5 Integration Cloud Services Architecture
Integration Cloud Service is a set of ADF-based Java applications deployed on Oracle's Global Business Unit Cloud Services 3.x Platform Services. The applications are deployed in a highly available, high performance, horizontally scalable architecture. As of release 19.1.000, Integration Cloud Services uses Oracle Identity and Access Management (OCI IAM) as its identity provider (IDP). Information about logical, physical and data architecture in this document focuses on how the architecture supports security.
Note:
Oracle Retail Integration Cloud Services deployment currently on versions 16.0.029 and lower currently use an instance of Oracle Identity Management (IDM) Suite within Integration Cloud Services as an IDP. As these live customers are upgraded to 16.0.030 and transitioned to GBUCS3, their authentication will be transitioned to use OCI IAM. Oracle Retail will not move any user and group information currently in the live SaaS customer's IDM suite to the customer's OCI IAM tenancy.
Architecture
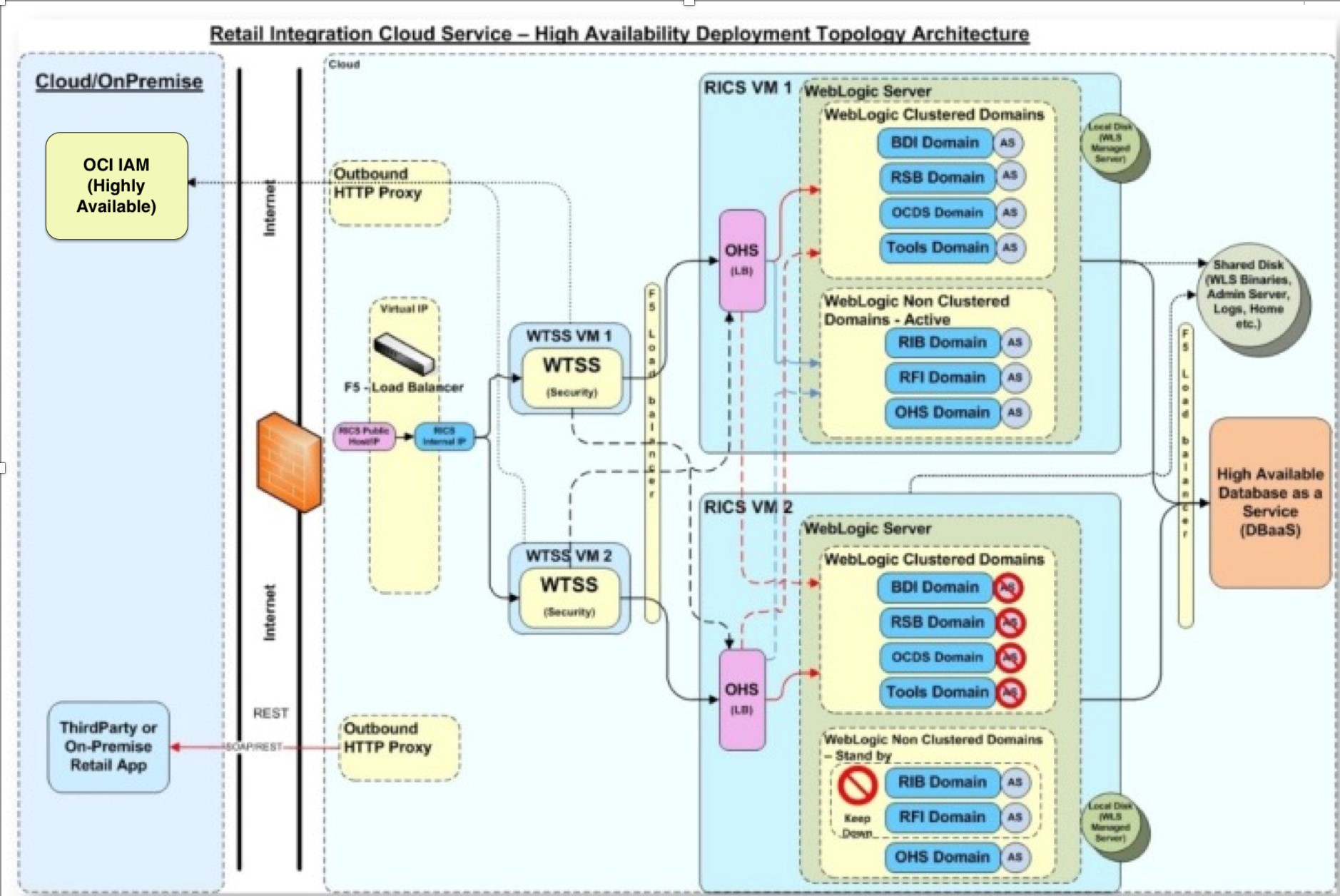
Most customer access to the Integration Cloud Service is via the web tier. The web tier contains the perimeter network services that protect the Integration applications from the internet at large.
All traffic from the web tier continues to the Web Tier Security Server (WTSS), which in turn uses the customer's OCI IAM tenancy to perform authentication. More information about authentication through OCI IAM is provided later in this document.
The application tier consists of several application servers. These servers provide the Integration applications, which allows integration between Oracle retail applications and external applications. Retail Integration Console (RICS) is a UI component that serves as dashboard for the integration. Retail Home is a UI component that can serve as a coordinated dashboard for many Oracle Retail cloud services.
The underlying container DBaaS includes one pluggable database (PDB). Applications are able to access the Integration schema on the Integration PDB. Transparent data encryption (TDE) is set during provisioning. Tablespaces that contain personal data are encrypted.
Integration Cloud Services applications integrate with external business systems via:
-
Native ReST Services
-
SOAP Services
Integration Cloud Services authenticates native rest services using OAUTH2.0 via OCI IAM. As a common authentication pattern is used, web service users are subject to the same strong controls as application users. All rest service calls are logged in the application logs.
Integration Cloud Service is deployed on a collection of single tenant VMs. Each VM resides in an appropriate tier and each tier resides in its own subnet. Communication between tiers within the Integration Cloud Service is limited by subnet ingress security lists.
To reduce attack surface, access to the Integration Cloud Service from the open internet is very limited. Business Users (via web browser) and external web service endpoints access application over https/443. Firewall and load balancer in the DMZ pass traffic to the WTSS server in the Authentication Tier, which in turn to requests authentication (through outbound proxy) from the customer's OCI IAM tenancy.
Within the Integration Cloud Service itself, traffic between tiers is very limited. Authenticated requests are passed from the AuthN Tier to the M-Tier. Access to the underlying DBaaS is only available via the M-Tier.
Outbound web service traffic is routed through the outbound proxy in the DMZ.
A subset of Oracle Retail AMS has very limited access to the underlying DBaaS and M-Tier via Bastion host. This access is limited to a small subset of Oracle employees as described in Oracle's Cloud Hosting and Delivery policy.
https://www.oracle.com/assets/ocloud-hosting-delivery-policies-3089853.pdf