Oracle Retail Bulk Data Infrastructure (BDI)
Batch (Bulk) data is still a predominant integration style within Oracle Retail and its customers.
The movement of bulk data remains important because some work is best suited to being performed in bulk. Batch processing was there in the early days; it is still here today; and it will still be here tomorrow. What has changed is the approach to batch processing.
Batch processing is typified by bulk-oriented, non-interactive, background execution. Frequently long running, it may be data or computationally intensive, executed sequentially or in parallel, and may be initiated through various invocation models, including ad hoc, scheduled, and on-demand.
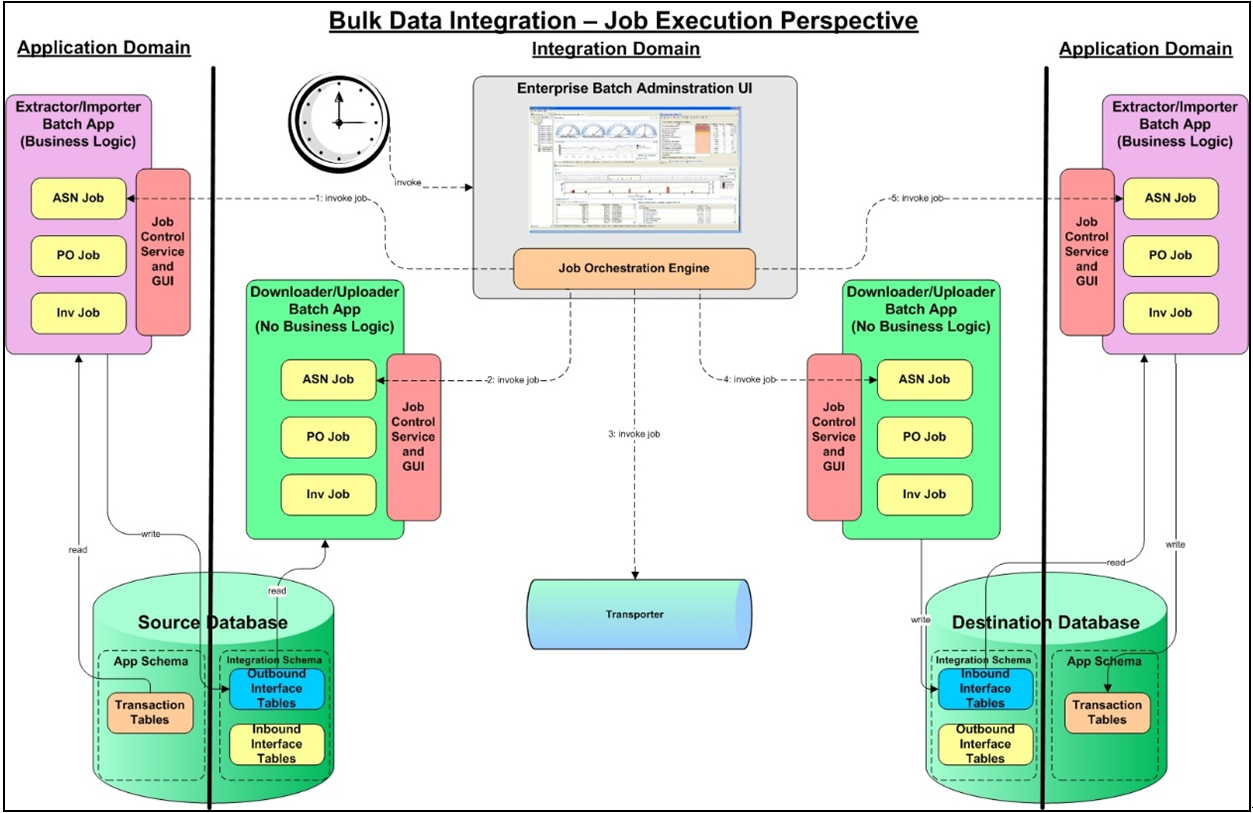
Batch applications have common requirements including logging, checkpoint, and parallelization. Batch workloads have common requirements such as operational control, which allow for initiation of, and interaction with, batch instances; such interactions include stop and restart.
BDI productizes the Oracle Retail bulk data flows for delivery to customers and provides the tooling that is required to automate the creation and packaging of the configurations and to manage the full life cycle.
BDI Responsibilities with Retail Applications
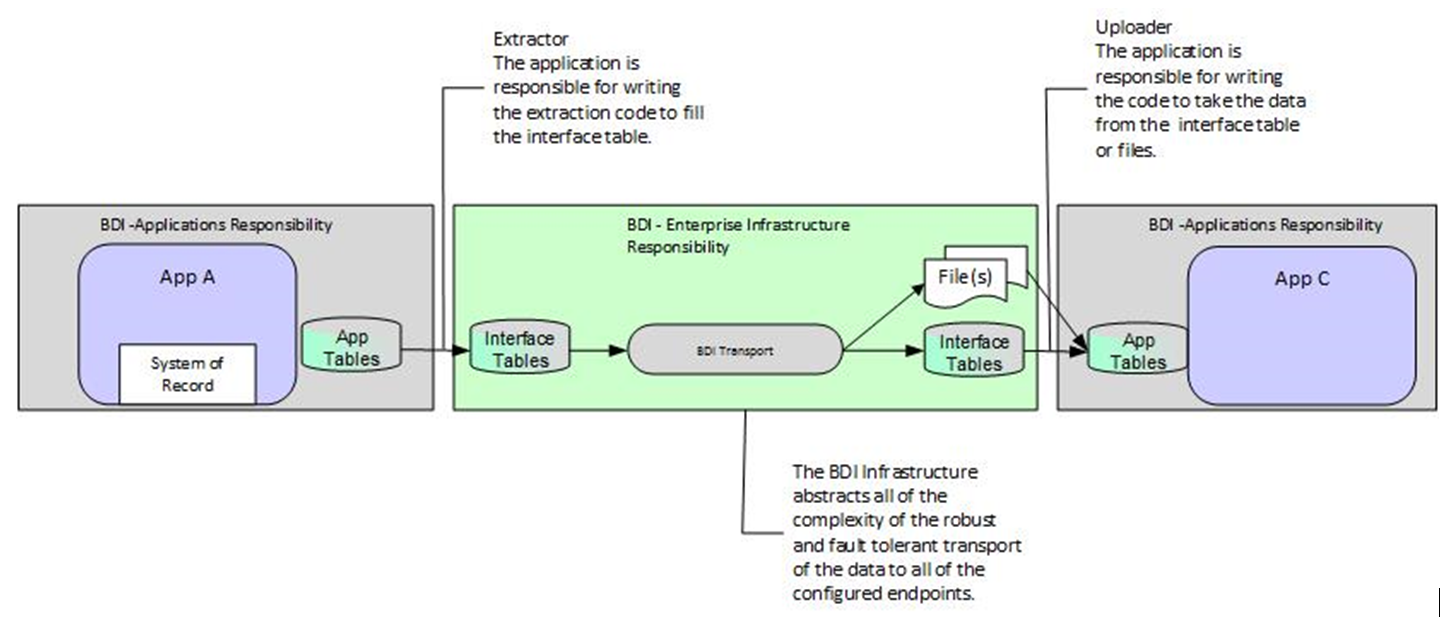
The goal of BDI is to provide an infrastructure to support the movement of bulk data between Oracle Retail applications using an agreed upon standard for the shape of the data produced from an application and delivered to an application.
The agreed upon standard is the shape of the data in the interface table structure and the file format. The standard of truth for both is the same and is described in an XML file that is a governable artifact that is part of the ICB process.
The producer of the data agrees to deliver to the BDI infrastructure Interface Tables the data that is shaped accordingly. The consumers understand that the BDI infrastructure will deliver to the BDI infrastructure interface tables or files that are shaped accordingly.
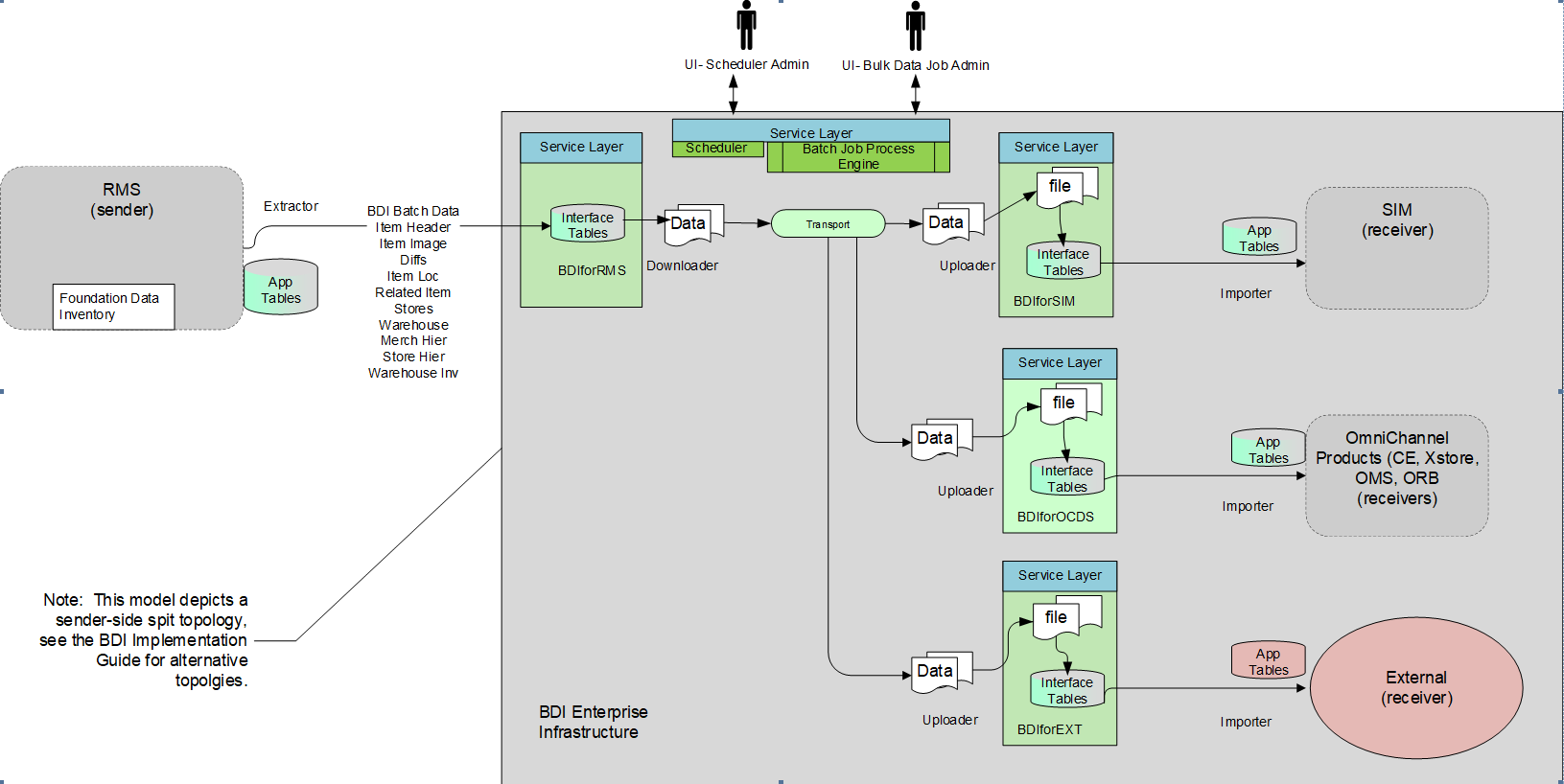
The core responsibility is taking the data published by the sender application and delivering it to all of the receiving applications, regardless if they are deployed on-premise or cloud and to do it in scalable, parallel execution threads with built in failure recoverability and granular job processing.
Figure 3-5 BDI enterprise Infrastructure Topology
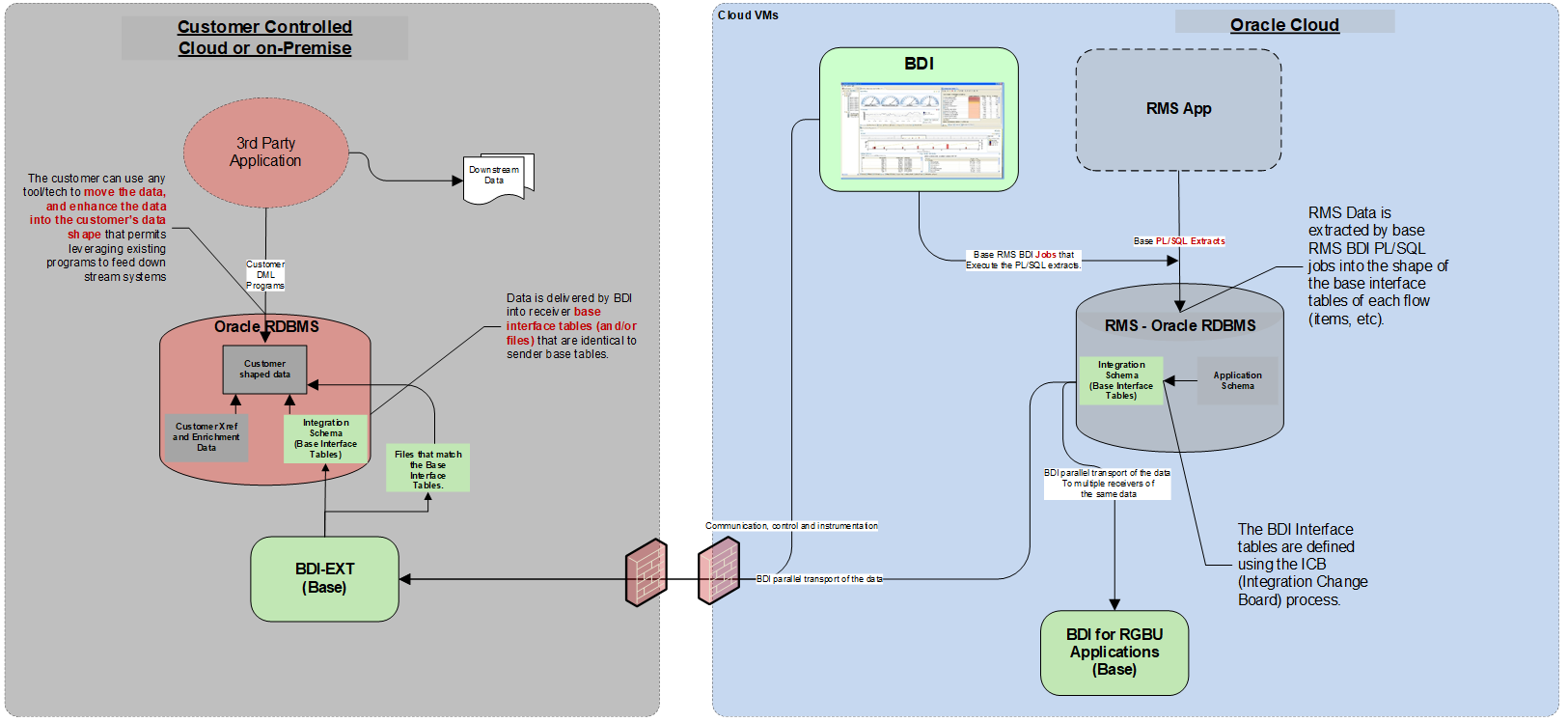
Third Party Integrations
Figure 3-6 BDI Third Party Integrations
The technology used by the sender application and the receiver application to extract and fill the interface tables and to upload the data from the interface tables is a decision made by each of the applications. There are templates and hooks provided to the application's teams to assist in development.
The BDI Infrastructure for each application is an application (BDIforApp) that is built and supplied by the integration team. There is one dedicated to each application and it is responsible for transforming the data to and from the BDI Transport to the integration interface tables or files that are transported to each of the configured receivers.
All BDI Infrastructure components are service enabled.
Figure 3-7 BDI Job Execution Perspective