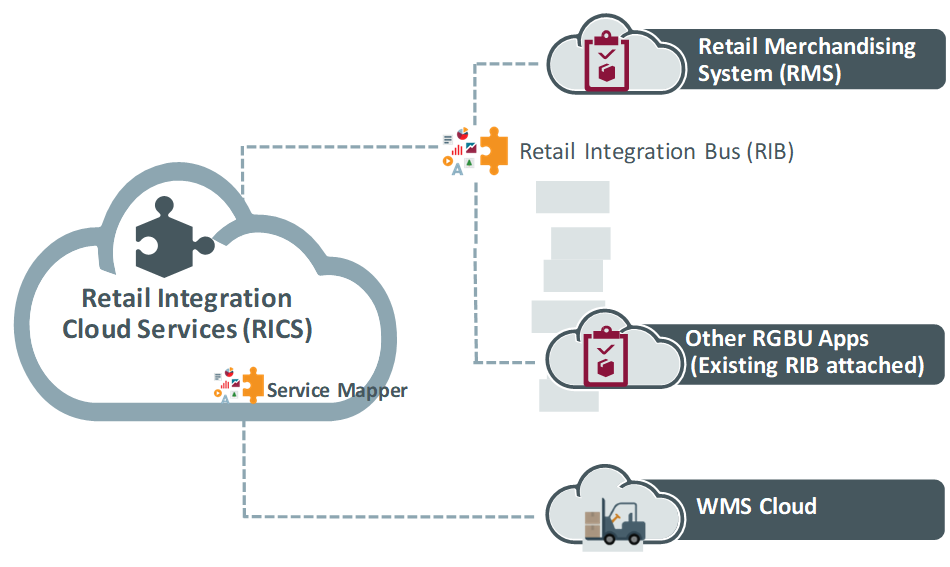
2 Retail Integration Cloud Service Components
Retail Integration Bus (RIB)
The Retail Integration Bus (RIB) is a fire-and-forget, asynchronous messaging backbone and designed as a "Pub/Sub" JMS messaging architecture, with additional application functionality added such as intelligent transformation, routing and error handling.
The RIB has been designed, and proven to handle retail volumes of messages, typically millions during a Tier 1 -Tier 1+ retailer's business day.
The design and architecture of the RIB infrastructure and the Oracle Retail Applications API's are based on two key requirements driven by the Oracle Retail Application's Business process models.
-
Preservation of Publication Sequence. The business event (message) must be delivered to all the subscribing applications in the order (FIFO) the business event (messages) was published by the publishing application.
-
Guaranteed Once-and-only-once Successful Delivery. The RIB must preserve and persist all business events (messages) until all applications (Subscribers) have looked at the message and have successfully consumed it or decided they do not care about that event (message).
The RIB is designed as an asynchronous publication and subscription messaging integration architecture.
The RIB interfaces are organized by message family. Each message family contains information specific to a related set of operations on a business entity or related business entities. The publisher is responsible for publishing messages in response to actions performed on these business entities in the same sequence as they occur.
Each message family has specific message payloads based on agreed upon business elements between the Oracle Retail applications.
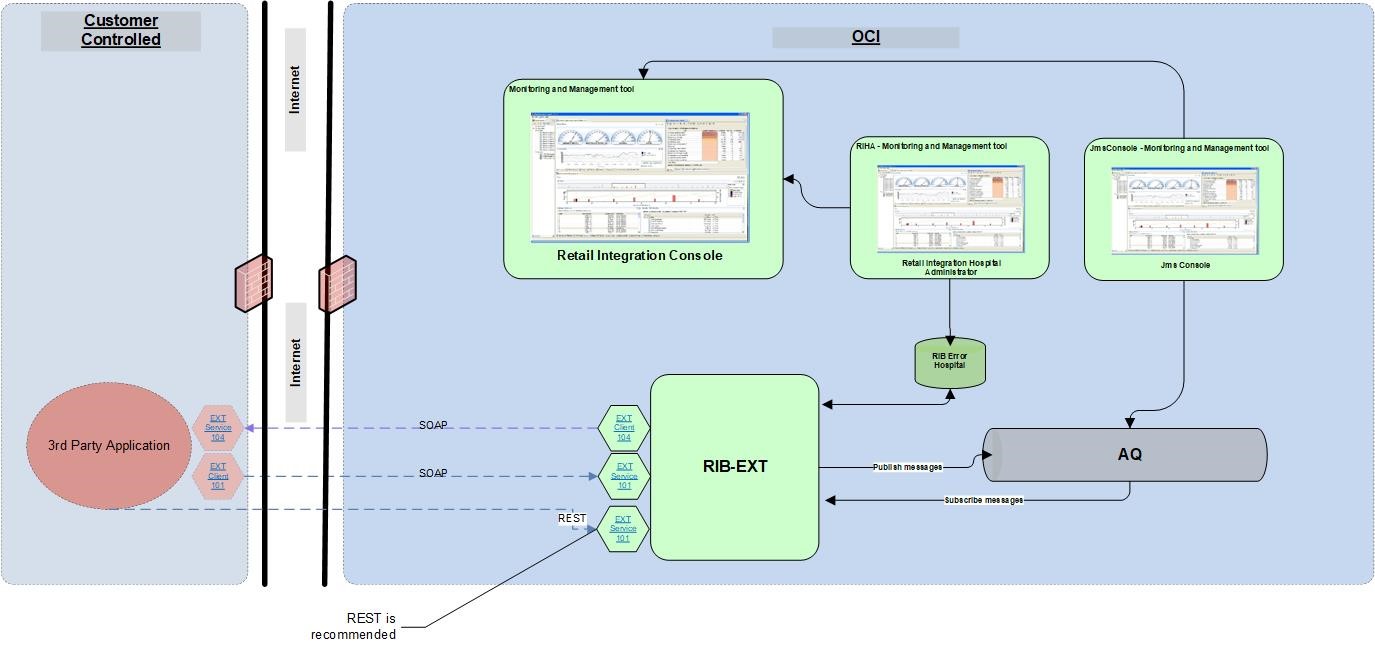
RIB-EXT
Third Party and Legacy Integration has been the corner stone of the Enterprise Integration components. To that end there are cloud focused enhancements to RIB and RIB-EXT.
RIB-EXT completes the ability of the Integration Cloud Service to expose the RIB as REST and SOAP services to 3rd Party deployed on-prem or in other cloud deployments.
RIB-EXT is a deployment time configurable component that supports pub/sub to/from the RIB and an external application by exposing the RIB as SOAP services to Retail Applications and third party deployed on-premises or in other cloud deployments.
-
RIB-EXT has all of the RIB flows available for the deployment time configuration based on the customer use cases.
-
RIB-EXT configuration is performed based on the customers use cases for data to and from the RIB.
Figure 2-1 RIBforEXT Information Flow
Oracle Retail Bulk Data Infrastructure (BDI)
Batch (Bulk) data is still a predominant integration style within Oracle Retail and its customers. The movement of bulk data remains important because some work is best suited to being performed in bulk. Batch processing was there in the early days; it is still here today; and it will still be here tomorrow. What has changed is the approach to batch processing.
-
BDI Architecture and Design is to be On-Premise and Hybrid Cloud ready.
-
Lightweight UI's and services provide full coverage and are both customer facing and operations facing.
-
-
BDI Provides a fully service enabled, fault tolerant, concurrent, high throughput infrastructure
-
BDI Transport layer moves data via services, not files.
-
Provides integration job process scheduling and is fully instrumented to provide end-to-end visibility and re-startability.
-
Automated restart recovery at a granular level.
BDI-EXT
BDI is an integration infrastructure product which can integrate Oracle Retail applications to third party applications. BDI external application is designed to address the complexities for third party integration with Oracle Retail application. In BDI, bulk data movement happens between sender and receiver application. External application can only be a receiver.
Please refer to the Oracle Retail Bulk Data Integration Guide – Concepts for the details
BDI is an integration infrastructure product which integrates Oracle Retail applications and third-party applications. BDI Bulk Data Export Service is designed to address the complexities for third party integration with Oracle Retail application. In BDI, bulk data movement happens between sender and receiver application.
Please refer to the Oracle Retail Bulk Data Integration Guide – Integration with External Applicationsfor the details
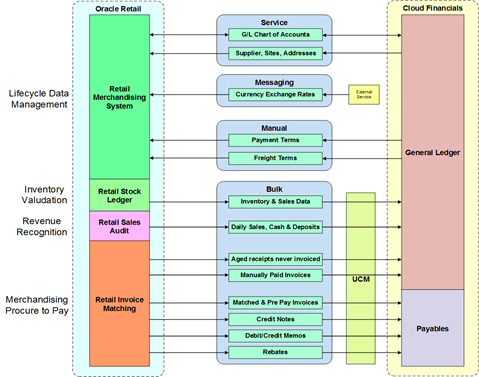
Retail Financial Integration (RFI)
The Oracle Retail Financial Integration (RFI) for E-Business Suite (EBS) / PeopleSoft Financials / CFIN provides integration to a robust enterprise financial system to complement the Oracle Retail Merchandising system in a retail customer environment.
Universal Service Mapper (USM)
The Universal Service Mapper (USM) is an application component of Retail Integration Cloud Service (RICS) that allows the definition, mapping, and configurations needed to support the integration between two heterogeneous applications. Typically this would be an Oracle Retail Application such as RMS, found in the Merchandise Foundation Cloud Service, and an application external to Oracle Retail such as Oracle Warehouse Management CS.
RICS USM supports two of the styles of integration used within Oracle Retail; message-based and service-based as inputs. Within the RGBU applications the message-based flows are across the RIB. It is typical that external applications are predominately service-based so the output of USM is a call is to an external service.
Service calls from an external service are transformed to the correct style and format of the internal application.
The functional requirement for the USM is to act as the place to transform the Oracle Retail application data style and the data format into the data format expected by the external application, and then to perform the transformations of the external application's response.
Figure 2-3 USM Process Flow
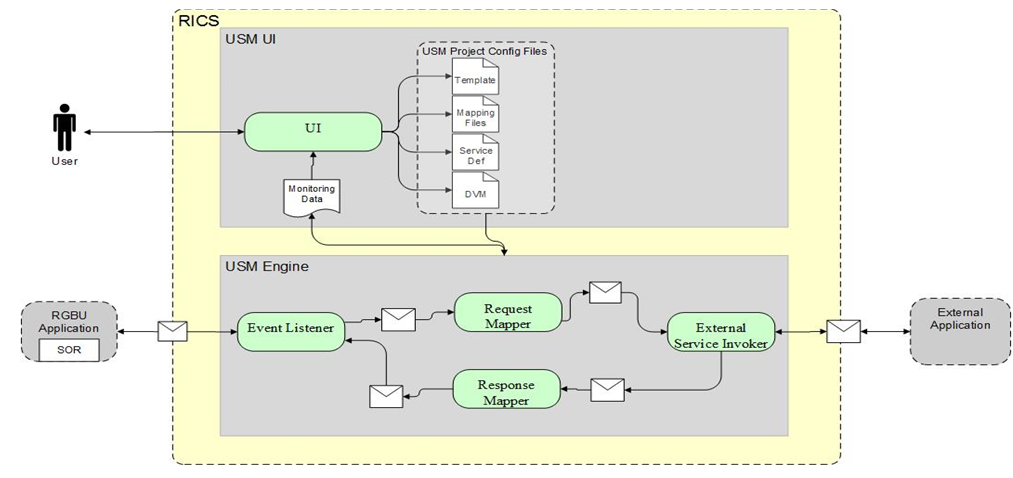
The USM User Interface provides the ability to create and manage Projects in USM and to view app statistics, metrics about the message flow and the system Logs
The USM Engine is the logic part of the system where the data is received from one application, mapped to other data and the mapped data is sent to other applications. Data is communicated through service calls.
-
USM hosts all the necessary web-services that are required by both the participating sender and the receiver applications.
-
USM has a configuration file of the service URLs to the participating applications.
-
USM has templates that contains the mapping information, the code that does the mapping and other configuration files to make the application work.
USM Architecture
Figure 2-4 USM Architecture
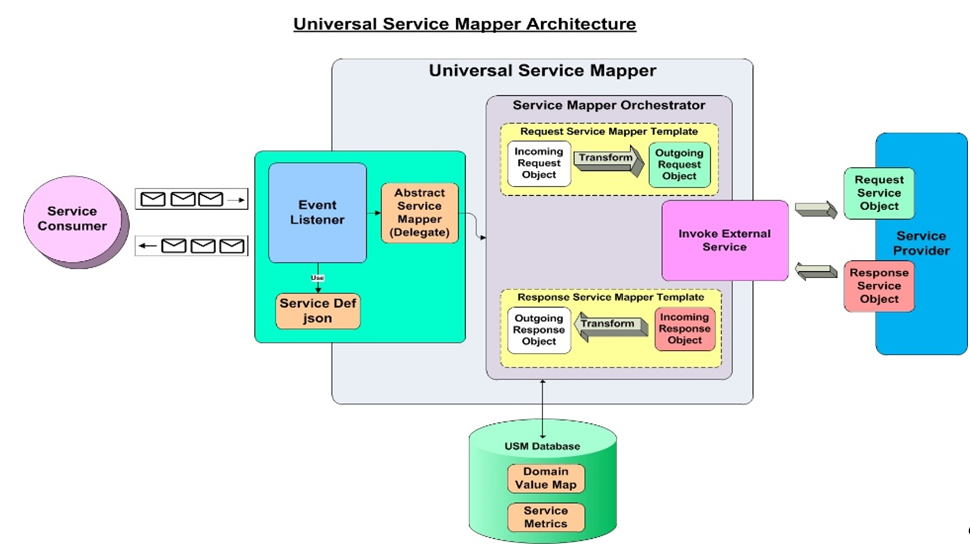
Universal Service Mapper has three major components:
-
Event Listener [Abstract Service Mapper, Service Def JSON]
-
Service Mapper Orchestration [Orchestrator, Template and DVM]
-
External Service Invocation and Service Provider
Event Listener
The Event listener is a service hosted by the USM application which is open to receiving data from any application that is connected to it. The application here is either RIB-LGF or WMS Cloud. The applications have the following URL pattern set in their target for USM.
http://<host>:<port>
When application sends data, the event listener internally calls the abstract service mapper which determines family, message type and the operation(s) from the message received by referring to the Service Def JSON file.
Service Mapper Orchestration
The abstract service mapper in turn now calls the Service mapper orchestrator which decides which what data is to be populated in the mapper templates. The orchestrator does the mapping, field by field, from the source application to destination application. Certain key-value pairs in the DVM in order to maintain context between the applications.
Service Provider and External Services
The Service Mapper Orchestrator calls the services hosted by the service providers after the mapping operations are completed. The service providers here are either RIB-LGF or WMS Cloud, which consume these services via USM. The calls are REST calls. USM holds the information necessary for it to call these services in a file with the prefix "external_env_json" for the respective application. These are stored as key-value pairs in JSON file
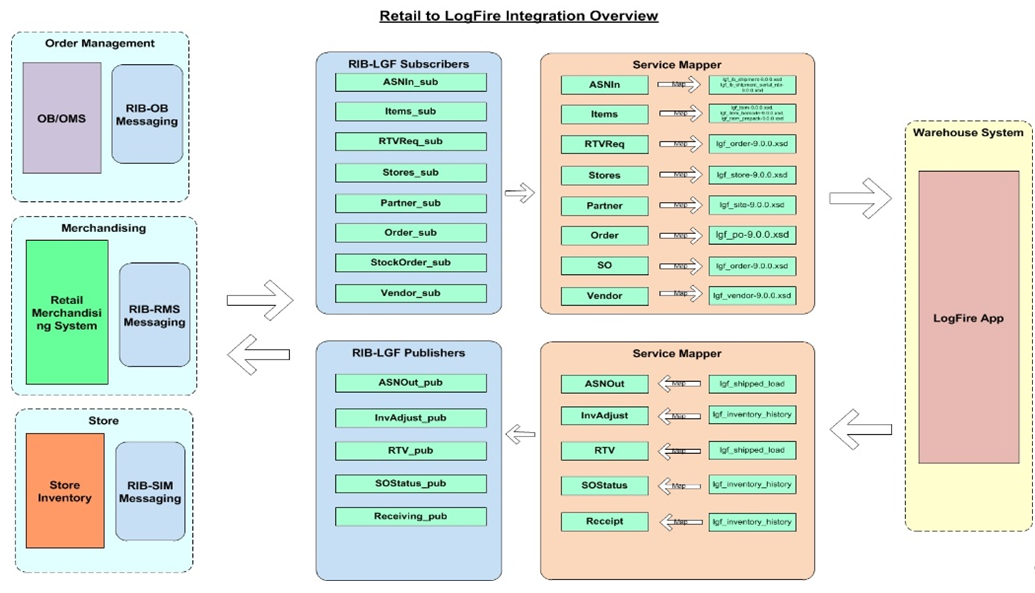
Oracle Warehouse Management CS (Logfire) Integration
Retail Integration Cloud Service (RICS) is used to integrate MFCS to Oracle Warehouse Management Cloud (WMS - LogFire).
RICS uses Universal Service Mapper (USM) to perform the mappings required to connect RICS payloads/services to LogFire interfaces. USM is used to transform and manage the integration flows in both directions.
Figure 2-5 WMS-RICS Mappings