1 Implementation Overview
Oracle Retail Data Store (RDS) is a set of infrastructure and tools that allows you to build extensions on top of Retail application data without affecting the original Retail applications. These extensions can consist of database objects, web services, and user interfaces. This Implementation Guide describes the solution and provides information about how you can use RDS.
The core of RDS is a data replication implementation that uses Oracle GoldenGate to replicate application data from Retail applications to a centralized Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW) database. The data is kept in sync with the source application database in near-real-time.
This data is made available through Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) and Application Express (APEX) workspaces. When a retailer subscribes to RDS, they are given the URLs and credentials to access these workspaces.
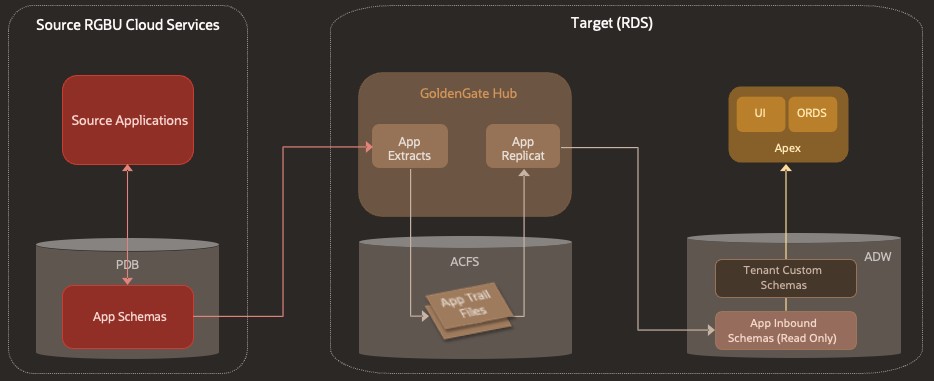
Figure 1-1 Data Replication to RDS via GoldenGate
-
PDB - Pluggable Data Base. The source applications in the RGBU that will be replicating to RDS store their data in pluggable database instances.
-
ACFS - ASM (Automatic Storage Management) Cluster File System. A file system used internally by GoldenGate to store the trail files that hold data replication information.
-
ORDS - Oracle Rest Data Services. An Oracle tool that allows customers to create web services connected directly to data in an Oracle database. RDS customers will use this to create web services to access their custom data.
-
APEX - Application Express. An Oracle tool that allows customers to create UI-based applications connected directly to data in an Oracle database. RDS customers will use this to create appliations that operate on their custom data.
-
ADW - Autonomous Data Warehouse. An Oracle Autonomous Database offering that is tailored toward data warehousing use cases. RDS stores its replicated data and the customer's custom data here.
Support for Audit and Delete Tracking
With basic replication, the data set in the source and target objects match. Records that are, for example, deleted in the source are deleted from the target. Records that are updated in the source are updated in the target, and the previous state of the data is lost. For a subset of products supporting RDS, an additional set of tables are used to track these changes so that custom processes in RDS have visibility to key changes in data. If a table has been marked for audit tracking, every DML operation causes a new record to be inserted into an RDS only audit tracking table. Audit tracking produces a running log of all changes that have been made to the source table. If a table has been marked for delete tracking, when a record is deleted, a new record is inserted into an RDS only delete tracking table. Please refer to the RDS Data Model guide for each supported product to understand if that product supports this feature and to get details on the tables identified for tracking.
Cross Schema Access
The ORDS and APEX workspaces have access to a read-write schema which can view its own application read-only schema's database views as well as view other application read-only schema's database views. In addition, read-write schemas can share custom created objects built upon read-only schema's database views with other read-write schemas.
As an example, Store Inventory Operations Cloud Service's read-write schema, SIOCS_RDS_CUSTOM, has access to the Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service read-only schema's database views. The read-write schema, SIOCS_RDS_CUSTOM, can create custom objects based on the read-only schema's database views owned by both SIOCS_RDS and MFCS_RDS. Inversely Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service's read-write schema, MFCS_RDS_CUSTOM, can create custom objects based on the read-only schema's database views owned by both MFCS_RDS and SIOCS_RDS.