Set Up the OCI Native Ingress Controller on OCI Kubernetes Engine with Virtual Nodes
Introduction
This tutorial walks through the process of setting up the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) native ingress controller on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Kubernetes Engine (OKE) with a virtual nodes node pool. Virtual nodes are different from regular instance-based worker nodes because they are a serverless solution that abstracts away the underlying compute instances. Unlike traditional worker nodes, which rely on specific virtual machine instances, virtual nodes dynamically scale based on workload demands and do not require manual management of the underlying infrastructure. This makes them ideal for workloads that need automatic scaling and reduced operational overhead.
In this tutorial, we will set up the OCI native ingress controller on OKE using virtual nodes. We will configure workload identity policies, enable the ingress add-on, and deploy ingress resources with Kubernetes manifests.
By following these tasks, you can expose your applications and manage ingress traffic using OCI Load Balancer capabilities, all while leveraging the operational simplicity of virtual nodes. This setup streamlines traffic management and supports production-grade workloads in a scalable, cost-efficient manner.
Objectives
- Set up and configure the OCI native ingress controller on OKE to manage ingress resources efficiently.
Task 1: Create Workload Identity Principal Policy
Before enabling the OCI native ingress controller, create a workload identity principal policy. Virtual nodes are serverless and do not use OCI Compute instances, so they require workload identity instead of instance principals. This policy lets the ingress controller manage resources in your compartment.
-
Go to the OCI Console, navigate to Identity & Security, Identity and click Policies.
-
Create a policy and enter a policy name. For more information, see Create a Policy using OCI Console.
-
Click Show manual editor and enter the following policy statements, replacing the
locationandcluster-ocidwith your specific values.Note:
<location>should be replaced with the compartment where your resources are located.<cluster-ocid>should be replaced with the OCID of your OKE cluster.
Allow any-user to manage load-balancers in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to use virtual-network-family in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage cabundles in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage cabundle-associations in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage leaf-certificates in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to read leaf-certificate-bundles in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage leaf-certificate-versions in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage certificate-associations in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to read certificate-authorities in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage certificate-authority-associations in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to read certificate-authority-bundles in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to read public-ips in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage floating-ips in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to manage waf-family in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to read cluster-family in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'} Allow any-user to use tag-namespaces in <location> where all {request.principal.type = 'workload', request.principal.namespace = 'native-ingress-controller-system', request.principal.service_account = 'oci-native-ingress-controller', request.principal.cluster_id = '<cluster-ocid>'}
Task 2: Enable OCI Native Ingress Controller Add-On
Once the required workload identity principal policy is in place, you can proceed to enable the OCI native ingress controller add-on for your OKE cluster. This add-on allows the use of an OCI Load Balancer to manage ingress traffic efficiently.
-
Navigate to your OKE cluster in the OCI Console.
-
Scroll down and click Add-ons.
-
In the Add-ons page, click Native Ingress Controller.
-
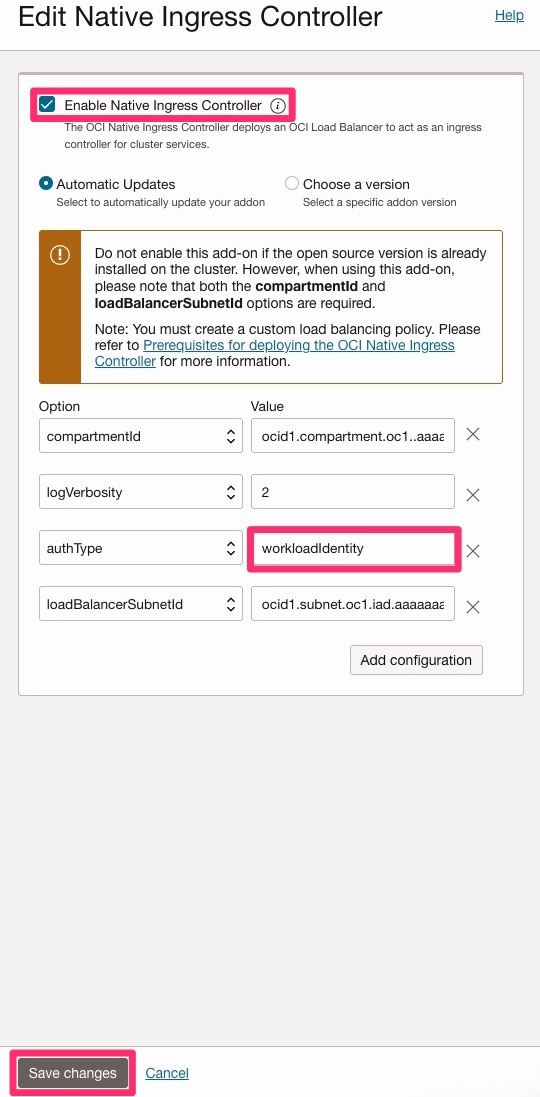
In the Edit Native Ingress Controller page, select Enable Native Ingress Controller and enter the following information under Option.
compartmentId: Enter your compartment OCID.loadBalancerSubnetId: Enter your load balancer subnet OCID.authType: EnterworkloadIdentity.
-
Click Save changes to apply the settings.
Note: This configuration is required for virtual node pools, as mentioned previously they are serverless and do not support instance principal authentication. Workload identity is the supported authentication method in this case.
Task 3: Deploy Ingress Resources to Enable Native Ingress Functionality
In this task, create the required Kubernetes resources to enable ingress functionality using OCI native ingress controller. These include the IngressClassParameters, IngressClass, and the actual Ingress object.
-
Review the purpose of each resource.
- IngressClassParameters: Specifies OCI specific config like compartment OCID, subnet, and bandwidth.
- IngressClass: Links Kubernetes ingress functionality to OCI’s ingress controller.
- Ingress: Defines how traffic is routed to your services.
-
Replace placeholder values in the YAML.
- Replace
<your compartment ocid>with your actual Compartment OCID. - Replace
<your load balancer subnet ocid>with the OCID of your Load Balancer subnet.
- Replace
-
Apply the YAML manifest. Save the following YAML code to a file, for example
native-ingress.yaml.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: test-web-app namespace: default spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: test-web template: metadata: labels: app: test-web spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx:latest ports: - containerPort: 80 readinessProbe: httpGet: path: / port: 80 initialDelaySeconds: 3 periodSeconds: 5 resources: requests: cpu: "100m" memory: "128Mi" limits: cpu: "500m" memory: "256Mi" apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: test-web-service namespace: default spec: selector: app: test-web ports: - protocol: TCP port: 80 targetPort: 80 apiVersion: ingress.oraclecloud.com/v1beta1 kind: IngressClassParameters metadata: name: native-ic-params namespace: native-ingress-controller-system spec: compartmentId: "ocid1.compartment.oc1..aaaaaaaa2eimxxxxxxxxxxz4lkcety52hfdg6wdoff6744yn4hrshofla" subnetId: "ocid1.subnet.oc1.iad.aaaaaaaaa72ie4xxxxxxxxxrxxrly6nmkb77qxt6mi2t5pvrdhge32q" loadBalancerName: "test-web-ingress" isPrivate: false maxBandwidthMbps: 400 minBandwidthMbps: 100 apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: IngressClass metadata: name: native-ic-ingress-class annotations: ingressclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true" spec: controller: oci.oraclecloud.com/native-ingress-controller parameters: apiGroup: ingress.oraclecloud.com kind: IngressClassParameters name: native-ic-params scope: Namespace namespace: native-ingress-controller-system apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: test-web-ingress-quickstart namespace: default annotations: oci.oraclecloud.com/load-balancer-type: "lb" oci.oraclecloud.com/healthcheck-protocol: "HTTP" oci.oraclecloud.com/healthcheck-port: "80" oci.oraclecloud.com/healthcheck-path: "/" oci.oraclecloud.com/healthcheck-return-code: "200" spec: ingressClassName: native-ic-ingress-class rules: - host: test.example.com http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: test-web-service port: number: 80 - http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: test-web-service port: number: 80 -
Run the following command to apply the manifest.
kubectl apply -f native-ingress.yaml -
Verify the resource creation.
kubectl get ingressclassparameters kubectl get ingressclass kubectl get ingress
Task 4: Test the OCI Native Ingress Controller Load Balancer
Note: Make sure the required ports (for example,
80and/or443) are open in your VCN’s Security List and/or Network Security Group (NSG) before testing the OCI Load Balancer IP address.
To verify that your OCI native ingress controller is working correctly, follow these steps:
-
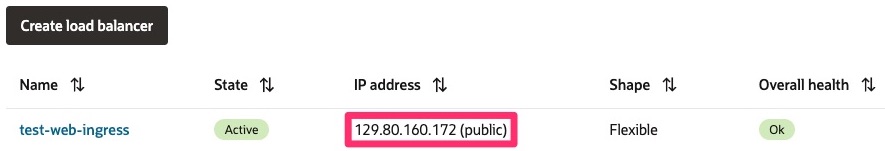
Use
kubectlto retrieve the IP address of the ingress resource.kubectl get ingress -
Copy the IP address shown in the output.

-
Open your web browser and paste the IP address in the address bar.

-
If your setup is correct, you should see the default response from your deployed service.
You can also verify that the OCI Load Balancer has been properly created in the OCI Console by navigating to the navigation menu, select Networking and click Load Balancer.
Next Steps
With this tutorial, you have successfully configured the native ingress controller on OKE using virtual nodes. This setup allows you to manage ingress traffic with OCI Load Balancer service while benefiting from the scalability and simplicity of a serverless Kubernetes environment. You are now ready to deploy production-grade workloads with streamlined traffic management and minimal infrastructure overhead.
Related Links
-
Granting Permissions to the OCI Native Ingress Controller Cluster Add-on
-
Installing the OCI Native Ingress Controller as a Cluster Add-on
-
Creating IngressClassParameters, IngressClass, and Ingress Resources
Acknowledgments
- Author – JP Santana (Master Cloud Architect)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Set Up the OCI Native Ingress Controller on OCI Kubernetes Engine with Virtual Nodes
G34232-03
Copyright ©2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates.