1 Implementation Overview
Oracle Retail Data Store (RDS) is a centralized data infrastructure that consolidates data from one or more Oracle Retail Cloud Services, depending on your subscription. It enables the customization of retail data without modifying the underlying cloud services. See "Data Replication to RDS via GoldenGate".
Your extensions—including database objects, web services, and APEX applications—are built on top of the replicated data, which serves as the foundation for your enhancements. This consolidation is achieved by replicating data from multiple cloud services into a single RDS instance using Oracle’s Golden Gate. Not every database object in the source is replicated. Each Oracle Retail Cloud Service App team selects database objects for replication-based business value and suitability for replication.
This Implementation Guide provides an overview of RDS and explains how you can use it to extend one or more cloud services.
Figure 1-1 Data Replication to RDS through GoldenGate
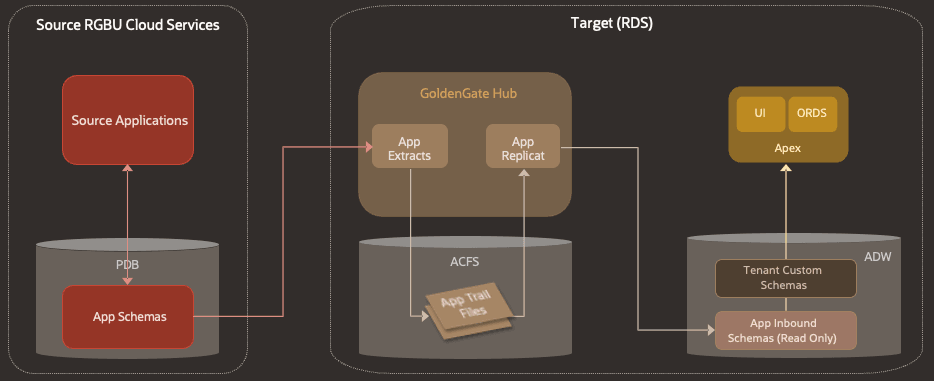
-
PDB - Pluggable Data Base. The source applications in the RGBU that will be replicating to RDS store their data in pluggable database instances.
-
ACFS - Advanced Cluster File System. A file system used internally by GoldenGate to store the trail files that hold data replication information.
-
ORDS - Oracle Rest Data Services. An Oracle tool that allows customers to create web services connected directly to data in an Oracle database. RDS customers will use this to create web services to access their custom data.
-
APEX - Application Express. An Oracle tool that allows customers to create UI-based applications connected directly to data in an Oracle database. RDS customers will use this to create applications that operate on their custom data.
-
ADW - Autonomous Data Warehouse. An Oracle Autonomous Database offering that is tailored toward data warehousing use cases. RDS stores its replicated data and the customer's custom data here.
Schema Architecture
The schema architecture of RDS consists of read-only replicate schemas that mirror source cloud service data and read-write custom schemas for extensions.
-
Replicated data from each cloud service is structured into a primary replicate schema and, if required, one or more auxiliary replicate schemas (only some cloud services require auxiliary schemas).
-
Replicate schemas (both primary and auxiliary) are strictly read-only and mirror the data in the source cloud service.
-
No modifications can be made to replicate schemas in RDS. This includes adding indexes, partitions, or other database objects. It also includes changing history retention rules. RDS will mirror the source cloud service history retention rules.
Each replicate schema (both primary and auxiliary) is linked to a custom schema, which is read-write.
-
Each custom schema is granted
SELECTprivileges on views in all replicate schemas, meaning it can query data from its associated replicate schema and from other cloud services. -
All extensions reside in the custom schema.
Unlike replicate views, custom database objects are not accessible by default to other schemas. The schema owner must explicitly grant access privileges before they can be accessed by other schemas.
Audit and Delete Tracking
By default, basic replication ensures that the source and target datasets remain identical. When a record is deleted from the source, it is deleted from the target. When a record is updated, the previous state is lost, because the target reflects only the most recent changes.
For a subset of RDS-supported products, audit and delete tracking tables provide visibility into historical changes.
-
Audit Tracking: If a table is enabled for audit tracking, every
INSERT,UPDATE, orDELETEoperation inserts a new record into an RDS-only audit tracking table, maintaining a historical log of all changes. -
Delete Tracking: If a table is enabled for delete tracking, whenever a record is deleted from the source, a new record is inserted into an RDS-only delete tracking table instead of being permanently removed.
At this time, only the Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service supports audit and delete tracking.
APEX Workspaces
Each primary custom schema is associated with an APEX workspace.
-
When logging into the APEX UI, you will select a workspace to work within.
-
Your APEX UI session will be connected to the primary custom schema associated with that workspace, providing access to custom objects and replicated views within the RDS environment.
Auxiliary Workspaces
RDS includes three auxiliary APEX workspaces:
-
RDS_CUSTOM_1
-
RDS_CUSTOM_2
-
RDS_CUSTOM_3
These workspaces are isolated environments that do not inherently contain database objects or have access to other schemas. They are intended for sandboxing code, segmenting development efforts, and refining security policies.
Usage and Access Control
Default State:
-
No direct access to any schema objects.
-
No preloaded content or privileges.
Granting Access to Other Schema Objects:
-
Access to specific tables, views, procedures, or packages can be selectively granted from other schemas.
Examples:GRANT SELECT ON schema_name.table_name TO rds_custom_1; GRANT EXECUTE ON schema_name.procedure_name TO rds_custom_1; -
Refining Security and Limiting Access:
-
Access can be restricted to only necessary objects.
-
Views can be used to control data exposure by creating limited result sets.
CREATE VIEW schema_name.view_name AS SELECT column1, column2 FROM schema_name.table_name WHERE condition; GRANT SELECT ON schema_name.view_name TO rds_custom_1;
-
-
Security Considerations
-
Least Privilege Principle: Workspaces should only be granted access to necessary objects.
-
No Direct DML Access: By default, these workspaces should not have
INSERT,UPDATE, orDELETEpermissions unless explicitly required.
-
-
Potential Use Cases
-
Restricted Access: Providing read-only access to custom database objects.
-
Sandboxing Code: Developers can test PL/SQL code or APIs within a controlled environment.
-
Segmentation of Data Access: Access can be granted selectively to different workspaces for different use cases. Privilege Model.
-
Security Refinement: Restrict access to specific views instead of direct table access to improve data governance.
-
Privilege Model
RDS is a SaaS environment that enables the extension of Oracle Retail Cloud Services. RDS follows a fixed privilege and architecture model that cannot be customized. More specifically, its privilege model follows the least privilege principle and cannot be modified.
The RDS privilege model is designed to provide developers with the necessary privileges to:
-
Develop secure applications and services in a controlled environment.
-
Perform diagnostic activities in a live environment when troubleshooting issues.
The same tools and privileges are used for both development and diagnostics. However, while development occurs in a controlled setting, diagnostic activities are performed in a live environment where direct development is not expected.
Developer Access in RDS
There are three broad categories of developers based on how they interact with RDS:
-
Database Developers – Access RDS through the APEX UI or a private endpoint, typically working with PL/SQL and database logic.
-
Report Developers – Access RDS through Oracle Analytics Server (OAS) and focus on authoring reports. Report developers have a role of *ContentAuthor.
-
Report Consumers - Access RDS through OAS and focus on viewing reports. Report consumers have a role of *Consumer.
See the RDS Security Guide for details on user roles.
The privilege models employed for each user category differ in meaningful ways but never exceed the baseline RDS privilege model.
Database Developer Privileges
-
Any database developer with access to a primary custom schema (excluding
RDS_CUSTOM_1,RDS_CUSTOM_2, andRDS_CUSTOM_3) hasSELECTprivileges on all replicated data. -
By default, database developers do not have access to database objects in other custom schemas.
Restrictive Custom Privilege Models
The schemas RDS_CUSTOM_1, RDS_CUSTOM_2, and
RDS_CUSTOM_3 begin with no privileges to other schemas. These
schemas support a more restrictive privilege model than standard RDS. Conceptually, they
serve as Custom Privilege Models 1, 2, and 3, where access can be granted
incrementally.
Report Developer Privileges (Oracle Analytics Server)
The Oracle Analytics Server (OAS) as a development environment is used for constructing reports.
Supported Cloud Services
-
Report developers have
SELECTaccess to all tables and views in RDS, including:-
Replicated data
-
Custom tables and views
-
-
Report developers can be restricted to specific tools:
-
Data Visualization
-
BI Publisher
-
-
Report developers can both create reports and set report permissions, but those permissions encompass either everybody or nobody.
Supported Cloud Services
The supported cloud services are listed in the "Supported Cloud Services" table. Each listed service has a:
-
Cloud service name: the name it is commonly known as
-
A workspace name: the name seen in the APEX UI launch screen
- The primary custom schema name, the schema within which extentions reside
-
The primary replication schema, the schema in which replicated objects reside
-
Auxiliary replication schema, if any
Table 1-1 Supported Cloud Services
| Cloud Service Application | Workspace Name | Primary Custom Schema | Primary Replication Schema | Auxiliary Schema |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merchandising Foundation | MFCS | MFCS_RDS_CUSTOM | MFCS_RDS | |
| Customer Engagement | CE | CE_RDS_CUSTOM | CE_RDS | |
| Store Inventory Operations | SIOCS | SIOCS_RDS_CUSTOM | SIOCS_RDS | |
| Order Broker | OB | OB_RDS_CUSTOM | OB_RDS | |
| XOffice | XO | XO_RDS_CUSTOM | XO_RDS | XO_XADMIN |
| Supplier Evaluation | SE | SE_RDS_CUSTOM | SE_RDS | |
| Brand Compliance | BC | BC_RDS_CUSTOM | BC_RDS | |
| Retail Integration | RICS | RICS_RDS_CUSTOM | RICS_RDS | |
| Supply Chain Hub | RSCH | RSCH_RDS_CUSTOM | RSCH_RDS | |
| Order Administration | OM | OM_RDS_CUSTOM | OM_RDS | |
| N/A | RDS CUSTOM 1 | RDS_CUSTOM_1 | ||
| N/A | RDS CUSTOM 2 | RDS_CUSTOM_2 | ||
| N/A | RDS CUSTOM 3 | RDS_CUSTOM_3 |