9 Interpreter Configuration and Connectivity
An interpreter is a program that directly executes instructions written in a programming or scripting language without requiring them previously to be compiled into a machine language program. Interpreters are plug-ins that enable users to use a specific language to process data in the backend. Examples of Interpreters are jdbc-interpreter, spark-interpreters, python-interpreters, etc. Interpreters allow you to define customized drivers, URLs, passwords, connections, SQL results to display, etc.
In OFS MMG, Interpreters are used in Notebooks to execute code in different languages. Each Interpreter has a set of adjusted and applied properties across all notebooks. For example, using the python-interpreter makes it possible to change between versions, whereas the jdbc-interpreter offers to customize the URL, schema, or credentials. In OFS MMG, you can either use a default interpreter variant or create a new variant for an interpreter. You can create more than one variant for an interpreter. The benefit of creating multiple variants for an Interpreter is to connect different versions of interpreters (Python version: 3, Python version: 2, etc.). This helps to connect a different set of users and database schema. For example, OFS MMG schema, BD schema, etc. OFS MMG provides secure and safe credential management such as Oracle Wallet (jdbc wallet), Password (jdbc password), or KeyStores to link to interpreter variants to access secured data.
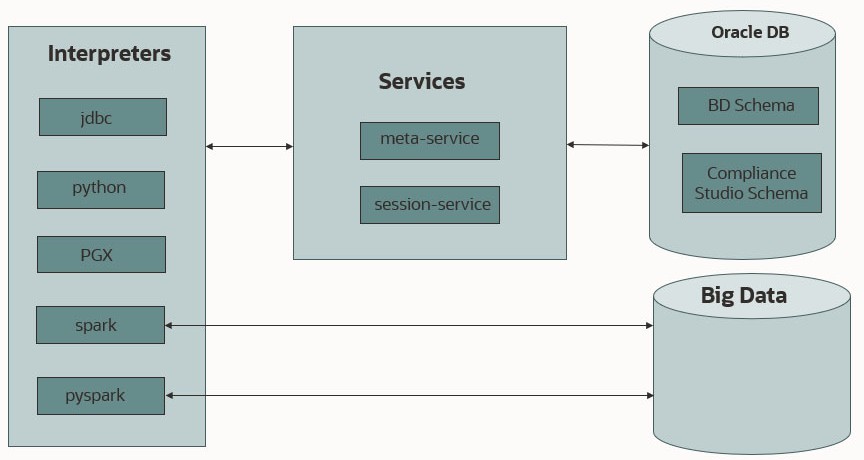
The following image illustrates the examples of interpreters used in OFS MMG and database connections.
Figure 9-1 Examples of Interpreters