7 Climate Scorecard
The Climate Scorecard is an integral part of the Oracle Financial Services Climate Change Analytics Cloud Service solution. With the increasing effects and impacts of climate risk, financial institutions need a mechanism to integrate climate risk into their overall Enterprise Risk Management practices. Further, the reporting/disclosure requirements from various climate change-related reporting standards and/or frameworks require reporting entities to disclose their processes for identifying, assessing, and managing climate-related risks.
To facilitate banks and financial institutions to confidently integrate climate risk into their risk management, this framework on Climate Scorecard by Oracle Financial Services enables a financial institution to measure, monitor, and assess its financial exposures. This is achieved by way of rating its customers based on various climate change-related factors like carbon emissions, governance, climate targets, and so on. CCA defines climate change factors as those factors that can materially influence the climate risk assessment of a rated customer.
OFS CCA’s Climate Scorecard Framework performs an assessment based on several quantitative and qualitative parameters. Users, additionally, have the option to add custom parameters and sub-parameters to meet internal policies and/or practices. This objective evaluation is based on several publicly available information and other information obtained from the customers.
Assessment Process
To arrive at the overall customer Climate Rating, weights are assigned at a sectional level (quantitative vs. qualitative) and to each parameter as well. Additionally, users can configure slabs for each parameter by specifying the upper and lower limits for them. Users can either accept the pre-configured setup or configure these weights, and slabs based on their internal risk management policies and practices.
Quantitative Parameters
Oracle Financial Services’ Climate Change Analytics’ Climate Scorecard model comes along with several pre-packaged quantitative parameters to factor in climate risk in the overall risk assessment process. These parameters are important to assess a customer based on numerical values attached to climate risk metrics and disclosures. Users can utilize the Data Model Extensions module to add custom quantitative parameters per their requirements.
- GHG Emissions – Total reported greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions of the rated customer
- Emissions Intensity – Popular emissions intensity metrics like economic emissions intensity of the rated customer
- Emission Targets – Climate targets set by the rated customer
For more details on the pre-packaged quantitative parameters, see the Reference Guide on MOS.
Qualitative Parameters
Similar to Quantitative Parameters, the Climate Scorecard model comes with several pre-packaged qualitative parameters to factor in climate risk in the overall risk assessment process. Users can utilize the Data Model Extensions module to add custom qualitative parameters per their requirements.
- Governance – Metrics on the Board of Directors, Management involvement in managing climate risk
- Level of disclosures – Maturity level of the rated customer in the form of several climate change disclosures made
- Sector and Industry Classification – Categorization of the rated customer based on the sector and industry it belongs to
For more details on the pre-packaged qualitative parameters, see the Reference Guide on MOS.
Output
Depending upon the underlying data, a score is assigned to each parameter which is then aggregated to arrive at the final score. Based on the final score, each customer gets assigned a Climate Rating and Rating Reference. Climate Rating is an alphabetic symbol assigned to a customer, for example, AAA is the highest rating symbol, and Highly Positive is the Rating Reference attached to it.
| Rating Symbol | Rating Reference |
| AAA | Highly Positive |
| ABB | Moderate |
| BBB | Neutral |
| CCC | Highly Negative |
Note:
The preseeded values may change depending on the user selection from the Climate Scorecard screen.| Number of Ratings | 4 |
| AAA | 3.51-4 |
| ABB | 2-3.5 |
| BBB | 1.51-2 |
| CCC | 0.9-1.5 |
For more details on the various rating levels, rating symbols, and rating references, see the Reference Guide on MOS.
Figure 7-1 Climate Scorecard Process Flow
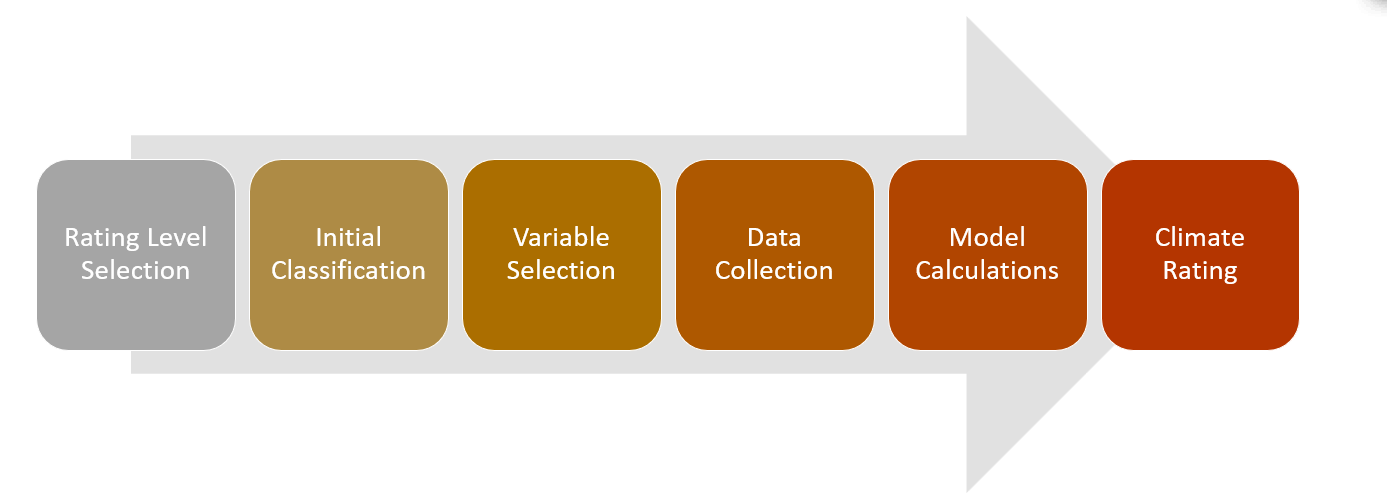
- Rating Level Selection- Select the desired Rating Level from the <Screen name> UI based on the available options such as 4, 5, 6, and so on. The rating symbols, rating references, and increasing or decreasing the available band of ratings are non-editable by the user. For more information on how to use this feature, see the section on Climate Scorecard UI. For information on the rating levels, symbols, and rating references, see the Reference Guide on MOS.
- Initial Classification - Select relevant legal entity(s), industry classification type, customer category, customer type, and so on to proceed with various variable selections.
- Variable Selection- Confirm, copy, or modify weights, and slabs across each parameter. For custom parameters generated using the Data Model Extensions module, the user must copy the score and slab type of an existing parameter.
- Data Selection- The framework utilizes existing counterparty-related data from the staging and FSI tables.
- Model Calculations- The framework then performs the assessment process by computing a score for each parameter, and section (quantitative and qualitative) based on the user definition in the Climate Scorecard UI screen and underlying data.
- Climate Rating- Obtain the final climate rating and rating reference at each counterparty level.