A.1 Multiprocessing Model
By default, multiprocessing is disabled for all applications. Multiprocessing is enabled by setting application-specific parameters located under the Common Object Maintenance > Process Tuning.
The following applications and features have multiprocessing settings:
- Asset Liability Management – Deterministic and Stochastic Processing
- Balance Sheet Planning – Deterministic Processing
- Funds Transfer Pricing – Standard and Stochastic Processing
Note:
BSP does not support Stochastic Processing.OFSAA multiprocessing is based on the concept of a unit of work. A unit of work is a set of rows from the database. A single OFSAA process becomes multiple processes by dividing the single process according to distinct sets of rows. Units of work are distributed to worker processes until all processes have been completed. To achieve multiple parallel processes, the following options must be configured:
- Creating a list or lists of units of work
- Defining the number of worker processes to service the units-of-work lists
- Defining how the worker processes service the unit-of-work lists
Figure A-1 Main OFSAA Process
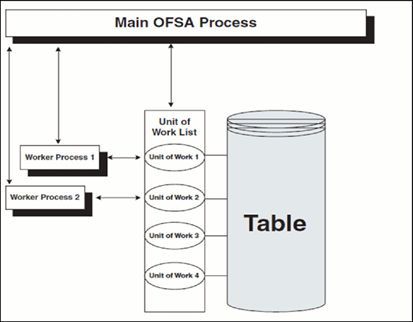
- The main process makes a list of all units of work that must be processed.
- The main process spawns worker processes. Each worker process is assigned a unit of work by the main process.
- When all units of work have been completed, the worker process exits and the main process finishes any clean-up aspects of processing.
- During processing the following is true:
- Each worker process must form its own database connection.
- A unit of work is processed only by a single worker process.
- Different units of work are processed at the same time by different worker processes.
Note:
If data is not distributed well across physical devices, I/O contention may offset the advantage of parallelism within OFSAA for I/O bound processing. It is recommended that users choose a dimension or combination of dimensions that produce a relatively equal distribution of data records.