Provision Oracle Exadata Database Service in Oracle Database@AWS
Introduction
Oracle Database@AWS is a strategic partnership between Oracle and Amazon Web Services (AWS) that enables applications running in AWS Regions to use Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure running on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) in AWS. AWS applications and services such as Amazon Kinesis and Amazon QuickSight can now have low-latency, native access to Oracle databases running on Oracle Exadata Cloud Infrastructure and take advantage of Oracle Database 23ai features like AI Vector Search.
Like other AWS resources, the Oracle Database@AWS architecture requires an Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to provide networking for application resources within an AWS Region. An application hosted within the VPC communicates with Oracle Database@AWS within the ODB network using the ODB peering connection in the same availability zone. This configuration enables a direct, secure, and low latency connection between applications in the VPC and Oracle Database@AWS. In addition, Oracle Database@AWS operating in an OCI child site collocated in the same AWS Region has an OCI Virtual Cloud Network (VCN) that extends to the parent OCI region to enable access to other resources in OCI. OCI manages the network between the OCI child site and the parent OCI region. AWS manages the network connection between the ODB network and the application VPC.

Leveraging AWS and OCI automation, it is easy to start running Oracle Exadata Database Service in Oracle Database@AWS. Provisioning Oracle Exadata Database Service requires the following four simple tasks:
- Create the ODB network.
- Create the Exadata Infrastructure.
- Create an Exadata VM cluster in the Exadata Infrastructure.
- Create an Oracle Database in an Exadata VM cluster.
Objectives
- Provision ODB network, Exadata Infrastructure, Exadata VM cluster and Oracle Database 23ai.
Task 1: Create the ODB Network
An ODB network is a private isolated network that hosts OCI infrastructure in an AWS availability zone (AZ). The ODB network consists of a CIDR range of IP addresses. The ODB network maps directly to the network that exists within the OCI child site, thus serving as the means of communication between AWS and OCI.
Note: You will require an AWS account and request a private offer for Oracle Database@AWS from AWS Marketplace.
-
Log in to the AWS Management Console and open the Oracle Database@AWS Console using
https://console.aws.amazon.com/odb/. -
Click ODB networks and Create ODB network or directly click Create ODB network under Step 1.

-
In the Create ODB network page, enter ODB network name, Availability Zone, Client subnet CIDR, Backup subnet CIDR and Domain name prefix.

-
Click Create ODB network.
-
You can set up peering between an ODB network and a VPC, which enables applications to connect to your Exadata Database. After ODB peering is set up, EC2 instances or applications in the VPC can connect to Exadata Databases in the ODB network.

Task 2: Create the Exadata Infrastructure
Oracle Exadata Database Service colocated in AWS supports dedicated Exadata Infrastructure with a minimum configuration of 2 and maximum of 32 database servers and 3 storage servers up to 64, that are internally connected by a high-speed, low-latency internal Remote direct memory access (RDMA) network fabric that requires no configuration. Exadata Infrastructure within an AWS data center integrates the hardware with the networking resources needed to securely connect to other services in the cloud. With Oracle Exadata Database Service, Oracle performs monthly security and quarterly infrastructure updates. You can specify the quarterly infrastructure maintenance schedule that meets your business requirements.
-
To create the Exadata Infrastructure, select Exadata Infrastructures and click Create Exadata Infrastructure.
Note: Assume that your OCI tenancy has been linked through the private offer.

-
In Step 1 - Configure general settings, enter Exadata infrastructure name, select Availability Zone where the Exadata Infrastructure will be provisioned in, and click Next.

-
In Step 2 - Configure Exadata Infrastructure, indicate the Exadata Infrastructure shape. The minimum configuration is already filled in for you with two Database servers and three Storage servers. You can have up to 32 database servers and 64 storage servers on a single Exadata Infrastructure, and then click Next.
Note: Make sure the limits for the number of database and storage servers has been set within your OCI linked tenancy.

-
In Step 3 - Configure maintenance and tags, all fields are optional. Select the maintenance window of Oracle-managed schedule or Customer-managed. With Customer-managed you can choose the month in the quarter, week of the month, day of the week, starting hour, and how long in advanced you want to be notified based on your business requirements.
Patching mode allows you to specify rolling or non-rolling maintenance and you enable a timeout period before maintenance starts on the database server to allow you to perform manual checks or run scripts.
You can enter up to 10 email addresses that will be notified of upcoming maintenance updates. Optionally, you can add Tags to be used to search and filter your AWS resources or track AWS costs, and then click Next.
Note: Infrastructure maintenance scheduling can be updated from the OCI Console.

-
In Step 4 - Review and create, review the Exadata Infrastructure configuration.
You can click Cancel to cancel the creation of the Exadata Infrastructure, Previous to go back and update values, Create Exadata Infrastructure to proceed with the creation.

-
After the Exadata Infrastructure is successfully created, you can see the following information.
-
Summary: View the configuration of the Exadata Infrastructure.
- Database servers: View database servers and resources.
- Exadata VM clusters: View Exadata VM clusters that have been created in this Exadata Infrastructure.
- Autonomous VM cluster: View Autonomous VM clusters that have been created in this Exadata Infrastructure.
- OCI maintenance: Link to OCI Console to update the Exadata Infrastructure maintenance schedule.
- Tags: View tags that have been associated with this Exadata Infrastructure.
-
OCI resources: Find a link to access the OCI Console directly for this Exadata Infrastructure

-
Task 3: Create an Exadata VM Cluster in the Exadata Infrastructure
Each Exadata Infrastructure database server contains one or more virtual machine (VM) guests. With support for multiple virtual machine clusters (MultiVM), you can support up to eight VMs per database server and host a total of eight VM clusters per Exadata database system. When you provision the VM cluster, you specify system resources allocated to the VM clusters that will support your Oracle database workloads.
-
To create an Exadata VM cluster, select Exadata VM clusters and Create VM Cluster.

-
In Step 1 - Configure general settings, enter VM cluster name, confirm Time zone, License options and click Next.

-
In Step 2 - Configure infrastructure settings, enter the following information and click Next.
-
Exadata infrastructure name: Select the Exadata Infrastructure the VM cluster will be created on.
-
Grid Infrastructure version: Select the Oracle Grid Infrastructure version of the release (19c and 23ai) you want to install on the VM cluster.
Note: The Oracle Grid Infrastructure release determines the Oracle Database releases that can be supported on the VM cluster. For example, you cannot run an Oracle Database release that is newer than the Oracle Grid Infrastructure software release.
-
Exadata image version: Select the Exadata system software version. This determines Operating System (OS) version and features available in the guest VM image.
-
Database servers: Select the DB server(s) the VM image will be created on.
-
Configuration Allows you to allocate resources to your VM. Enter the following information.
-
CPU core count: Enter OCPU count per VM to allocate that number of OCPUs to each of the VM clusters’ virtual machine compute nodes. Minimum is two OCPUs per VM.
-
Memory: Enter the memory per VM to allocate to each VM. The minimum per VM is 30 GB.
-
Local Storage: Enter the local storage per VM to allocate local storage to each VM. The minimum per VM is 60 GB.
Note: Each time you create a new VM cluster, the space remaining out of the database server local space is utilized for the new VM cluster.
-
Enter Per cluster Exadata storage in multiples of 1 TB. The minimum is 2 TB.
-
Storage allocation:
-
Enable storage allocation for local backups: Select if you intend to perform database backups to the local Exadata storage within your Oracle Exadata Cloud Infrastructure instance. The storage configuration option for local backups cannot be changed after VM cluster creation.
-
Enable storage allocation for Exadata sparse snapshots: Select if you intend to use snapshot functionality within your VM cluster. The storage configuration option for sparse snapshots cannot be changed after VM cluster creation.
-
-

-
-
In Step 3 - Configure connectivity, select ODB network created in Task 1, enter a Host name prefix, SSH key pairs used to access the VM cluster.
You can click Cancel to cancel the creation of the VM cluster, Skip to Review and Create to skip the step, Previous to go back and update values, or Next to proceed with the VM cluster configuration.

-
In Step 4 - Configure diagnostics and tags, this step is optional. By enabling OCI diagnostic collection, Oracle Cloud operations and you will be able to identify, investigate, track, and resolve guest VM issues quickly and effectively. Subscribe to events to get notified about resource state changes.
Note: You can opt out of this feature at any time.
You can add Tags to be used to search and filter your AWS resources or track AWS costs and click Next.

-
In Step 5 - Review and create, review the VM cluster information and click Create VM Cluster.

-
After the VM cluster is successfully created, you can see the following information.
-
Summary: View the configuration of the VM cluster.
- Configuration: View VM cluster configuration.
- Connectivity: View the network configuration and SSH key pairs.
- Tags: View tags that have been associated to this Exadata Infrastructure.
- Monitoring: View the VM cluster metrics such as CPU utilization, load average, memory utilization, and more.
-
OCI resources: Find a link to jump to the OCI Console directly to this VM cluster and the Exadata Infrastructure.

-
Task 4: Create Oracle Database
-
Oracle Database creation is managed from the OCI Console. With the tight integration between OCI and AWS, a direct link is available from the AWS Management Console. Click VM cluster name or Manage in OCI.

-
Oracle Database is a VM cluster resource. In the Exadata VM Cluster Detail page, click Databases and Create database.


-
In the Basic information for the database section, enter the following information.
-
Provide the database name: Enter the database name.
Note: You need to meet the following requirements.
- Maximum of eight characters.
- Contain only alphanumeric characters.
- Begin with an alphabetic character.
- Cannot be part of the first eight characters of a
DB_UNIQUE_NAMEon the VM cluster.
-
Provide a unique name for the database (Optional): If not specified, the system automatically generates a unique name value, as
<db_name>\_<3_chars_unique_string>\_\<region-name\>.Note: If you enter a unique name, you need to meet the following requirements.
- Maximum of 30 characters.
- Contain only alphanumeric or underscore (
_) characters. - Begin with an alphabetic character.
- Unique across the VM cluster. Recommended to be unique across the tenancy.
-
Select a Database version: Select a database version.
-
Provide a PDB name (Optional):. If not specified, the system automatically generates a name value.
Note: You need to meet the following requirements.
- Maximum of eight characters.
- Contain only alphanumeric or underscore (
_) characters. - Begin with an alphabetic character.
- To avoid potential service name collisions when using Oracle Net Services to connect to the PDB, ensure that the PDB name is unique across the entire VM cluster.
-
Database Home source: Select database home source.
- Select an existing Database Home.
- Create a new Database Home and enter Database Home display name.
-
Enable database Unified Auditing
-
Database Image (Optional): Database image to use a desired Oracle-published image or a custom database software image that you have created in advance.

-
-
In the Create administrator credentials section, create administrator credentials for sys password.
-
Password: Enter password.
Note: You need to meet the following requirements.
- Must be 9 to 30 characters.
- Contain at least two uppercase, two lowercase, two numeric, and two special characters. The special characters must be (
_), (#), or (-). - The password must not contain the username (
SYS,SYSTEM, and so on) or the word Oracle either in forward or reversed order and regardless of casing.
-
Confirm password: Confirm the sys password you specified.
-
(Optional) Select Use the administrator password for the TDE wallet.

-
-
In the Configure database backups section, configure database backups by specifying the settings for backing up the database to OCI Object Storage.
- Enable automatic backup: Select to enable automatic backups for this database.
- Backup Destination: Backup destination default is Amazon S3.
- Deletion options after database termination: Specify backup retention if database is terminated
- Schedule day for full backup: Select day of week for the full backup to run
- Schedule time for full backup: Select the window of time for the full backup to run
- Schedule time for incremental backup: Select the window of time for the incremental backup to r

-
Click Show advanced options.
-
In the Management section, enter the following information.
-
Oracle SID prefix (Optional): Oracle SID prefix is the Oracle Database instance number and is automatically added to the SID prefix to create the
INSTANCE_NAMEdatabase parameter. TheINSTANCE_NAMEparameter is also known as the SID. The SID is unique across the cloud VM cluster. If not specified, SID prefix defaults to thedb_name.Note: You need to meet the following requirements.
- Maximum of 12 characters.
- Contain only alphanumeric or underscore (
_) characters. - Begin with an alphabetic character.
- Unique in the VM cluster.
-
Character set: Character set for the database. The default is AL32UTF8.
-
National character set (Optional): National character set is the national character set for the database. The default is AL16UTF16.

-
-
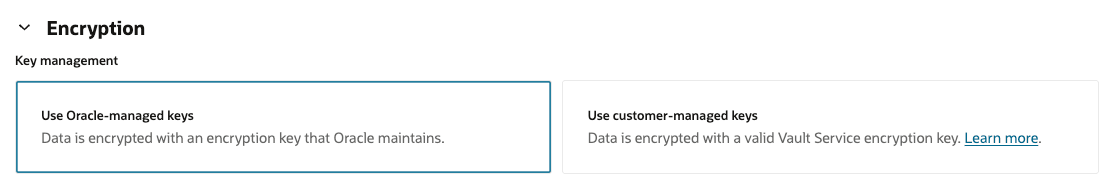
In the Encryption section, to manage your database keys select Use Oracle-managed keys or Use customer-managed keys. For more information about the options to manage your database keys, see Security Guide for Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
-
In the Tags section, select Tag namespace. Tagging allows you to define Tag key(s) and Tag value(s) and associate them with resources. You can then use the tags to help you organize and list resources based on your business needs. For more information about tags, see Tagging Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure Resources.

-
-
Click Create Database to proceed with the Oracle Database provisioning.

Next Steps
You are now ready to migrate your data to your new Oracle Database. Take a look at Oracle Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM) to help you with your migration needs.
Related Links
-
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure Overview
-
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure How To’s Video Playlist
Acknowledgments
- Authors - Tammy Bednar, Leo Alvarado (Product Management)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Provision Oracle Exadata Database Service in Oracle Database@AWS
G20569-06
Copyright ©2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates.