Interterminology Mapping
Inter-terminology Mapping provides support for any type of relationship, including equivalence, between two different terminologies. Relationships that can be defined include (but not restricted to) broader-than, narrower-than, and clinical-to-administrative relationships.
Inter-terminology Mapping is implemented using cross maps. A cross map defines the relationship between a source concept and a target concept. A number of cross maps are aggregated into a Map Set. ETS specifies file formats for map sets and cross maps. The HDR Loader job loads these files into ETS tables.
Interterminology Mapping Using Cross Maps
Interterminology mapping provide a mechanism by which concepts from a source version in one terminology can be mapped to concepts from a target version in another terminology. Mappings are typically tailored for a specific application. For example, a data-aggregating or reporting application may require a mapping between specialized SNOMED-CT codes and coarse ICD-9-CM codes. A data retrieval application may use mappings with the opposite semantics (from less granular classifier codes to more detailed codes). These examples serve to illustrate that mappings serve multiple purposes, and not all cross maps indicate equivalence. Those cross maps that truly do indicate equivalence must be explicitly flagged by the author of the cross maps. This section describes the steps you should follow to indicate equivalence between concepts from two different terminologies using interterminology mapping files.
See also:
- The Implementation Guide for a detailed procedure on how to define interterminology mapping using cross maps and how to load the map set files.
Guidelines: Cross Maps
The ETS Cross mapping model is based on the SNOMED CT cross mapping model. Cross-mapping mechanisms provide support for the following:
- Mapping a single concept to a target code (a one-to-one mapping).
- Mapping to a set of Target codes (a one-to-many mapping).
The current structure does not support:
- Mapping a set of Concepts to a Target.
The relationship between these tables is shown by the following chart:
Figure 8-1 ETS Cross Mapping Relationship
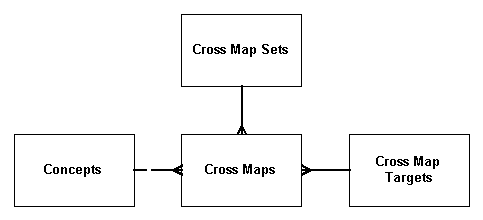
A map set defines a mapping between two coding scheme versions, such as Terminology A version 2003 and Terminology B version 2.01. Each map set is composed of multiple cross maps. Each cross map consists of a source concept and one or more target concepts, such as a source concept from Terminology A and one or more target concepts from Terminology B—to which it maps.
Loading Cross Maps Provided by the College of American Pathologists
The principal difference between cross map files distributed by the College of American Pathologists (with SNOMED CT) and those expected by ETS loaders is that the SNOMED CT files could contain data regarding multiple map sets in a single file. The map set file may contain multiple rows, each pertaining to a different map set. The cross map file may contain cross maps relating to multiple map sets, and the map targets file may contain targets used by multiple map sets (targets related to multiple coding schemes).
To make the SNOMED CT files suitable for ETS loading, split the files into map sets. The map set file should contain only one row, representing one map set. The cross maps file should contain only rows containing the map set ID of the chosen map set. The map targets file should contain only targets related to the target coding scheme specific to the map set.
See also:
- /ets/hdr-ets-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT/db/execute/readme from hdr-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.zip for the cross-map table structures.