6.4.1.2.1 Creating a Model
To create a model, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the Prepayment Model Data Analysis Summary page.
- Click Add. The Create Prepayment Model Analysis page is displayed.
- Follow the steps mentioned in below sections:
- Model Details
- Portfolio Definition
- Exploratory Data Analysis
- Risk Factor Selection
- Model Evaluation
- Click Submit/Save after entering all details in above sections.
Step 1: Model Details
- From Prepayment Model Analysis tab, click
Start. The Model Details page is
displayed.
Figure 6-188 Model Details
- Enter the following details:
- Model Name: Name of Process. The Data Creation Process Name should be unique. Any special characters are not applicable.
- Folder: Folder Name where you want to save the process.
- Description: Description of Process. The maximum limit of this field is 300 characters. You can enter special characters in this field.
- Read only Access: Select this option, if you want to make the process Readonly.
- Click Continue.
Step 2: Portfolio Definition
- Navigate to the Portfolio Definition section.
The Portfolio Definition window is displayed to set
Portfolio.
Figure 6-189 Portfolio Definition
- Enter the following details:
- Dimension:Select the Dimension.
- Currency: Select the Currency. The Currency drop-down displays the list of active currencies.
- Folder: Select the Folder from which you want to pick the Hierarchy.
- Filter: Select the Filter.
- Hierarchy: You can specify some processing parameters at product-currency combination. Hierarchies in selected Folder will be listed and you can select one from the available list of hierarchies.
- Select Product(s) from Member Tree of
Assumption Browser. The Assumption Browser has following two tabs:
Member Tree and Search Results
- Member Tree: Member Tree tab
shows the hierarchical structure and allows you to define rules
by selecting the node members from the browser. Select Node and
Click Menu icon next to it to view the available options.
Status of node is also displayed in Member Tree section, for example Selected, and so on. To select member hierarchy, following options are available:
- Expand self, child and descendants: Allows to expand the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
- Expand selected member/branch: Allows to expand the selected node
- Select UnSelect self, child: Allows to unselect the selected node itself along with its child
- Select UnSelect self, child and descendants: Allows to unselect the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
- Select Defined self, child: Allows to select the selected node itself along with its child.
- Select Defined self, child and descendants: Allows to select the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
- UnSelect self, child and descendants: Allows to unselect the selected node itself along with its child and descendants.
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Left) icon to view the code value left to the Node name.
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Right) icon to view the code value right to the Node name.
Here, you can perform the following tasks on the selected node(s):
- Add
- Edit
- View
- Delete
- Copy
- Search Results: You can also
search the members based on the filters. This section shows the
searched node(s). To search a member, follow these steps:
- Navigate to Assumption Browser section of the Rule Definition page.
- Enter the Member ID, Name, Status, or Is Leaf in Search Criteria.
- Click Search. The searched member(s)
will be displayed in Search Results section of
Assumption Browser .
Here, you can perform the following tasks on the searched node(s):
- Add
- Edit
- View
- Delete
- Copy
Click Show Parentage icon to view the Parent-child Node level hierarchy details of selected Node.
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Left) icon to view the code value left to the Node name.
Use Show Numeric Code Values (Right) icon to view the code value right to the Node name.
- Member Tree: Member Tree tab
shows the hierarchical structure and allows you to define rules
by selecting the node members from the browser. Select Node and
Click Menu icon next to it to view the available options.
Step 3: Exploratory Data Analysis
- Navigate to the Exploratory Data Analysis
section. The Exploratory Data Analysis window is
displayed to define Exploratory Data Analysis Parameter. This window is used to
perform EDA calculations.
Figure 6-190 Exploratory Data Analysis
- Enter the following details:
- Sample Size Model Population (As of Date Range):Sample size of dataset for EDA You can define a date range within which one wants to use data for model creation as model population. By Default, Date range would be populated as below: End Date: Max (As of Date) available in Model input Table Start Date: Max [min (As of Date), End Date – 10 Years]
- Do Sampling Sample Size (Multiplier)
:Select this option to create model based on a data
Sample rather than the whole population. By default, Do Sampling is
enabled. This would enhance performance due to lesser number of records
considered for modelling, without degrading model quality. After
selecting sample size for EDA, you can select multiplier value. This
indicates sample size required for model creation. For example, if 1000,
records are selected as sample size for EDA, and multiplier is 6, then a
minimum of 1000*6 = 6000 records would be required for model creation.
Note: This checkbox is enabled only if Do Sampling checkbox is selected.
This window gives complete information about all the risk factors along with prepayment rates. It helps you do decide what all factors could influence the customer’s prepayment behavior and would be best for model building. You can hover over any graph and zoom in to enhance the visibility of the graph. OFS ALM User Guide | 345 Click Model Summary to navigate back to the Model Summary window after saving all inputs/EDA graphs defined/generated till this point. Click Re-Calculate if you want to change the sample size and redo the EDA again. change the sample size and click Re-Calculate. If you have performed EDA multiple times (for example, three versions V1, V2, V3.), then use Versions (EDA) to view them. For example, when you are on the EDA screen and performing the EDA 3rd time, but still want to go with the 2nd EDA version, then select that version and subsequent processing would be based on V2. If you have run the EDA only once, then this drop-down will not be available. When you hover over Sample size for EDA, it displays Default value (callout) as Default Value is 5000.
Click Pair Plot to generate Pair Plot/Grid along with other EDA graphs. Pair Plot/Grid is a detailed graph, that can further slow down the processing. So you can explicitly select the pair plot checkbox and click on calculate to perform the EDA.
- Click Continue.
Step 4: Risk Factor Selection
- Navigate to Risk Factor Selection section.
By default, all the risk factors will be disabled.
Figure 6-191 Risk Factor Selection
- Select the Risk Factor as Manual or Auto.
Manual Select: When you change the risk factor selection mode to ‘Manual Select’, then all the risk factors would be available for selection; maximum 3 factors can be selected after that all the risk factors would be disabled again.
Auto Select: When you are in 'Auto Select' mode, System would perform required calculations, corelation/collinearity analysis in the backend based on the required number of risk factors (Maximum 3), System would auto-select the best representative set of risk factors as per the input data.
Click Risk Factor Selector button.Figure 6-192 Risk Factor Selector
Note:
If you want to change sample size and re-calculate EDA again, click Exploratory Data Analysis step and perform EDA with updated sample size. Again, the process starts from that step onwards, and updated EDA plots/graphs would be saved for the model.
- Click Continue.
Step 5: Model Evaluation Section
- Navigate to Model Evaluation section.
Figure 6-193 Model Evaluation Section
Click Calculate to view all the evaluation parameters and quality plots.
Figure 6-194 Calculating Model Evaluation
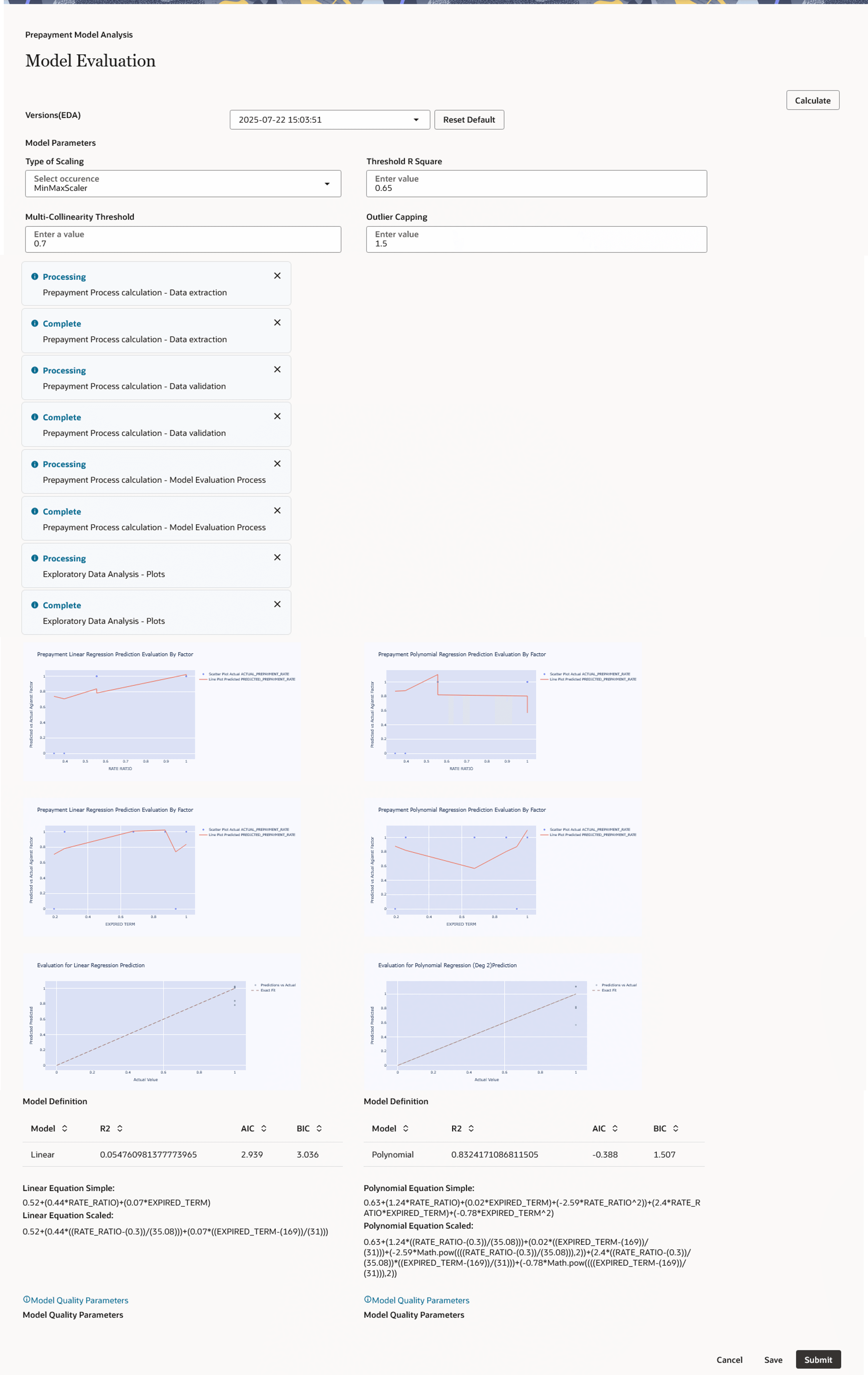
Click Calculate again if you are not satisfied with the model quality to change the model parameters and revise the model definition. You can zoom the graph to enhance visibility. If you are changing parameters and generating different versions of the model, then you can see all the versions, generated with different set of model parameters in the Versions (EDA) drop-down. If you have run “model evaluation’ only once, then this drop-down would not be available. As per the selected version, the model details window is also updated. The Model Details window helps you to evaluate the model fit. It has the following comparisons: Predicted Values Vs Risk Factor 1,2,3, as per the number of risk factors considered for model building. This will dynamically adjust as per the number of risk factors selected. Predicted Values Vs Test Sample. Sample prepayment matrix as per both the models (Linear and Polynomial).
Click Model Quality Parameter link to view Model Summary window, after saving all details. To verify the model quality, all the model statistics are given on a different screen, which would be available with Model Quality Parameter link like R2, F value, P – Value, and so on.Figure 6-195 Model Quality Parameter
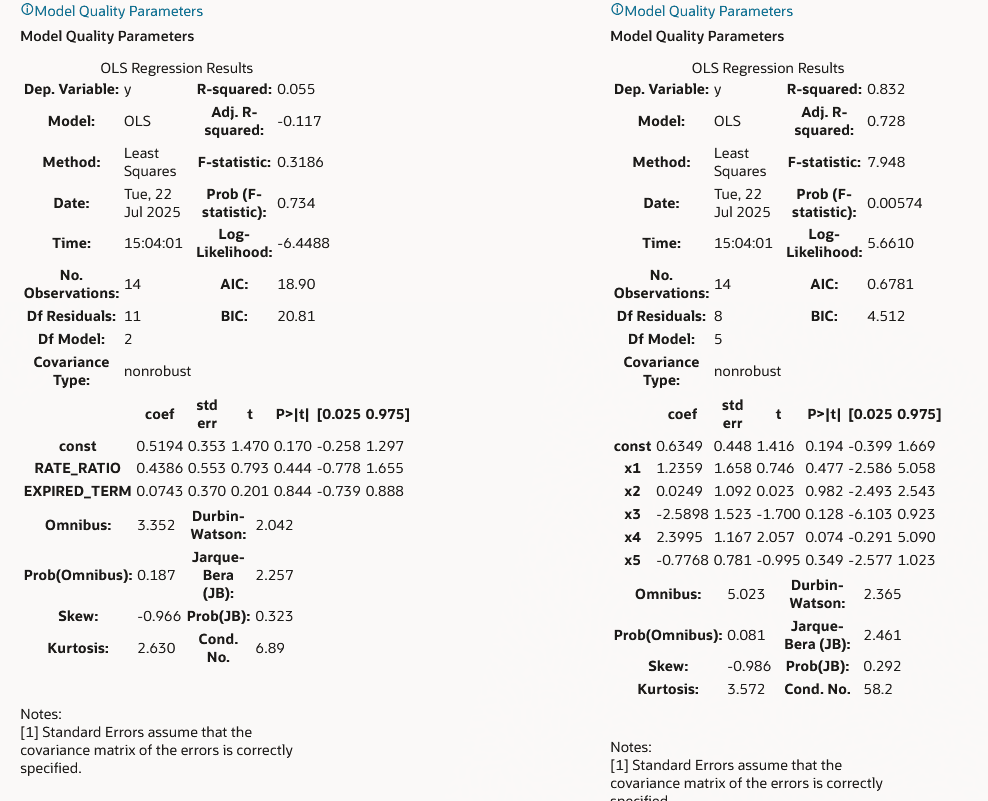
Add row using Add +. You can add multiple rows or delete multiple rows using buttons in panel 1. Default sample matrix is10*10, but once you re-define sample, matrix can be truncated to any dimensions. The redefined matrix will be saved along with model. Model summary parameters like R2 , AIC and BIC. Both (Linear/Polynomial) models are produced when the system compares model generated R2 against the R2 threshold defined by the user. The final option is given to you to choose any one of these models. Based on infrastructure availability and model complexity, you can choose any one of linear/polynomial model.
Click Save Model to save the model. Same model could be referred to populate prepayment rate matrix. Click Calculate again to re-evaluate model based on changed model parameters.
Note:
If you want to change sample size and re-calculate EDA again, click Exploratory Data Analysis step and perform EDA with updated sample size. Again, process would start from that step onwards and updated EDA plots/graphs would be saved for the model. If you want to update selected risk factors, click Risk Factor Selection step and change risk factors. Again, process would start from that step onwards and updated risk factors would be saved for the model.The Reset Default button on every step would help to delete all the calculations done in subsequent steps. That is, if you have done EDA and selected particular EDA version to do further calculations like ‘Risk factor Selection’ or ‘Model Evaluation’. In case you are not satisfied with model, you can go back to EDA, click Reset Default to clear out the details/calculations performed in subsequent stages and do recalculate with a different set of parameters. Following are the default values/usage of Parameters:
Table 6-45 Parameter Details
Parameter Details Default Value EDA Sample Size This would allow you to define a sample size for exploratory data analysis. A bigger sample would increase CPU and memory usage, but it would better represent the model population. You have the option not to use sampling by setting Do_Sampling parameter to false. Procedure for the same is given in next section. Type of scaling Many a times, risk factors are not in consistent range, e.g. one of the risk factor’s values could be in 1-500 range but another risk factor could be just in 2-3 range. So, risk factor 1 would influence the model more and you would get a biased model. So, to make all the risk factors consistent, scaling is used. There are two types of scaling: Min-Max Scaling = (X – min)/(max – min) Standard = (X – Mean)/Std. Deviations
Threshold R2 R-squared values range from 0 to 1 and are commonly stated as percentages from 0% to 100%. An Rsquared of 100% means that all movements of prepayment rate (dependent variable) are completely explained by movements in the chosen risk factors (independent variable(s). Multi collinearity Threshold For model creation if two risk factors/variables are highly correlated or correlation > 0.7, they would make model unstable. So based on this value, if variables are highly correlated or above defined threshold, one of them would be dropped while model creation. Outlier Capping This would allow user to reject values beyond certain percentile. Sometimes, input data has few extreme values which could distort the model. So you could reject those values and get a stable model. Exploratory Data Analysis:
Sample Size (EDA) - 5000
Model Population Range - It would be auto-populated based on the data in risk factor table. Maximum would be 10 years older from latest available date. In case you think, older data is not relevant, as of date range can be updated.
Model Evaluation:
Type of scaling – min Max Scaler Threshold R2 – 0.65 Outlier capping – 1.5 Percentile Multi-collinearity Threshold – 0.7
- Click Submit to create the Data Creation process. The created process will be displayed on Prepayment Model Data Creation Process Summary page.