Populate a Workspace
- Navigate to the Workspace Summary page. The page displays workspace records in a table.
Figure 6-11 Workspace Summary Page
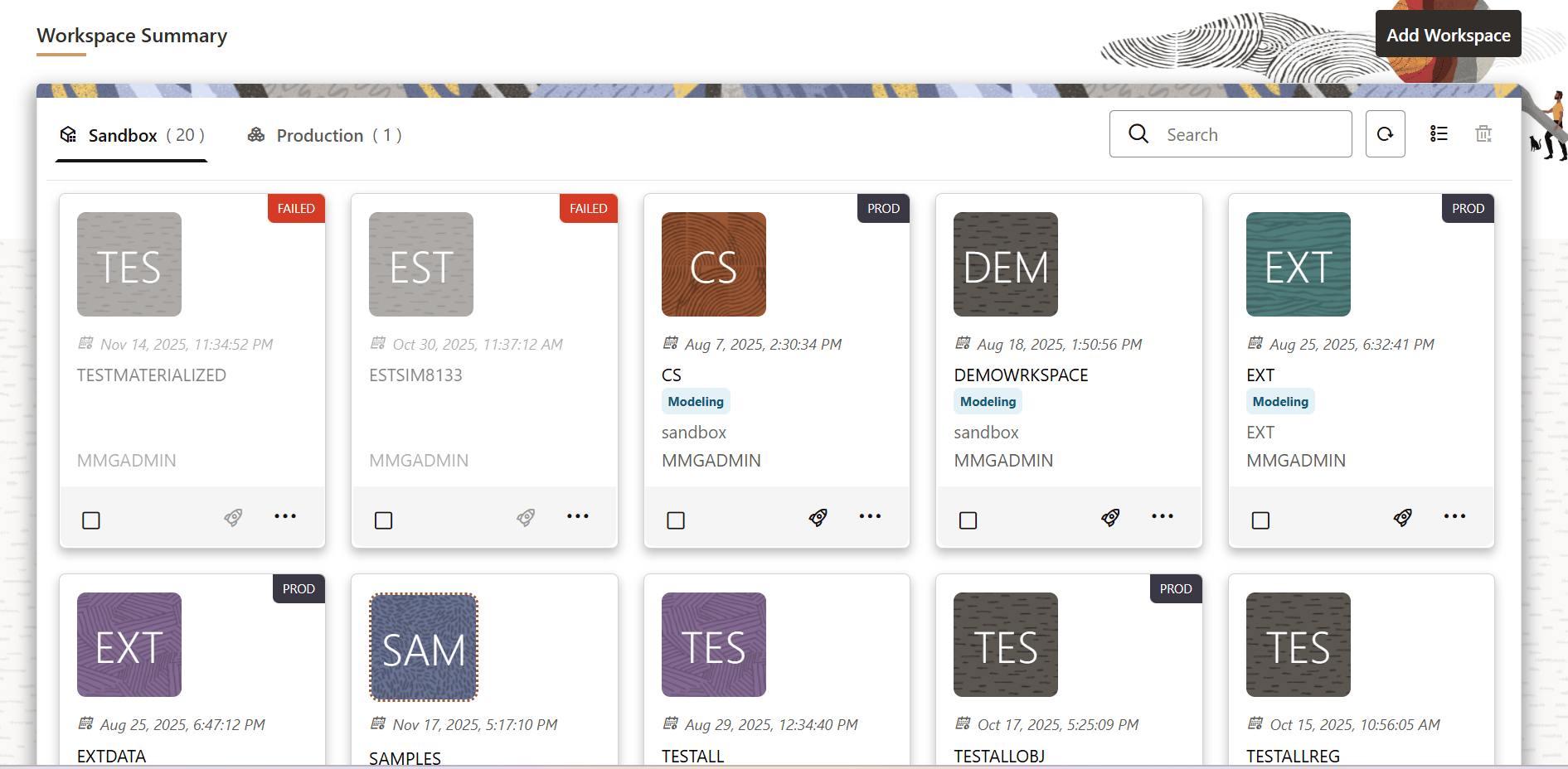
- Click the Action icon within the
desired workspace tile and then select Populate to
populate the workspace with data from a dataset in the Populate
Workspace window.
Figure 6-12 Populate Workspace window
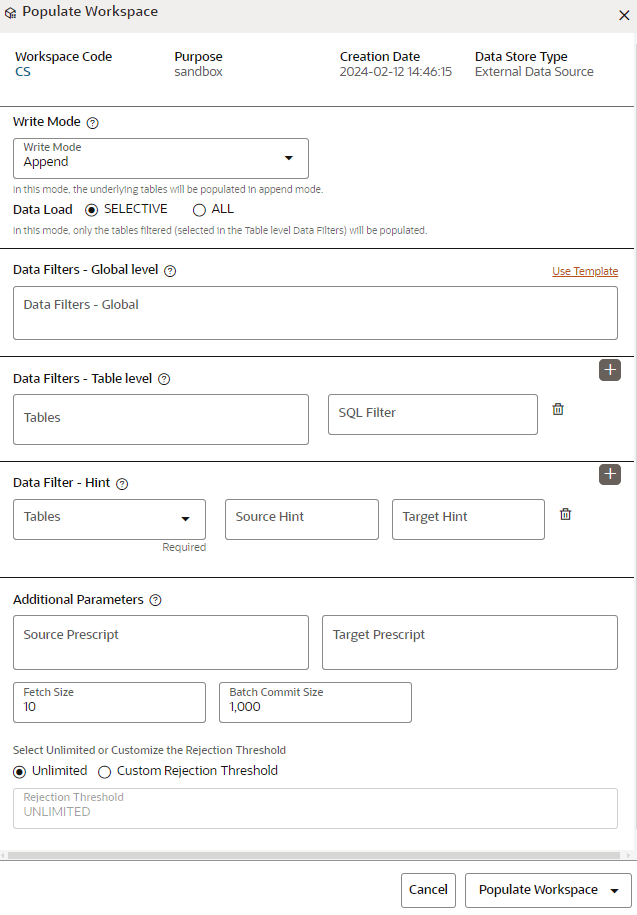 The following table provides descriptions for the fields in the Populate Workspace window.
The following table provides descriptions for the fields in the Populate Workspace window.Table 6-2 Details for the Populate Sandbox Window
Field Description Workspace Code Displays the code of the workspace. Purpose Contains the description of the workspace. Creation Date The date and time on which the workspace was created. Data Source Type The source of the data. The value can be the OFSAA Data Schema or an External Data Source. Write Mode You can either overwrite the existing data (truncate and insert) or append to the existing data. - Overwrite: In this mode, the underlying tables are truncated (overwritten on existing data) followed by an insert operation.
- Append: In this mode, the underlying tables will be populated (added to the existing data) in the append mode.
Data Load You can select a few tables or add all the tables from the source. The available options are: - SELECTIVE: In this mode, only the filtered tables (selected in the Table level Data Filters) are populated.
- ALL: In this mode, all the underlying tables mapped to the workspace are populated along with the specified filters for specific tables.
Data Filter- Global Level Enter the data filter that needs to be applied on all the tables selected for data sourcing. For example: If MISDATE is equal to Today, then it is applied to all tables (wherever it is available) for selected Data Sources during population. If this field is not found (MISDATE) in the tables, it is not updated.
Or
Click Use Template to open the Template pop-up window. Select a template from the Template drop-down list.
On selecting the template, any pre-filled values will be overridden with the template provided values.
Data Filter- Table level You can provide the data filters individually for the tables. Select the table and enter the SQL filter. Additionally, click the Add icon to add more rows or click the Delete icon to delete a row. Note:
You can provide multiple table names for the same SQL filter.
For example, there are two tables called Student and Employee in the target data source, and the following filters are applied:
MISDATE as Today for Student and Employee tables
ID as 1 for the Student table
Then, the Student table will be populated with the MISDATE and ID filters. The Employee table will be populated with only the MISDATE filter.
Note: Global filters are not applicable for those tables on which filters have been applied individually.
If the same table name is provided in more than one row, then the filter condition is generated as a conjunction of all the provided filters.
Data Filter - Hint You can provide database hints at table-level and SQL prescripts at the schema level for data load performance improvement during the workspace population. Additionally, click the Add icon to add more rows or click the Delete icon to delete a row. Select the table and enter source and target hint filters. You can add multiple filters by clicking the Add icon.
Note:
You can also pass runtime values in the workspace population for the user-defined parameters in the Data Filter – Global/Table field.
Example: Table Filter /Global Filter
[{"id":1,"filter":"CUSTOMER_ID =$CUSTID and INCOME =$income and CUSTOMER_NAME =$customerName","tables":["CUSTOMERS"]}]Additional Parameters:
{"fetch_size" :10, "batch_commit_size" :1000, "rejection_threshold" :"UNLIMITED", "write_mode" :"APPEND", "dynamic_parameters": [\{"key":"$CUSTID","value":"125"} ,{"key":"$income$","value":"30000"},{"key":"$customerName","value":"Cust125"}]}The Runtime parameters can be passed on as a part of the additional parameters json .Key = "dynamic_parameters" .It will replace all the $ values in Table filter /Global Filters.
Source Prescript Enter the source prescript of JDBC properties for data upload. Target Prescript Enter the target prescript of JDBC properties for data upload. Fetch Size Enter the Fetch size of JDBC properties for data upload Batch Commit Size Enter the Batch Commit size of JDBC properties for data upload Write Mode You can either overwrite the existing data (truncate and insert) or to append to the existing data. You can choose to either overwrite the data or append to the existing data. Rejection Threshold The following two options are available: - Unlimited - All the errors will be ignored during the data population.
- Custom Rejection Threshold - Enter the maximum of number of inserts that may fail any of the selected tables. You can provide the maximum number of inserts that can fail while loading data to a given table from all the sources. In the case of threshold breach, all the inserts into the particular target schema will be rolled back. However, it will continue populating the next target schema.
- Click Populate Workspace drop-down list to select
between the two options; Create Batch or
Create and Execute Batch. You can create the batch by using Create Batch, or create and execute by using the Create and Execute Batch option. When you select either one of these options, a workspace population task gets added to the batch.
- Create Batch: When you select this
option, it allows you to prepare the batch and then execute or schedule
the batch at a later time through the Scheduler
Service window.
The workspace population task execution can be tracked in the Monitor Batch window in the Scheduler Service.
- Create and Execute Batch: When you select this option, it allows you to create the batch and triggers the batch as well.
- For a workspace population task, you have to mandatory
check the logs to check if the target table is getting populated.
Workspace population logs can be found under:
<MMG_HOME>/OFS_MMG/logs/execution/<MISDATE>/<WORKSPACENAME>/workspace-population/
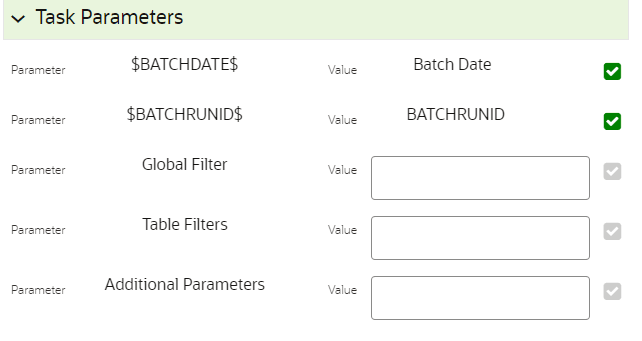
Figure 6-13 Task Parameters
- Create Batch: When you select this
option, it allows you to prepare the batch and then execute or schedule
the batch at a later time through the Scheduler
Service window.
- Enter the following parameters for workspace population. This step is optional.
- Additional Parameters: Enter the Additional Parameters in
following format:
{"fetch_size" :10, "batch_commit_size" :1000, "rejection_threshold" :"UNLIMITED", "write_mode" :"OVERWRITE"} - Global Filter: The provided input will be applied as a data filter on all the tables that are selected for data sourcing.
- Table Filter: You can provide data filters individually on
the tables here. You must provide multiple table names for the same SQL
filter. Global Filters will not be applicable for those tables on which
filters have been applied individually. In case the same table name is
provided in more than one rows here, the filter condition will be
generated as a conjunction of all the provided filters.
Enter the Table filters in following format:
[{"id":1,"filter":"<filter condition>","tables":["TABLE1","TABLE2"]}, {"id":2,"filter":"<filter condition>","tables":["TABLE2"]}]
Note:
You can run a workspace population for a given workspace any number of times. New tables may be added to the definition. Any new table added to the definition, that is not present in the target schema will be physicalized on update of the workspace. You can also add new sources if required.Any table that is deselected from the data sourcing definition will NOT be dropped.
- Additional Parameters: Enter the Additional Parameters in
following format: