2.1 Behavior Detection Architecture
An architecture is a blueprint of all the parts that together define the system: its structure, interfaces, and communication mechanisms. A set of functional views can describe an architecture.
The following views illustrate the implementation details of the architecture:
- Tiers: Illustrates system components and their dependencies.
- Deployment View: Illustrates the deployment of components to processing nodes.
- Security View: Emphasizes the security options between processing nodes through a specialized deployment view.
The architecture is composed of a series of tiers and components. Each tier can include one or more components that are divided into small installable units. A solution set requires installation of the associated components.
Tiers
- Oracle Financial Services Analytical Applications Infrastructure (OFSAAI): Oracle Financial Services Analytical Applications Infrastructure is the complete end-to-end Business Intelligence solution that allows you to tap your organization's vast store of operational data to track and respond to business trends. It also facilitates analysis of the processed data. Using OFSAAI, you can query and analyze data that is complete, correct, and consistently stored at a single place. It can filter data that you are viewing and using for analysis.
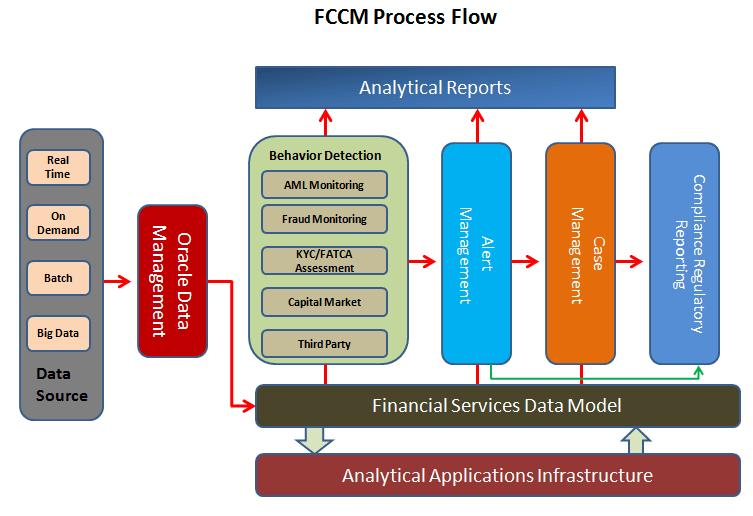
- Oracle Financial Services Behavior Detection Applications: Oracle solutions, such as Anti-Money Laundering, Fraud Detection, Alert Purge, Currency Transaction Reporting, and FATCA Management, extend the Oracle Financial Services Behavior Detection Applications pack. Each adds domain-specific content to provide the required services for addressing a specific business problem. It includes reusable domain artifacts such as scenarios, input data transformation code, and profiling scripts. A solution set also provides the required presentation packages and custom application objects for supporting user-interface functionality specific to the business domain.
- Oracle Financial Services Behavior Detection (OFSBD):
Oracle Financial Services Behavior Detection (OFSBD) contains the following
subsystems:
- Data Management: Provides data preparation
logical functions, which include adapters for files and messages.
The functions also include datamap XML for data derivations and
aggregations.
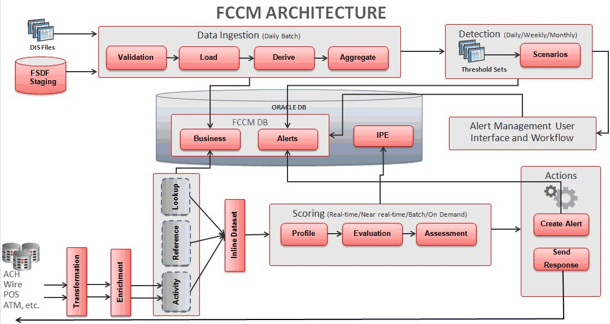
The Oracle Financial Services Ingestion Manager receives, transforms, and loads Market data, Business data (such as, Transactions or Orders and Trades), and Reference data (such as Account and Customer and Employee information) that alert detection processing requires. The template for receiving this information is defined in the Data Interface Specification (DIS). The Ingestion Manager typically receives Market data from a real-time Market data feed or file adapter interface, and both Business and Reference data through the file adapter interface. The Data Management subsystem transforms Market, Business, and Reference data to create derived attributes that the detection algorithms require (much of the loaded data is as is). The system extracts and transforms data and subsequently loads the data into the database. After loading the base tables, the Oracle client's job scheduling system invokes processing datamaps to derive and aggregate data. The Data Management component also uses the Fuzzy Name Matcher Utility to compare names found in source data with names in the Watch List.
The Oracle client implements Ingestion Manager by setting up a batch process that conforms to the general flow that this chapter describes. Typically, the system uses a job scheduling tool such as AAI Batch Scheduler to control batch processing of Ingestion Manager.
- Behavior Detection: Provides data access,
behavior detection, and job services, which include Oracle Financial
Services Behavior Detection (OFSBD), Financial Services Data Model
(FSDM), and scenarios specific to a particular solution set.
OFSBD uses sophisticated pattern recognition techniques to identify behaviors of interest, or scenarios, that are indicative of potentially interesting behavior. A pattern is a specific set of detection logic and match generation criteria for a particular type of behavior. These behaviors can take multiple representations in a firm’s data.
OFSBD detection modules are divided into scenarios that typify specific types of business problems or activities of interest. The scenarios are grouped into scenario classes that represent categories of behaviors or situations that have common underlying characteristics. The scenario class dictates the action choices available and the data that is displayed when an alert is created.
- Alert Viewer: Provides a user interface and
workflow for managing alerts, reporting, and searching business
data.
An alert represents a unit of work that is the result of the detection of potentially suspicious behavior by Oracle Scenarios. OFSBD routinely generates alerts as determined by the configuration of the application in your environment, typically nightly, weekly, monthly, and quarterly. Alerts can be automatically assigned to an individual or group of users and can be reassigned by a user. Alert Viewer contains the Alert Viewer to support triage of an alert, Correlations, and Watch List Management.
- Data Management: Provides data preparation
logical functions, which include adapters for files and messages.
The functions also include datamap XML for data derivations and
aggregations.
Deployment View
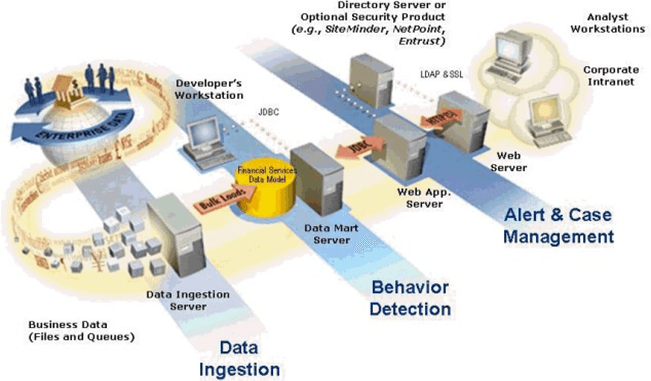
The OFSBD architecture from the perspective of its deployment illustrates deployment of the major subsystems across servers. Additionally, the deployment view shows the primary communications links and protocols between the processing nodes.
Figure 2-3 OFSBD Architecture - Deployment View
- Web browser
- Web server
- Web application server
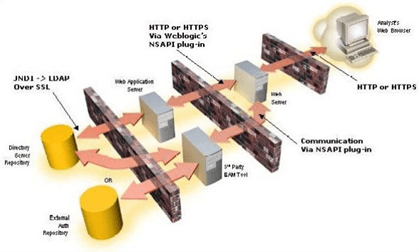
Security View
The security view describes the architecture and use of security features of the network in a Behavior Detection architecture deployment. Behavior Detection uses an inbuilt Security Management System (SMS) for its authentication and authorization. The SMS has a set of database tables which store information about user authentication.
Installation of 128-bit encryption support from Microsoft can secure the web browser. Oracle encourages using the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) between the web browser and web server for login transaction, while the web Application server uses a browser cookie to track a user's session. This cookie is temporary and resides only in browser memory. When the user closes the browser, the system deletes the cookie automatically.
Behavior Detection uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) security to encrypt passwords that reside in database tables in the ATOMIC schema on the database server and also encrypts the passwords that reside in configuration files on the server.
The EAM tool is an optional third-party pluggable component of the security view. The tool’s integration boundaries provide an Authorization header, form field with principal, or embedded principal to the web Application server through a web server plug-in. The tool also passes the same user IDs that the OFSBD directory server uses.
Table 2-1 Data Management Components
| Component | Directory Name | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Ingestion Manager | ingestion_manager | Java components, scripts, and stored procedures |
| Financial Services Data Model | database | Database utilities and database creation scripts |
| BDF Datamaps | bdf | Datamap XML and configuration parameters. |
Table 2-2 Behavior Detection Components
| Component | Directory Name | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Behavior Detection | behavior_detection | (Subsystem) |
| Behavior Detection | bdf | Datamap XML and configuration parameters. |
| Detection Algorithms | algorithms | C++ behavior detection algorithms |
| Scenario Manager | toolkit | Job and scenario editors |
Table 2-3 Alert Viewer Components
| Component | Directory Name | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| Alert Viewer Web | solution\am | JSPs used in Alert Viewer |
| Alert Viewer UI | ftpshare\< alert infodom>\erwin\forms | XMLs for rendering the UI |
| Web Services | services | Web services for watch list scanning and for the Alert Viewer supervisor (used when posting alerts to Behavior Detection) |
| Correlation | - | - |
| Administration Tools | admin_tools | Web-enabled Administration Tools |
| Watch List Management | - | - |