8.3 Right To Forget
The Right to be Forgotten (RTF) feature ensures that businesses protect sensitive Personally Identifiable Information (PII) related to party data. This functionality is available in Data Foundation Cloud Service (DFCS) and involves randomizing party data when it is no longer needed in the system.
RTF Process Overview
- The RTF process is executed as a PMF job.
- It is user-driven, requiring customers to input Party Identifiers that need to be forgotten.
- Users must provide Party Identifiers through a PMF input, with multiple IDs entered as comma-separated values.
- Before executing the RTF process, users must invoke the SCD process (DIM Incremental Process) to update the Party Dimension.
- Only Party IDs present in the Party Dimension will be considered for randomization.
RTF Execution Details
- For each RTF request, the service checks if the user has sensitive PII-related party data in any entity.
- If such data exists, the system fetches the list of affected entities and randomizes the PII-related data.
- The RTF Metadata Registration Table is preconfigured with Party Identifier (Business Term - BTO3899) for executing the RTF functionality.
RTF Data Visualization Reports
The following RTF-related information can be viewed in Data Visualization (DV) reports:
- Navigate to the Catalog menu, and open the Catalog application.
- Click on the Shared Folders tab.
- Navigate to Data Foundation Reports.
- Locate the Right To Forget folder in the list and click
Sensitive Data Anonymization. For more information, see Pre-Built Reports.
Figure 8-78 Data Visualization
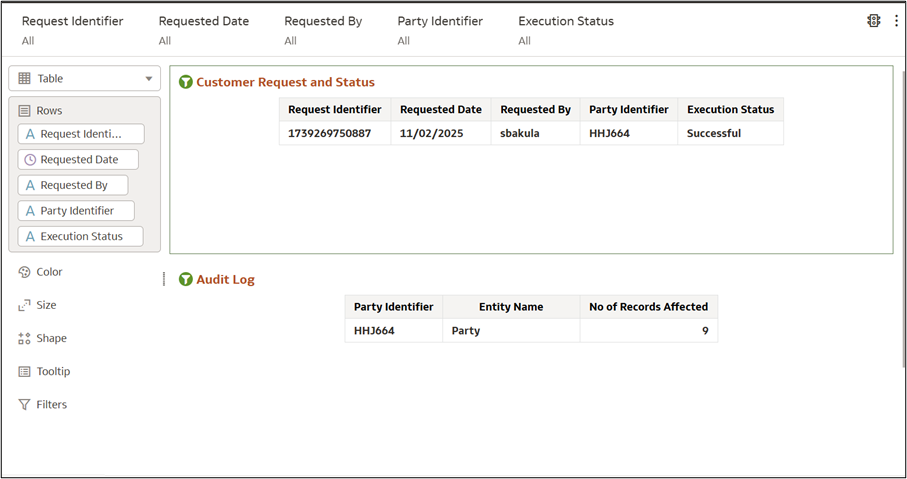
- Dashboard Sections:
- Customer Request and Status – Displays request details.
- Audit Log – Tracks affected records for accountability.
- RTF Customer Request Table – Stores details of each RTF request,
including:
- Request Identifier – Unique request number.
- Requested Date – Date of submission.
- Requested By – Username of requester.
- Party Identifier – Entity involved.
- Execution Status – Indicates success or failure.
- Reviewing the Audit Log:
- Party Identifier – Matches request ID.
- Entity Name – Type of entity affected.
- Records Affected – Number of modified records.
- Filtering and Searching Requests:
- Use filters (e.g., Date, Requested By, Status) to narrow results.
- Select a request to view details in the Audit Log.
- Verifying Execution Status & Impact:
- If successful, check affected records.
- If failed, troubleshoot using system logs.
- RTF Execution Status – Once the RTF Engine PMF process completes, the
system logs the execution status:
- If the Party ID is not found, the system updates the status as Not Available and exits.
- RTF Audit Log – Maintains execution records at the Entity Level,
including:
- Date of execution
- Number of records affected
Post-Execution Considerations
- Once an RTF request is successfully processed, the party data is randomized and secured.
- To maintain data integrity, users must ensure that the forgotten Party IDs do not re-enter the system during data loads from multiple sources into DFCS.
- Navigate to the Data Foundation for Banking home page.
Figure 8-79 DFCS RTF UI flow– Home Page
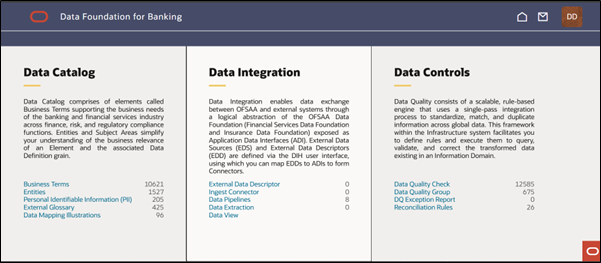
- Click on Data Pipelines under the Data Integration section. The
Process Modeller window will appear.
Figure 8-80 Process Modeller - Right to Forget
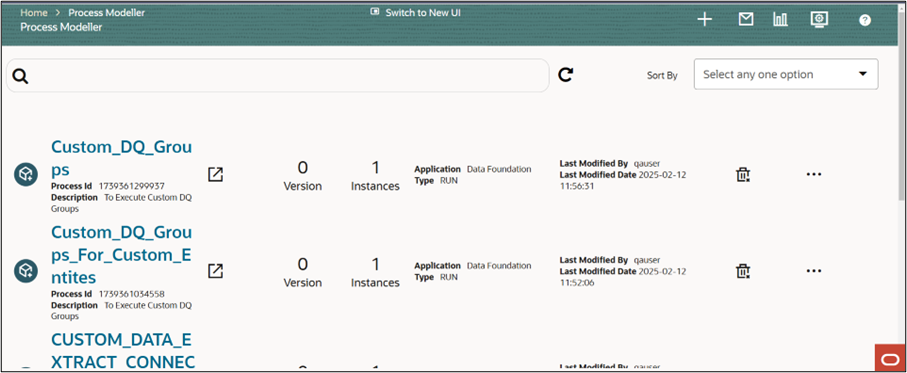
- In the Process Modeller search box, enter Right to Forget.
Alternatively, scroll down to locate the process manually.
Figure 8-81 RTF - Search
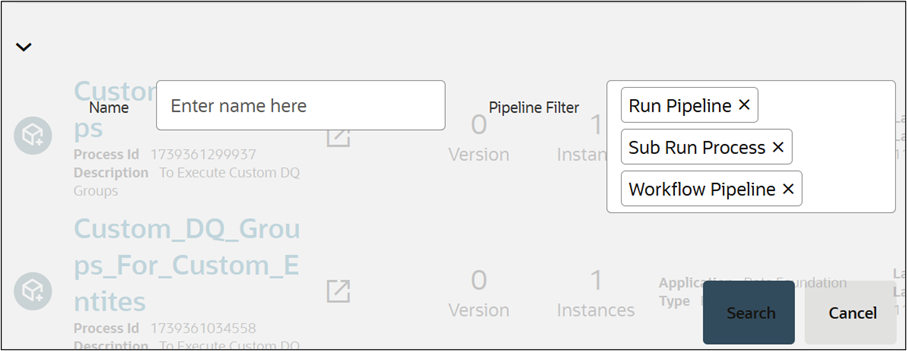
- Ensure that the Pipeline Filters are listed.
- Click Search to proceed or Cancel to modify the details.
- The Right to Forget process name will appear in the results.
Figure 8-82 Right To Forget - Search Result
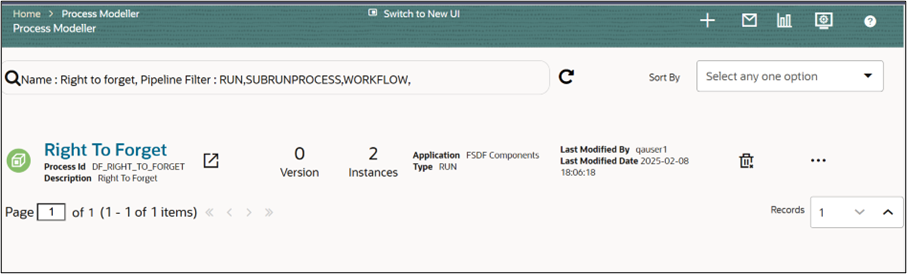
- On the Right To Forget window, the following options are available:
- Launch Process in New Window
- Version (Displays the process version)
- Instances (Shows active instances)
- Application Type (Displays application details)
- Modification Details (View last modified details)
- Delete (Remove the process)
- View (Check process details)
- Copy (Duplicate the process)
- Process Flow Monitor (Track execution flow)
- Execute Run (Run the process)
- Filter (Refine search results)
- In the Right to Forget window, locate and click on the Execute Run
option.
Figure 8-83 Execute Run
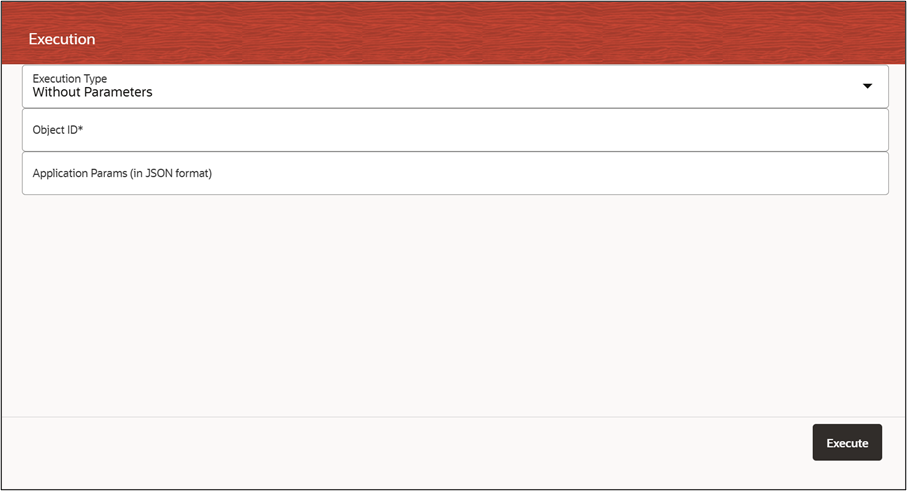
- Choose one of the following execution types:
- Without Parameters – Runs the process without requiring additional inputs.
- With Parameter – Requires user-specified inputs before execution.
- If executing With Parameter, enter the Object ID in the designated input field.
- Click on the Execute button to start the process.
- Track the execution progress in the Process Flow Monitor.
Figure 8-84 Process Flow Monitor
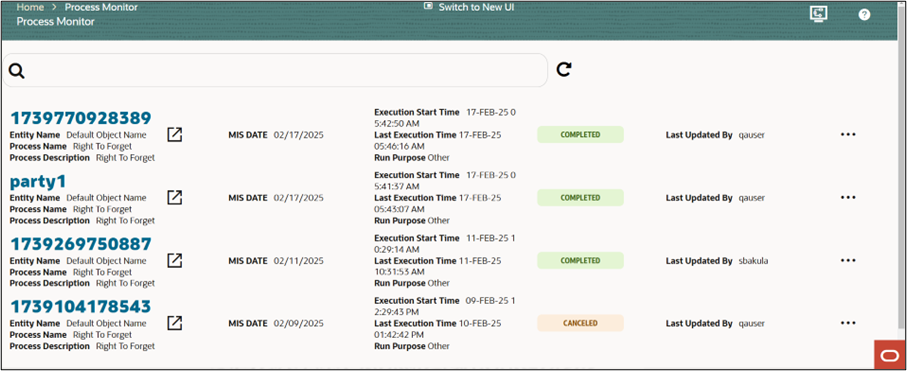
- Check logs for status updates and any potential errors.
- Click on the ellipsis (⋮) button next to the running process.
Figure 8-85 Modify Execute Run
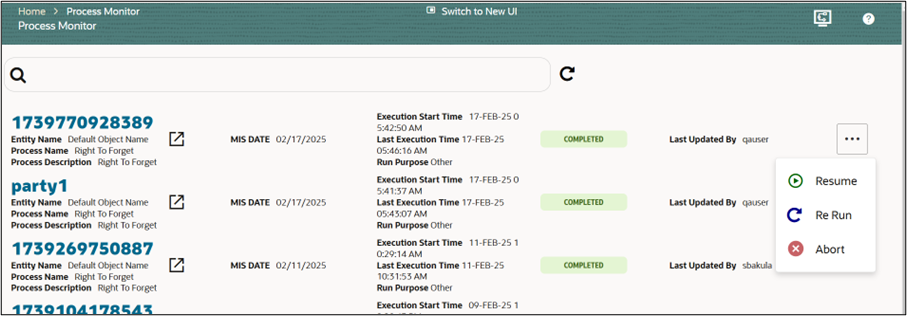
- Choose an Action:
- Resume – Continue a paused or failed execution.
- Re-Run – Restart the process execution from the beginning.
- Abort – Stop the execution immediately if necessary.
- Confirm Action (if prompted): Depending on the action chosen, you may need to confirm before proceeding.