1 About Financial Crimes and Compliance Management
This chapter describes Oracle Financial Services Financial Crimes and Compliance Management (FCCM) applications, how they are used by financial institutions and what a typical workflow would be.
In today's complex banking environment, there are many different factors that financial institutions must address to deter crime, safeguard their reputation, increase efficiency, minimize risk, and comply with regulatory agencies.
- Anti-Money Laundering Enterprise Edition (AML EE) monitors transactions to
identify possible money-laundering activities. These scenarios consider whether
the geographical location or entities involved warrant enhanced scrutiny;
monitor activity between accounts, customers, correspondents, and other entities
to reveal relationships that could indicate efforts to launder funds; address
sudden, significant changes in transaction activity that could indicate money
laundering or fraud; and detect other types of activities that are considered
potentially suspicious or indicative of money laundering.
For example, the Journals Between Unrelated Accounts scenario detects accounts that conduct journal transactions, within a specified period, to one or more accounts that do not share tax identifiers, do not share a customer, are not in the same household, and are not known to have a formal relationship. This behavior might indicate that money launderers have established a number of accounts using aliases or slightly different identifying information, and then moving money between accounts as part of a layering strategy, often consolidating the funds in a single account before removing them from the institution.
- Know Your Customer (KYC) assesses the risk associated with a customer by considering different attributes of the customer and enables financial institutions to perform Due Diligence, Enhanced Due Diligence, and continuous monitoring of customers. Cases generated in Know Your Customer can be managed within Enterprise Case Management to track investigations until they have been resolved or reported to the appropriate regulatory authorities.
- Enterprise Fraud Management (EFM) detects behaviors and patterns that evolve
over time and are indicative of sophisticated, complex fraud activity. These
scenarios monitor check and deposit / withdrawal activity, electronic payments,
such as funds transfer and payments completed through clearing house (ACH)
mechanisms, and ATM and Bank Card to identify patterns of activities that could
be indicate fraud, counterfeiting or kiting schemes, identity theft or account
takeover schemes. Fraud scenarios also monitor employee transactions to identify
situations in which employees, acting as insiders, take advantage of access to
proprietary customer and account information to defraud the financial
institution's customers.
For example, the Excessive Withdrawals at Multiple Locations scenario monitors a sudden increase in a customer’s withdrawals at ATMs that may indicate money laundering, terrorist financing, or an account takeover.
- Oracle Financial Services Currency Transaction Reporting (CTR) analyzes
transaction data from the organization and identifies any suspicious activities
within the institution that may lead to fraud or money laundering and must be
reported to the regulatory authorities. Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs) are
created either at the branches or through the end of day files, where the CTR
application aggregates multiple transactions performed at the branch, ATMs and
Vaults. Oracle Financial Services Currency Transaction Reporting then helps the
organization file the CTR online with the U.S. Financial Crimes Enforcement
Network (FinCEN) using a discreet form or uploaded in a batch form in a specific
text file format.
Unlike alerts for other Oracle Financial Services Behavior Detection products such as Anti-Money Laundering and Fraud which appear in an Alert Management user interface, CTR alerts are automatically processed and converted into CTR reports or Monetary Instrument Log reports which can be worked through the CTR user interface.
For example, the Bank Secrecy Act Currency Transaction Report scenario detects activity meeting the requirements for filing a Bank Secrecy Act Currency Transaction Report (CTR) and reconciles alerts generated by this scenario which are considered batch CTRs with Branch CTRs. The resulting CTRs are prepared for electronic filing in accordance with FinCEN's BSA Electronic Filing Requirements for Bank Secrecy Act Currency Transaction Report (BSA CTR).
- Enterprise Case Management (ECM) manages and tracks the investigation and resolution of cases related to one or more business entities involved in potentially suspicious behavior. Cases can be manually created within Enterprise Case Management or your firm may integrate other Oracle Financial Services solutions, such as Behavior Detection and Know Your Customer, which can be used to create cases.
- Regulatory Reporting supports the management, delivery, and resolution of required regulatory reports across multiple geographic regions and financial lines of business. Organizations are required to analyze and report any suspicious activities that may lead to fraud or money laundering within the institution to regulatory authorities.
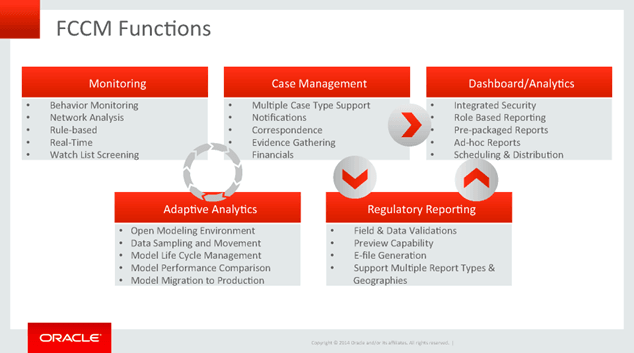
Functions
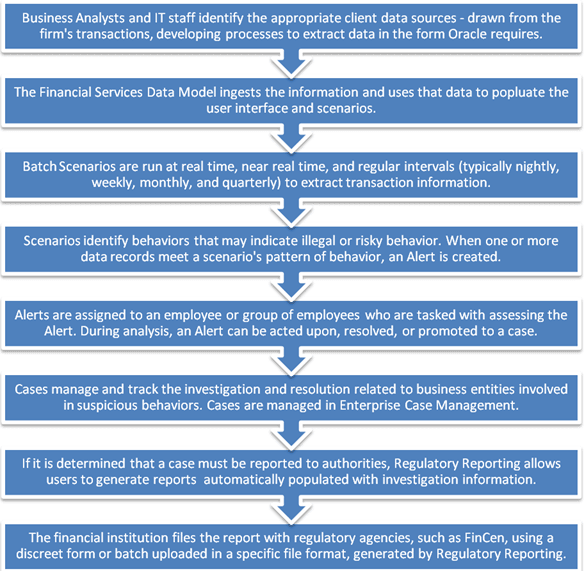
Workflow
Detailed information about these processes is available in the user documentation.