Create a Knowledge Graph with Oracle Autonomous Database and Property Graph Query Language
Introduction
This tutorial explores the concepts of graph theory, knowledge graphs, and how they are implemented using the Oracle Autonomous Database with Property Graph Query Language (PGQL). It also explains the Python implementation used to extract relationships from documents using LLMs and store them as graph structures in Oracle.
What is Graph?
Graph is a field of mathematics and computer science focused on modelling relationships between objects. A graph consists of:
-
Vertices (Nodes): Represent entities.
-
Edges (Links): Represent relationships between entities.
Graphs are widely used for representing data structures in social networks, semantic networks, knowledge graphs, and more.
What is a Knowledge Graph?
A knowledge graph is a graph-based representation of real-world knowledge where:
-
Nodes represent entities such as people, places, products, and so on.
-
Edges represent semantic relationships. For example, works at, part of, and more.
Knowledge graphs enhance semantic search, recommendation systems, and question-answering applications.
Why Use Oracle Autonomous Database with PGQL?
Oracle provides a fully managed environment to store and query property graphs:
-
PGQL is SQL-like and designed for querying complex graph patterns.
-
Oracle Autonomous Database allows running graph queries natively with property graph features, including creation, querying, and visualization.
-
Integration with LLMs enables automatic extraction of graph structures from unstructured data (like PDFs).
Comparison with Other Graph Query Languages
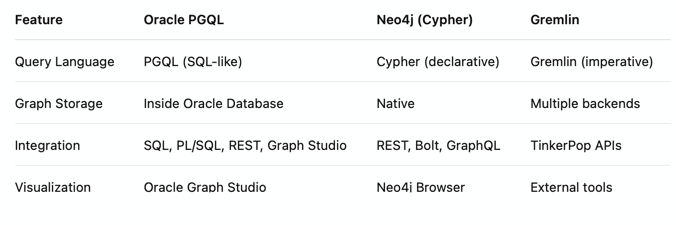
Advantages of Oracle Autonomous Database with PGQL vs Traditional Graph Databases
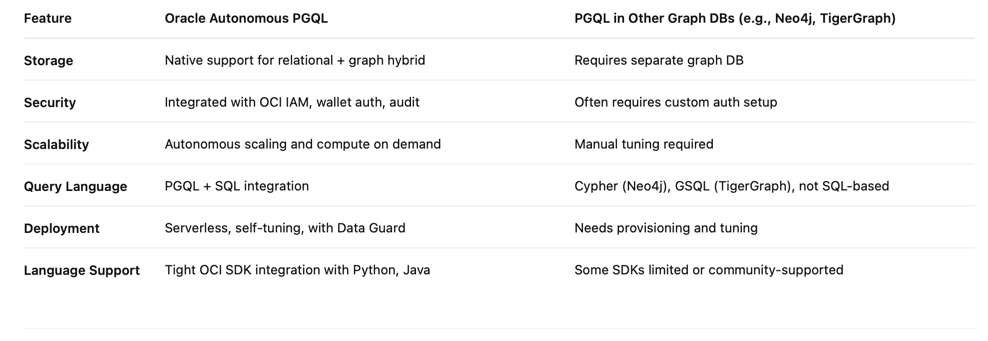
Objectives
- Create a knowledge graph with Oracle Autonomous Database and PGQL.
Prerequisites
- Install Python
version 3.10or higher and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Command Line Interface (OCI CLI).
Task 1: Install Python Packages
The Python code requires certain libraries for using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Generative AI. Run the following command to install the required Python packages. You can download the file from here: requirements.txt.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Task 2: Create an Oracle Database 23ai (Always Free)
In this task, we will learn how to provision an Oracle Database 23ai in Always Free mode. This version offers a fully managed environment, ideal for development, testing and learning, at no additional cost.
-
Log in to the OCI Console, navigate to Oracle Database, Autonomous Database and click Create Autonomous Database Instance.
-
Enter the following information.
- Database Name: Enter an identifying name for your instance.
- Workload Type: Select Data Warehouse or Transaction Processing, according to your needs.
- Compartment: Select an appropriate compartment to organize your resources.
-
Select Always Free to ensure that the instance is provisioned for free.
-
Create a secure password for the
ADMINuser, which will be used to access the database. -
Review the settings and click Create Autonomous Database. Wait a few minutes for the instance to be provisioned and available for use.
If you are not familiar with the process of connecting to the Oracle Autonomous Database, follow these links to understand and properly configure your code.
Note: You will need to connect to the database inside your Python code with the Wallet method.
Task 3: Download and Understand the Code
A very common use case for Graph is to use it as one of the components working together with LLMs and a knowledge base, such as PDF files.
We will use this tutorial: Analyze PDF Documents in Natural Language with OCI Generative AI as our foundation, which uses all the mentioned components. However, for the purpose of this document, we will focus on using Oracle Database 23ai together with Graph. Basically, the Python code (main.py) from the base material will be modified only in the parts that use Oracle Database 23ai.
These are the processes executed on this service:
-
Create the graph schema.
-
Extract entities and relationships using LLM.
-
Insert data into Oracle.
-
Build the property graph.
Download the updated Python graph code compatible with Oracle Database 23ai from here: main.py.
-
create_knowledge_graph:def create_knowledge_graph(chunks): cursor = oracle_conn.cursor() # Creates graph if it does not exist try: cursor.execute(f""" BEGIN EXECUTE IMMEDIATE ' CREATE PROPERTY GRAPH {GRAPH_NAME} VERTEX TABLES (ENTITIES KEY (ID) LABEL ENTITIES PROPERTIES (NAME)) EDGE TABLES (RELATIONS KEY (ID) SOURCE KEY (SOURCE_ID) REFERENCES ENTITIES(ID) DESTINATION KEY (TARGET_ID) REFERENCES ENTITIES(ID) LABEL RELATIONS PROPERTIES (RELATION_TYPE, SOURCE_TEXT)) '; EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN IF SQLCODE != -55358 THEN -- ORA-55358: Graph already exists RAISE; END IF; END; """) print(f"🧠 Graph '{GRAPH_NAME}' created or already exists.") except Exception as e: print(f"[GRAPH ERROR] Failed to create graph: {e}") # Inserting vertices and edges into the tables for doc in chunks: text = doc.page_content source = doc.metadata.get("source", "unknown") if not text.strip(): continue prompt = f""" You are an expert in knowledge extraction. Given the following technical text: {text} Extract key entities and relationships in the format: - Entity1 -[RELATION]-> Entity2 Use UPPERCASE for RELATION types. Return 'NONE' if nothing found. """ try: response = llm_for_rag.invoke(prompt) result = response.content.strip() except Exception as e: print(f"[ERROR] Gen AI call error: {e}") continue if result.upper() == "NONE": continue triples = result.splitlines() for triple in triples: parts = triple.split("-[") if len(parts) != 2: continue right_part = parts[1].split("]->") if len(right_part) != 2: continue raw_relation, entity2 = right_part relation = re.sub(r'\W+', '_', raw_relation.strip().upper()) entity1 = parts[0].strip() entity2 = entity2.strip() try: # Insertion of entities (with existence check) cursor.execute("MERGE INTO ENTITIES e USING (SELECT :name AS NAME FROM dual) src ON (e.name = src.name) WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (NAME) VALUES (:name)", [entity1, entity1]) cursor.execute("MERGE INTO ENTITIES e USING (SELECT :name AS NAME FROM dual) src ON (e.name = src.name) WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (NAME) VALUES (:name)", [entity2, entity2]) # Retrieve the IDs cursor.execute("SELECT ID FROM ENTITIES WHERE NAME = :name", [entity1]) source_id = cursor.fetchone()[0] cursor.execute("SELECT ID FROM ENTITIES WHERE NAME = :name", [entity2]) target_id = cursor.fetchone()[0] # Create relations cursor.execute(""" INSERT INTO RELATIONS (SOURCE_ID, TARGET_ID, RELATION_TYPE, SOURCE_TEXT) VALUES (:src, :tgt, :rel, :txt) """, [source_id, target_id, relation, source]) print(f"✅ {entity1} -[{relation}]-> {entity2}") except Exception as e: print(f"[INSERT ERROR] {e}") oracle_conn.commit() cursor.close() print("💾 Knowledge graph updated.")-
The graph schema is created with
CREATE PROPERTY GRAPH, linkingENTITIES(vertices) andRELATIONS(edges). -
Uses
MERGE INTOto insert new entities only if they do not exist (ensuring uniqueness). -
LLM (Oracle Generative AI) is used to extract triples of the form
Entity1 -[RELATION]-> Entity2. -
All interactions with Oracle are done through
oracledband PL/SQL anonymous blocks.
Now, you can:
-
Use PGQL to explore and query graph relationships.
-
Connect to Graph Studio for visualizations.
-
Expose the graph through an API REST or LangChain agent.
-
-
Graph Query Support Functions
There are two essential functions that enable semantic search and reasoning over the knowledge graph:
extract_graph_keywordsandquery_knowledge_graph. These components allow questions to be interpreted into meaningful graph queries using PGQL on Oracle Autonomous Database.-
extract_graph_keywords:def extract_graph_keywords(question: str) -> str: prompt = f""" Based on the question below, extract relevant keywords (1 to 2 words per term) that can be used to search for entities and relationships in a technical knowledge graph. Question: "{question}" Rules: - Split compound terms (e.g., "API Gateway" → "API", "Gateway") - Remove duplicates - Do not include generic words such as: "what", "how", "the", "of", "in the document", etc. - Return only the keywords, separated by commas. No explanations. Result: """ try: resp = llm_for_rag.invoke(prompt) keywords_raw = resp.content.strip() # Additional post-processing: remove duplicates, normalize keywords = {kw.strip().lower() for kw in re.split(r'[,\n]+', keywords_raw)} keywords = [kw for kw in keywords if kw] # remove empty strings return ", ".join(sorted(keywords)) except Exception as e: print(f"[KEYWORD EXTRACTION ERROR] {e}") return ""What it does:
-
Uses an LLM (
llm_for_rag) to transform natural language questions into a list of graph-friendly keywords. -
The prompt is designed to cleanly extract entities and terms that are relevant for searching the graph.
Why it is important:
-
It bridges the gap between unstructured questions and structured queries.
-
Ensures that only specific, domain-relevant terms are used for matching in the PGQL query.
LLM-enhanced behaviour:
-
Breaks compound technical terms.
-
Removes stop words (like what, how, and so on).
-
Normalizes text by lowercasing and deduplicating terms.
Example:
-
Input:
"What are the main components of an API Gateway architecture?" -
Output keywords:
api, gateway, architecture, components
-
-
query_knowledge_graph:def query_knowledge_graph(query_text): cursor = oracle_conn.cursor() sanitized_text = query_text.lower() pgql = f""" SELECT from_entity, relation_type, to_entity FROM GRAPH_TABLE( {GRAPH_NAME} MATCH (e1 is ENTITIES)-[r is RELATIONS]->(e2 is ENTITIES) WHERE CONTAINS(e1.name, '{sanitized_text}') > 0 OR CONTAINS(e2.name, '{sanitized_text}') > 0 OR CONTAINS(r.RELATION_TYPE, '{sanitized_text}') > 0 COLUMNS ( e1.name AS from_entity, r.RELATION_TYPE AS relation_type, e2.name AS to_entity ) ) FETCH FIRST 20 ROWS ONLY """ print(pgql) try: cursor.execute(pgql) rows = cursor.fetchall() if not rows: return "⚠️ No relationships found in the graph." return "\n".join(f"{r[0]} -[{r[1]}]-> {r[2]}" for r in rows) except Exception as e: return f"[PGQL ERROR] {e}" finally: cursor.close()What it does:
- Accepts a keyword-based string (often produced by
extract_graph_keywords) and constructs a PGQL query to retrieve relationships from the knowledge graph.
Key mechanics:
-
The
GRAPH_TABLEclause usesMATCHto traverse the graph from source to target node. -
It uses
CONTAINS()to allow partial and fuzzy search in node/edge attributes (e1.name,e2.name,r.RELATION_TYPE). -
Limits results to 20 to avoid flooding the output.
Why use PGQL:
-
PGQL is SQL-like but designed for graph traversal.
-
Oracle Autonomous Database supports property graphs, which allows seamless integration between relational and graph worlds.
-
Offers indexing, optimization, and native graph search capabilities that are enterprise-ready.
Oracle-Specific Notes:
-
The
GRAPH_TABLE()is unique to Oracle PGQL and allows queries over logical views of graphs defined through relational tables. -
Unlike Cypher (Neo4j), PGQL runs over structured data using SQL extensions, making it friendlier in RDBMS-heavy environments.
- Accepts a keyword-based string (often produced by
-
Task 4: Run the Chatbot
Run the following command to run the chatbot.
python main.py
Related Links
-
Analyze PDF Documents in Natural Language with OCI Generative AI
-
Getting Started with Property Graphs in Oracle Database 23ai
Acknowledgments
- Author - Cristiano Hoshikawa (Oracle LAD A, Team Solution Engineer)
More Learning Resources
Explore other labs on docs.oracle.com/learn or access more free learning content on the Oracle Learning YouTube channel. Additionally, visit education.oracle.com/learning-explorer to become an Oracle Learning Explorer.
For product documentation, visit Oracle Help Center.
Create a Knowledge Graph with Oracle Autonomous Database and Property Graph Query Language
G38755-02
Copyright ©2025, Oracle and/or its affiliates.