7.1.9.2.9 Product Characteristics
This canvas shows information related to Product Characteristic rules.
Figure 7-252 Product Characteristics Report
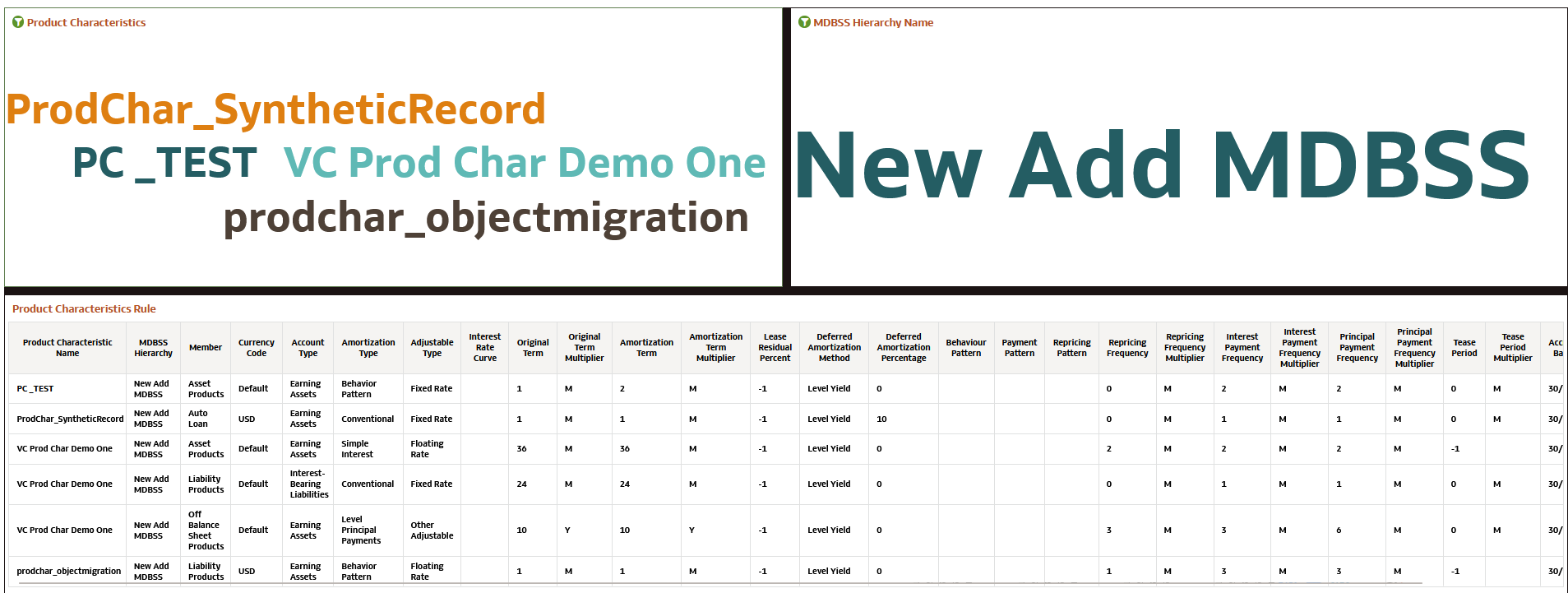
This canvas shows information related to Product Characteristic rules.
Figure 7-252 Product Characteristics Report
