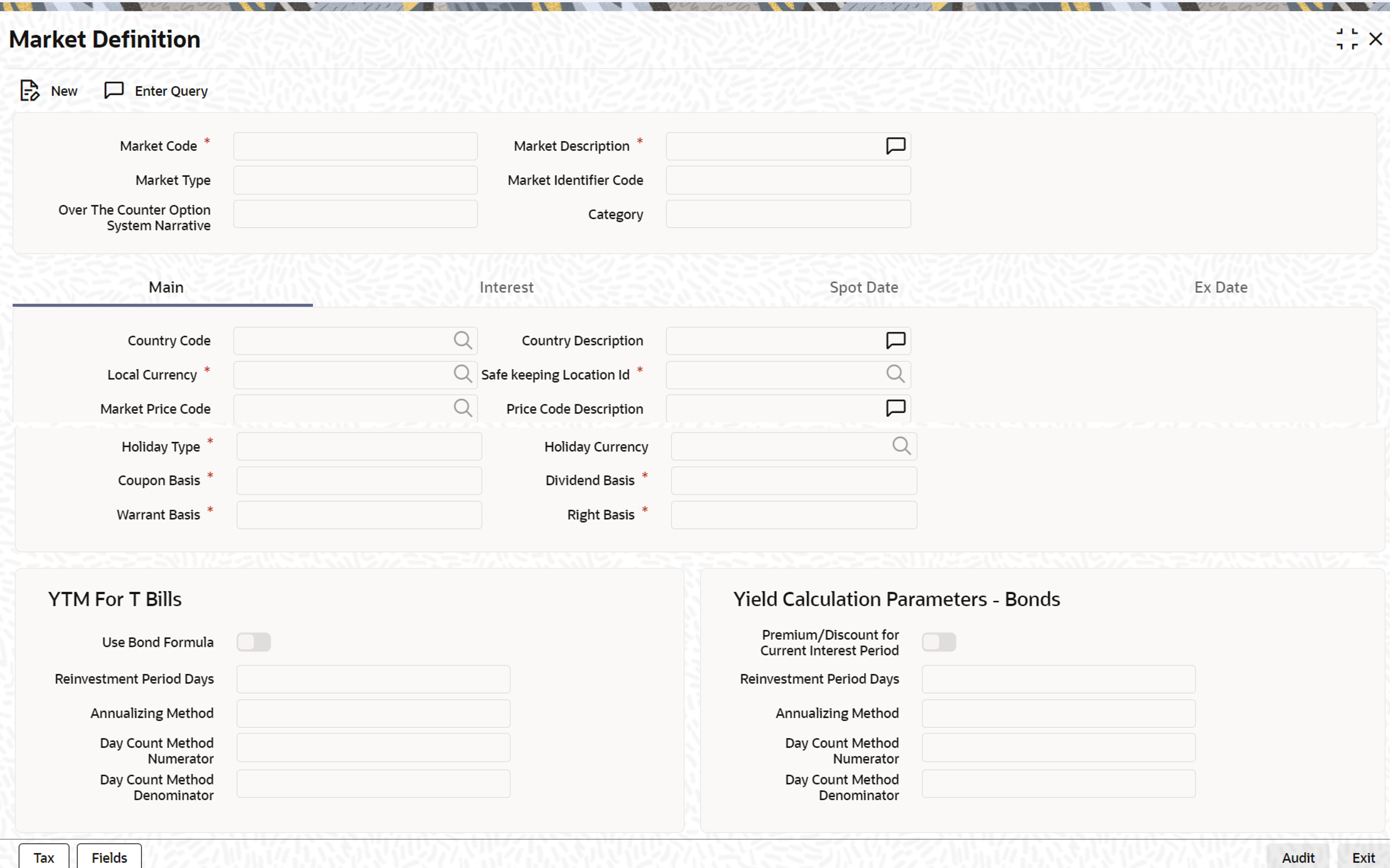
The Market Definition screen is displayed.
- On Market Definition, specify the fields.
For more information on fields, refer to the below table.
Before maintaining, the interest calculation method, and the relevant spot and ex dates, etc., certain basic details about the market place need to be maintained.
Apart from the other main details, you can specify the Yield Calculation Parameters for Bonds and T-bills for each market definition record that you maintain.
Table 3-16 Market Definition - Field Description
Field Description Market Code This is a Mandatory field.
Indicates the market in which the security involved in the deal is traded.
The market in which the security is traded is defaulted from the Security Definition screen. You can change the default.
Market Type Choose the Market type from the list of options:
- Stock Exchange
- Over the Counter
- LBL_DERVT_EXCHANGE
- Others
Market Description This is a Mandatory Field.
Specify the Market Description details as required.
Country Code Specify the country to which the market belongs.
Local Currency Specify the local currency of the country in which the market is situated.
Safe Keeping Location Id The Safe Keeping location to and from which the securities will be delivered.
Price Code Specify the price code from which the security price is to be picked up for this market.
YTM method for T-Bills The basis for YTM calculation for T-Bills can either be:
- Simple Interest
- Effective (Compound) interest
Use Bond Formula Enable the Use Bond Formula option, YTM is calculated using the effective interest formula (typically used for bonds).
For Bonds and T-Bills with the effective interest method of YTM calculation, you need to specify the following details:
Reinvestment Period The effective interest formula assumes that payments are reinvested at the same rate as the yield of the T-Bill/Bond (coupon schedules) until the maturity of the security. You have to specify this period in terms of days.
Annualizing Method For Bonds and for T-Bills, with effective interest you need to specify the annualizing method. This is the method by which the System computes the periodic YTM.
The options available are:
- Simple
- Compound
If the Annualizing method is Compound, the Annual YTM is computed as follows:
Y0=[(1=1/Y0)A/P-1]If the Annualizing method is Simple, the annual YTM is computed as follows:
Y0=[Y0(A/P)]
Where
- y0 is the Periodic YTM
- Y0 is the Annual Deal YTM
- A is the Day Count Method – Denominator (this is picked up from your maintenance in the Security Definition screen).
- P is the Period of Reinvestment. If Null, defaulted to A/n
Apart from these details, you need to specify the Day Count Denominator and Numerator methods for all Bonds and T-Bills.
Note:
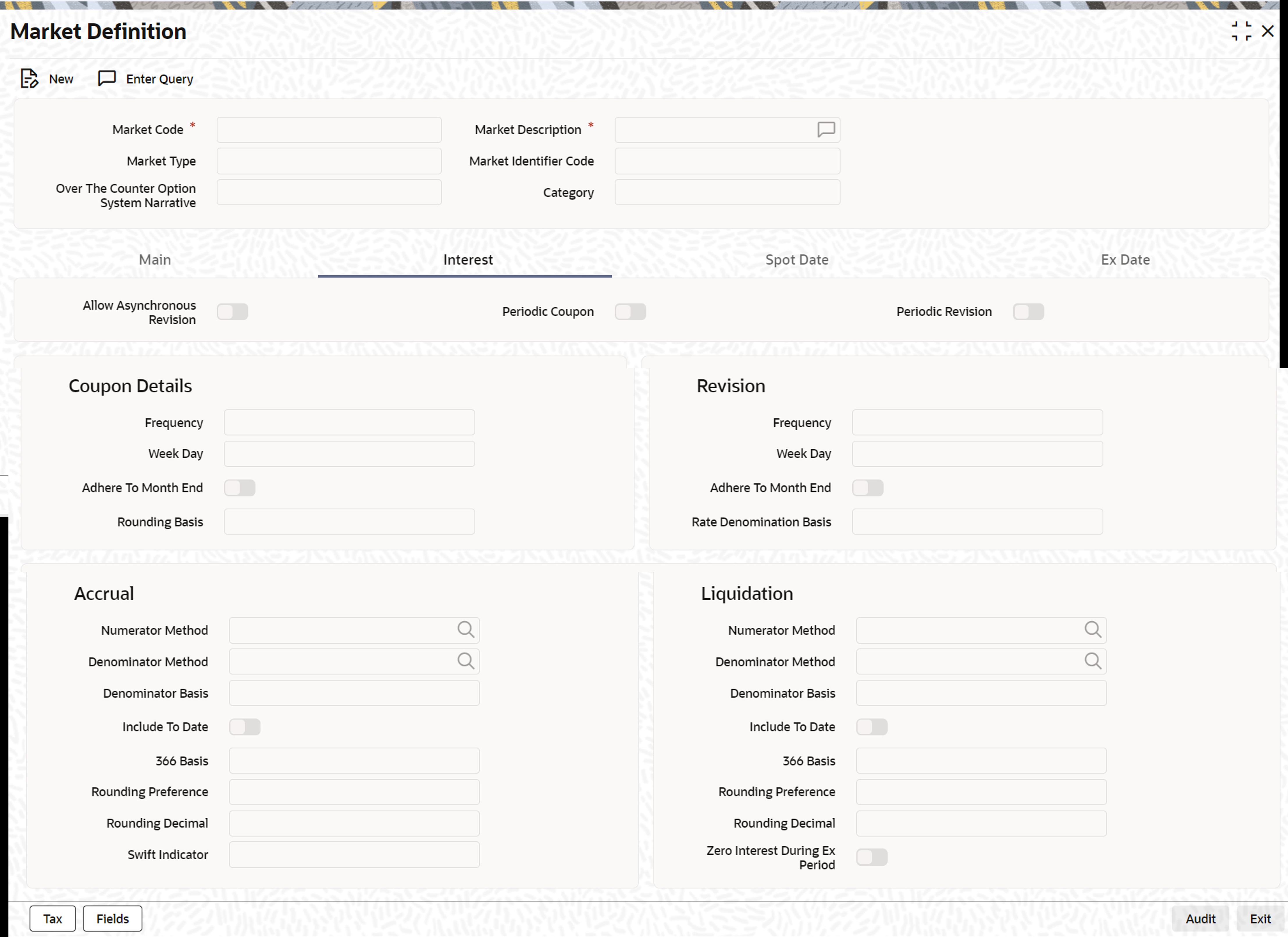
All the details maintained here are picked up and defaulted to the Securities Definition screen. You are allowed to change the information, at the time of defining securities - On the Market Definition Interest screen, click Interest
The Market Definition Interest screen is displayed.
- On the Market Definition screen, specify the fields.
For more information on fields, refer to the below table.
The interest details that you define here will be picked up, and defaulted, in the interest section of the Securities Definition screen. However, while defining security details you have the option of changing these details.
The details maintained here are specific to the interest calculation methods, applied during accruals and liquidation. It is not necessary to specify, the same day count method for calculating interest on accruals as well as on liquidation. The system allows specifying two different day count methods for calculating interest, one for accruals and the other for liquidation.
Table 3-17 Interest Types Description
Interest Type Description Actual / Actual Click on Actuals in Numerator Method field, click on Actuals in Denominator Method field. The Actual number of days in the period/ The Actual number of days in that year.
Actual /365 Click on Actuals in Numerator Method field; click on 365 days in the Denominator Method field. The number of actual calendar days for which calculation is done / 365days in a year.
Actual / 365 –Japanese Click on Actual Japanese in Numerator Method field; click on 365 in Denominator Method field. This is similar to the Actual/365 method except that leap days are always ignored, in the numerator day count calculation.
Actual / 365 – ISDA Sum of (A) and (B) where:
A = Interest accrual days falling within the leap year / 366
B = Interest accrual Days not falling within the leap year/ 365
The denominator is the actual number of days in a year.
Click on 365 ISDA in Numerator Method field; click on Actual in Denominator Method field.
Actual /360 The actual number of calendar days for which calculation is done / 360 days. Click on Actual in Numerator Method field; click on 360 in ‘Denominator Method’ field.
ACTUAL/ACT-ICMA The relevant number of days in a period from Start date to end date divided by the number of days in the Interest Period in which the relevant period falls.Click on ACTUAL in Numerator Method field; click on ACT-ICMA in Denominator Method field.
Denominator Method Select the denominator method from the adjoining drop-down list. This list displays the following values:
- 360
- 365
- 364
- ACTUAL
- ACT-ICMA
Rounding Preference Select the required rounding preference option on the basis of decimal position. The adjoining drop-down list displays the following values :
- Truncate
- Round Up
- Round Down
- Round Near
Note:
This field will be enabled only if the rounding basis is selected as ‘Per Unit’.
Rounding Decimal Specify the decimal places to apply the rounding preference on the coupon day count calculation value.
Note:
This field will be enabled only if the rounding basis is selected as ‘Per Unit’.
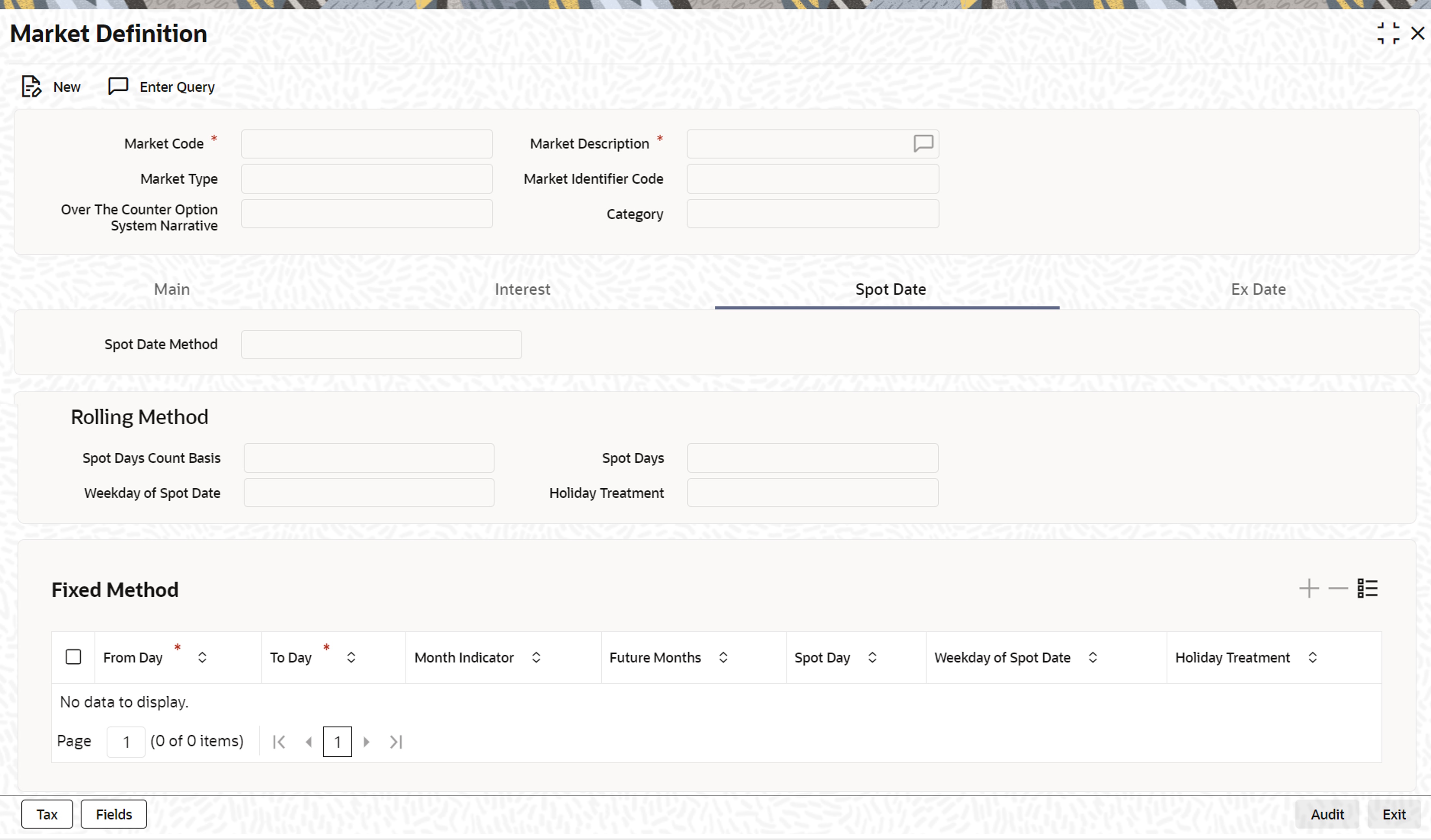
- On the Market Definition screen, click Spot Date.
The Spot Date tab is displayed.
- On the Spot Date tab, specify the details.
In this section, indicate the method by which Spot Date is calculated. Spot date is calculated to keep a track of deal settlements. You can click on the respective tab to go to this section of the screen.
There are two methods for calculating the spot-date. It can be calculated as a certain number of days from the trade date of the security. It can also be fixed for a market place for a specific range of trade dates.
There are two methods for calculating the spot-date. It can be calculated as a certain number of days from the trade date of the security. It can also be fixed for a market place for a specific range of trade dates.
Table 3-18 Spot Date - Field Description
Field Description Rolling
If the spot date calculation method indicated is rolling, then you can specify the spot day count basis.
Spot Day Count Basis There are two options available for this field:
- Calendar days – spot days will be expressed as calendar days
- Working days - spot days will be expressed as working days
Weekday of Spot Date Indicate your preference of weekday for the spot date, if you have specified the calculation method as rolling.
If the weekday of the spot date computed is different from the preferred weekday then, the spot date computed will be moved forward to the preferred weekday.
Holiday Treatment Once you indicate a preferred weekday for the spot date, it is required to specify the holiday treatment for the preferred weekday. If you choose to ignore this option, the spot date will be retained on the holiday. If not, as specified by you, it will be moved forward to the next working day or moved back to the previous working day.
When the spot day method specified is Fixed, indicate the details relating to the range of trade dates and the corresponding spot date for each slab. You also have to specify whether the spot date lies in the current month or a future month. You can select the relevant option from the pick-list available for the month indicator.
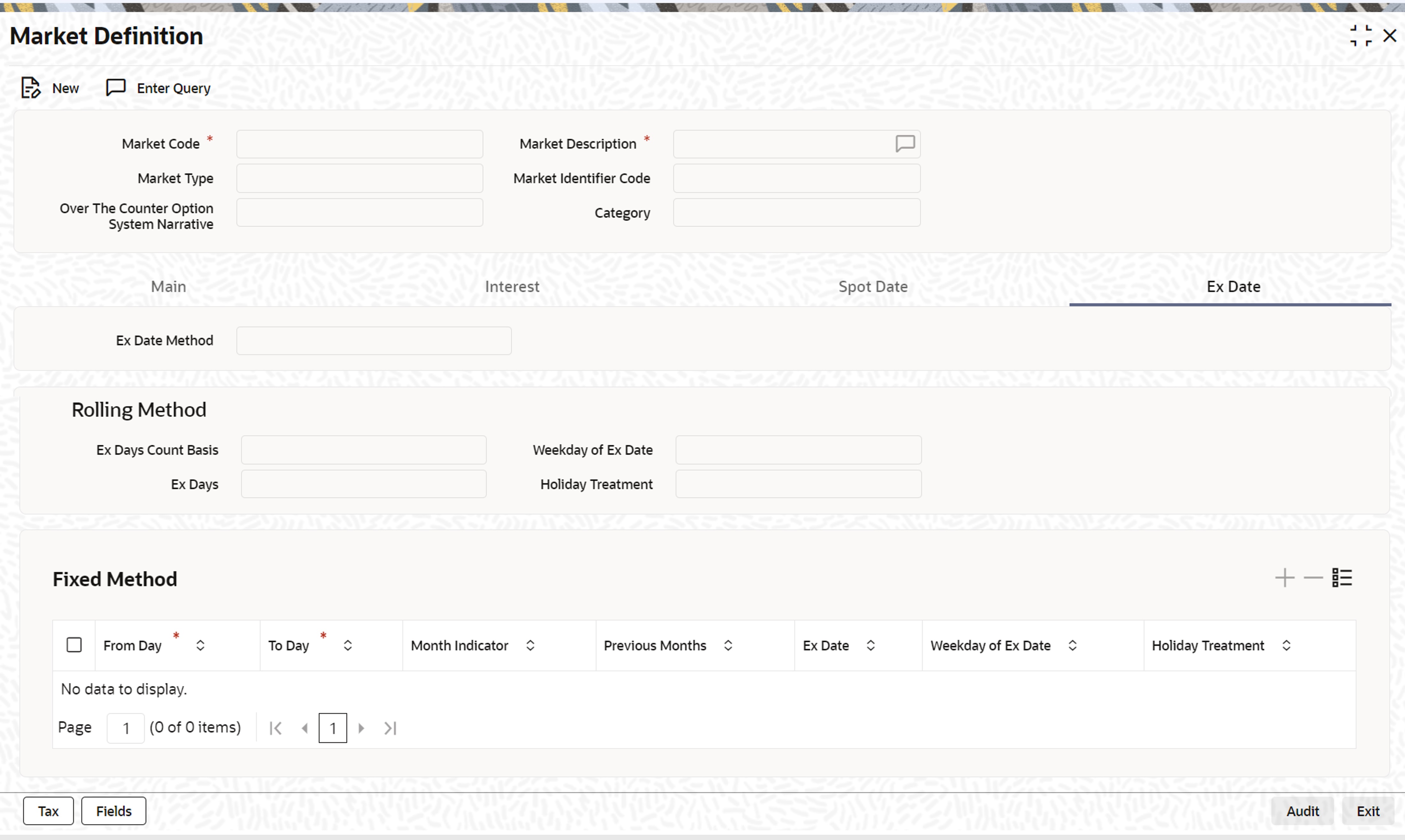
- On the Market Definition screen, click Ex Date.
The Market Definition Ex-Date tab is displayed.
- On Ex Date tab, specify the fields.
There are different methods for calculating the ex date. It can be calculated as a certain number of ex days, prior to the next coupon date of the security or it can be fixed for a market place for a specific period.
Table 3-19 Ex Date - Field Description
Field Description Expiry Date Method If the expiry date calculation method indicated, is rolling then you can specify the expiry date count basis.
Expiry Days Count Basis
express the expiry days as calendar days or as weekdays.
Weekday of Expiry Date Specify your preference for the weekday for the ex-date. The concept of weekday, of the ex-date and the holiday treatment, is the same as that of Spot date.
Fixed Method If the ex-date specified is fixed, then maintain certain mandatory details such as the From and To dates, the month indicator, and the holiday treatment. The information that you maintain here, is similar to the information entered for the spot date. This is so only if the spot date method specified, is fixed. However, in such a case, the ex-date will be before the event date.
Parent topic: Branch Parameters